7 QC Tools are also known as Seven Basic Quality Tools and Quality Management Tools. These graphical and statistical tools are used to analyze and solve work-related problems effectively.
The 7 Quality Tools are widely applied by many industries for product and process improvements, and to solve critical quality problems.
7QC tools are extensively used in various Problem Solving Techniques which are listed below:
- 8D Problem Solving Methodology.
- PDCA Deming Cycle for Continuous improvement in product and processes.
- Lean Manufacturing for 3M Waste elimination from processes.
- Various phases of Six Sigma-DMAIC to reduce process variations.

Table of Contents
WHAT ARE 7 QC TOOLS?
The 7 quality tools are simple graphical and statistical tools but very powerful in solving quality problems and process improvement.
These statistical tools are very easy to understand and can be implemented without any complex analytical competence or skills.
The 7 tools of quality are generally used by quality control and quality assurance engineers to solve product or process-related quality issues on a daily/weekly/monthly basis and to reduce/eliminate non-value-added activities like product rework, repair, and rejection.
7 QC Tools List | Quality Tools
The list of 7 QC tools are:
- Check Sheet
- Fishbone Diagram
- Histogram
- Pareto Chart
- Control Chart
- Scatter Diagram
- Stratification Diagram (Some lists replace stratification withProcess Flowchart)
Click on the above links to Explore QC tools.
7 Tools of quality | Brief Explanation
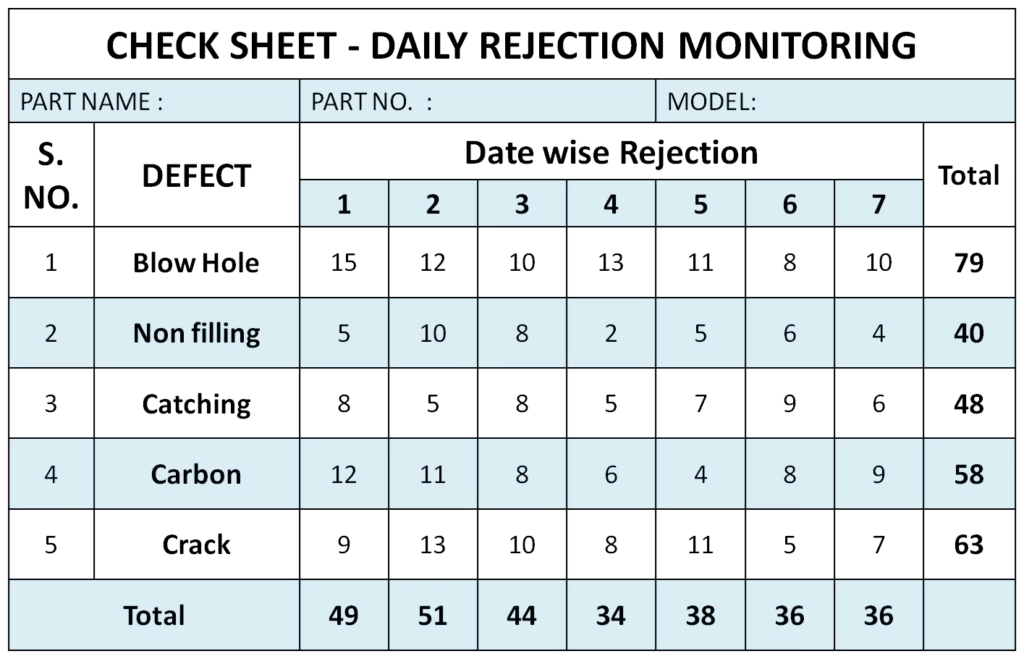
Check Sheet
The check sheet is used for collecting, recording, and analyzing the data. Data collection is an important activity in the problem-solving process as it provides a basis for further action. Data may be numerical, observations and opinions, etc.
Fishbone Diagram
Fishbone diagram is also called as Cause and Effect diagram and Ishikawa diagram. It helps to Identify all possible potential causes and select the real/best potential cause which contributes to the problem/effect. The brainstorming technique is used for potential cause identification.
In a brainstorming session, all 4M or 6M factors are taken into consideration to identify the potential causes. 4M or 6M factors are – Man, Machine, Method, Material, Measurement, and Mother nature also called Environment.
Histogram
A Histogram is a pictorial representation of a set of data, and the most commonly used bar graph for showing frequency distributions of data/values. Histogram frequency distribution chart is widely used in Six Sigma problem solving process.
Pareto Chart
The Pareto chart helps to Narrow the problem area or prioritize the significant problems for corrective measures. The pareto principle is based on the 80-20 rule. It means that 80 percent of the problems/failures are caused by 20 percent of the few major causes/factors which are often referred to as Vital Few.
And the remaining 20 percent of the problems are caused by 80 percent of many minor causes which are referred to as Trivial Many. Hence, it gives us information about Vital few from Trivial many.
Control Chart
A control chart is also known as the SPC chart or Shewhart chart. It is a graphical representation of the collected information/data and it helps to monitor the process centering or process behavior against the specified/set control limits.
A control chart is a very powerful tool to Investigate/disclose the source of Process Variations present in the manufacturing processes. Tells when to take necessary action to eliminate the Common or Random or Chance variations and Special causes of variations.
The control chart helps to measure and analyze the process capability and performance (Cp and Cpk and Pp and Ppk) of the production process.
Scatter Diagram
A Scatter diagram is also known as Correlation Chart, Scatter Plot, and Scatter Graph. A Scatter graph is used to find out the relationship between two variables. In other words, it shows the relationship between two sets of numerical data. Scatter graph shows a Positive or Negative correlation between two variables.
Independent variable data and dependent Variable data are customarily plotted along the horizontal X-axis and Vertical Y-axis respectively. Independent variable is also called controlled parameters.
Stratification Diagram
A technique used to analyze and divide a universe of data into homogeneous groups is called -Strata. Stratification tools are used when the data come from different sources or conditions, such as data collected from different shifts, machines, people, days, suppliers and population groups, etc.
Process Flow Chart
AProcess Flow Chart(PFC) is a diagram of the separate steps of a operations/process in sequential order. PFC is also known asprocess flow diagram(PFD), and Process Map.
WHY DO WE NEED 7 QC TOOLS
We need Quality Tools for :
- Problem Solving – making decisions & judgments.
- For Process Measurement.
- For continual improvement in products, processes, and services.
- To improve Quality, Productivity, and Customer Satisfaction.

“95% of the problem is solved when clearly defined”
“95% of quality-related problems in the organization can be solved by using seven fundamental quantitative tools.”
7QC Tools benefits
The major benefits of QC tools are:
- To analyze and solve quality problems effectively.
- Improve product and process quality.
- Enhance customer satisfaction.
- Reduce cost due to poor quality.
- Helps in investigating the potential causes and real root cause of the problem for taking effective countermeasures.
- Check sheet helps in data collection and recording for quality problem analysis.
- Identify and reduce the process variation using the SPC quality tool.
- The Pareto QC tool helps to narrow down the quality problem using the 80/20 rule.
- Helps in identifying the various sources of variations present in the process.
- Improve the employee’s analytical and problem-solving skills.
The new seven QC Tools are used for planning, goal setting, and problem-solving. These are explained below :
Affinity Diagram – KJ Method. This tool is used for Pinpointing the Problem in a Chaotic Situation and generating solution strategies.
Gathers large amounts of verbal data such as ideas, opinions, and issues, and organizes the data into groups based on natural relationships.
Tree Diagram – Also known as Systematic diagram or Dendrograms, Hierarchy diagram, Organisation chart, and Analytical Tree.
This diagram is used for systematically pursuing the best strategies for achieving an objective.
The advantages of the tree diagram are that it facilitates agreement among the team and is extremely convincing with strategies.
Relation Diagram – It is used for cause identification. For finding solutions strategies by clarifying relationships with Complex Interrelated Causes.
Allows for “Multi-directional” thinking rather than linear. Also known as Interrelationship diagrams.
Process Decisions Program Charts (PDPC) – Also called Decision Process Chart. It is used to produce the desired result from many possible outcomes.
The chart is used to plan various contingencies.
PDPC enables problems to be pinpointed.
Matrix Diagram – used for Clarifying Problems. It clarifies relationships among different elements.
Matrix Data Analysis – Matrix + Num. Analysis.
This can be used when the Matrix diagram does not give sufficient information.
This is used in various fields like process analysis, new product planning, market surveys, etc.
Arrow Diagram – Gantt Chart + PERT/CPM Chart.
An arrow diagram is employed for understanding optimal schedules and controlling them effectively.
This shows relationships among tasks needed to implement a plan.
This diagram is extensively used in PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) and CPM (Critical Path Method).