The audit process follows the PDCA approach( Plan – Do – Check – Act ).
The work of the audit process can be divided into the following stages:
- Audit planning & Preparation
- Audit execution
- Audit reporting
- Follow-up

Table of Contents
Audit process – Audit planning & Preparation
The audit planning and preparation steps include:
- Appointing and audit co-ordinator
- Defining the scope of the audit
- Deciding frequency
- Preparing audit programme
- Making audit schedule/plan
- Document review
- Preparation of audit checklists
Audit Means | Audit Definition
Auditing is a systematic, independent, and documented method/process for gathering audit information and objectively analyzing it to determine the extent to which the audit criteria are met.
Types of Audit
Audits are classified into major two categories:
First Classification
- Adequacy Audit
- compliance Audit
Second Classification
- Internal Audit
- External Audit
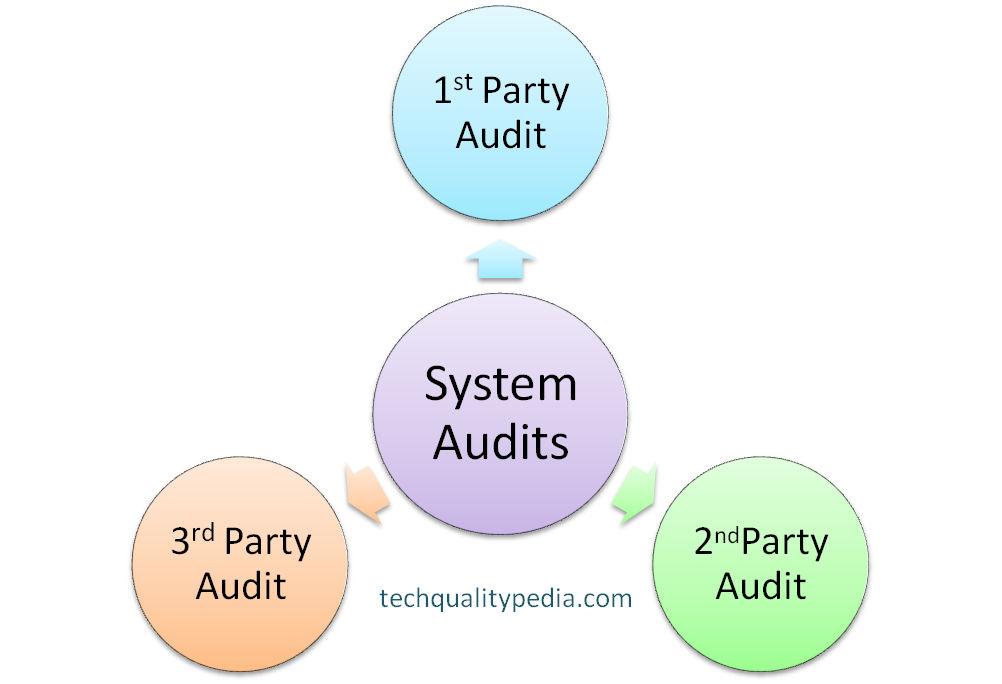
Internal Audit
- First Party Audit (Us on Us) – e.g. Product and Process audit, System audit by internal qualified auditors.
External Audit
- Second Part Audit (Us on them or them on us) – e.g. Customer audit at supplier end, an audit by the consultant.
- Third-Party Audit – Registration audit by third party e.g. Re-certification and Surveillance audit by certification bodies like BSI, DNV, UL, BVQI, TUV, etc.
Audit objectives
General objectives of an audit include:
- To determine conformity/Non-conformity of management system elements.
- To determine the effectiveness of the implemented management system in meeting the system objectives.
- To improve the management system.
- To permit registration/certification of a company’s management system.
Specific objectives of an audit include:
- To evaluate a supplier before establishing a contractual relationship.
- To verify a supplier for continued conformance to a management system under contractual relationship.
- To evaluate an organization’s own management system.
Who qualifies to be an internal auditor ?
- Trained personnel (Own staff or hired professional).
- Independent.
- May not be a specialist, but has a general understanding of the area of audit.
- Knowledge of the relevant standard.
Auditor’s Seven Friends
- What?
- Why?
- When?
- Where?
- Who?
- How?
- Show me?
Audit Samples
- Documents
- Equipment
- Personnel
- Products
- Activities
- Records etc.
Information sources for selection of samples are-
- History or findings of previous audits.
- Customer complaints reported.
- Internal customers.
- Management concerns.
Audit standards
There are various management standards used for auditing the organization’s management system.
Some of the widely used audit standards are listed below:
- ISO 9001: Quality Management Standard – for any kind of industry/sector.
- IATF 16949: Quality Management Standard – for automotive industries.
- AS9100: Quality Management Standard – for aerospace industries.
- ISO 14001: Environmental Management Standard – for environment safety.
- ISO 45001: Occupational Health and Safety standard – for worker’s safety.
- SA8000: Social Accountability Standard.
Audit Report format
Audit report format generally consists of following details:
- Audit ref. no.
- Audit date
- Client name
- NC no.
- NC description with objective evidence
- Correction and Corrective action plan with responsibility and target date
- CAP review and verification with date
- CAP closure status.
Download Audit report format and NC report format
You’ll also like:

3tjnkj
F*ckin’ amazing issues here. I’m very satisfied to see your article. Thank you so much and i’m looking ahead to touch you. Will you please drop me a mail?
Hey! I know this is somewhat off topic but I was wondering which blog platform are you using for this site? I’m getting fed up of WordPress because I’ve had problems with hackers and I’m looking at alternatives for another platform. I would be fantastic if you could point me in the direction of a good platform.
xiqm8g
wy6y0e
Somebody necessarily lend a hand to make seriously posts I would state. That is the very first time I frequented your web page and so far? I surprised with the analysis you made to create this particular publish extraordinary. Wonderful job!
of course like your web site but you have to take a look at the spelling on several of your posts. Several of them are rife with spelling problems and I to find it very troublesome to tell the reality nevertheless I?¦ll certainly come again again.
I really like your writing style, excellent information, appreciate it for putting up : D.
Excellent blog! Do you have any tips for aspiring writers? I’m hoping to start my own website soon but I’m a little lost on everything. Would you recommend starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There are so many choices out there that I’m totally confused .. Any ideas? Appreciate it!
Hello.This post was really remarkable, especially since I was investigating for thoughts on this subject last Sunday.
I’ve recently started a web site, the information you provide on this web site has helped me tremendously. Thank you for all of your time & work. “Never trust anybody who says ‘trust me.’ Except just this once, of course. – from Steel Beach” by John Varley.
Today, I went to the beachfront with my children. I found a sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She placed the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear. She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is entirely off topic but I had to tell someone!
Thanks for sharing superb informations. Your website is very cool. I am impressed by the details that you have on this site. It reveals how nicely you perceive this subject. Bookmarked this website page, will come back for extra articles. You, my pal, ROCK! I found simply the information I already searched everywhere and just couldn’t come across. What an ideal website.
I’m really loving the theme/design of your web site. Do you ever run into any browser compatibility problems? A small number of my blog visitors have complained about my site not operating correctly in Explorer but looks great in Opera. Do you have any suggestions to help fix this problem?
Your place is valueble for me. Thanks!…
This really answered my problem, thank you!
I want to show my affection for your kindness in support of men who need help on that area. Your very own dedication to passing the solution all-around was extremely valuable and has regularly made professionals just like me to attain their goals. Your personal helpful guidelines signifies this much a person like me and further more to my office workers. Many thanks; from each one of us.
naturally like your website but you have to check the spelling on several of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling issues and I find it very troublesome to tell the truth nevertheless I will definitely come back again.
Together with every thing that seems to be developing throughout this specific subject matter, many of your perspectives happen to be somewhat radical. On the other hand, I am sorry, but I can not give credence to your whole plan, all be it radical none the less. It appears to us that your commentary are not completely rationalized and in reality you are yourself not wholly convinced of the point. In any event I did enjoy looking at it.
Hey there! I’ve been reading your blog for some time now and finally got the courage to go ahead and give you a shout out from Atascocita Tx! Just wanted to mention keep up the good work!
I just could not go away your website prior to suggesting that I actually loved the standard info a person supply for your visitors? Is gonna be again steadily to inspect new posts
As I site possessor I believe the content matter here is rattling wonderful , appreciate it for your efforts. You should keep it up forever! Best of luck.
Greetings! Very helpful advice on this article! It is the little changes that make the biggest changes. Thanks a lot for sharing!
We’re a group of volunteers and starting a brand new scheme in our community. Your website offered us with useful info to work on. You’ve performed an impressive process and our whole group might be grateful to you.
I appreciate, cause I found just what I was looking for. You have ended my 4 day long hunt! God Bless you man. Have a nice day. Bye
I like what you guys are up also. Such intelligent work and reporting! Carry on the excellent works guys I have incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it’ll improve the value of my website :).
Outstanding post however , I was wondering if you could write a litte more on this topic? I’d be very grateful if you could elaborate a little bit more. Cheers!
I’ve recently started a web site, the info you provide on this website has helped me greatly. Thanks for all of your time & work. “It is a great thing to know our vices.” by Cicero.
It is in reality a nice and useful piece of info. I am glad that you shared this helpful info with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
Greetings! Very helpful advice on this article! It is the little changes that make the biggest changes. Thanks a lot for sharing!
Wow, incredible weblog structure! How lengthy have you been running a blog for? you made running a blog glance easy. The overall look of your web site is great, as neatly as the content material!
There is noticeably a bunch to realize about this. I feel you made certain nice points in features also.
I have been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this website. Thank you, I will try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your web site?
Thank you, I’ve recently been searching for info about this topic for ages and yours is the greatest I’ve discovered till now. But, what about the bottom line? Are you sure about the source?
Wonderful work! This is the type of info that should be shared around the web. Shame on the search engines for not positioning this post higher! Come on over and visit my site . Thanks =)
Thank you, I’ve just been searching for information about this subject for ages and yours is the greatest I have discovered till now. But, what about the conclusion? Are you sure about the source?
I like what you guys are up also. Such clever work and reporting! Carry on the superb works guys I have incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it will improve the value of my web site :).
I don’t even know how I stopped up right here, but I thought this post was once great. I do not understand who you might be however definitely you’re going to a well-known blogger in case you are not already 😉 Cheers!
This is the right blog for anyone who wants to find out about this topic. You realize so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I actually would want…HaHa). You definitely put a new spin on a topic thats been written about for years. Great stuff, just great!
Great post and right to the point. I don’t know if this is actually the best place to ask but do you guys have any thoughts on where to hire some professional writers? Thanks 🙂
I want to show my appreciation for your generosity giving support to all those that require guidance on the area. Your real commitment to getting the solution all-around appeared to be extremely good and has without exception allowed those like me to get to their pursuits. Your own warm and friendly report entails a whole lot to me and somewhat more to my fellow workers. Many thanks; from everyone of us.
Normally I do not read article on blogs, but I wish to say that this write-up very forced me to try and do it! Your writing style has been surprised me. Thanks, quite nice article.
I?¦ve been exploring for a bit for any high quality articles or weblog posts on this kind of area . Exploring in Yahoo I finally stumbled upon this website. Studying this information So i?¦m glad to convey that I’ve an incredibly just right uncanny feeling I found out exactly what I needed. I so much without a doubt will make sure to don?¦t put out of your mind this site and give it a look on a relentless basis.
Having read this I thought it was very informative. I appreciate you taking the time and effort to put this article together. I once again find myself spending way to much time both reading and commenting. But so what, it was still worth it!
This web site is really a walk-through for all of the info you wanted about this and didn’t know who to ask. Glimpse here, and you’ll definitely discover it.
I have recently started a web site, the information you offer on this site has helped me tremendously. Thanks for all of your time & work.
Thanks , I’ve just been searching for information about this subject for a long time and yours is the greatest I have came upon so far. But, what concerning the bottom line? Are you sure concerning the supply?
Very interesting points you have observed, thanks for putting up. “In a great romance, each person plays a part the other really likes.” by Elizabeth Ashley.
Thankyou for this post, I am a big big fan of this site would like to go along updated.
Hello There. I found your weblog using msn. This is a really neatly written article. I will make sure to bookmark it and return to learn more of your helpful info. Thanks for the post. I will certainly comeback.
very good submit, i certainly love this web site, keep on it
Hey! I just wanted to ask if you ever have any problems with hackers? My last blog (wordpress) was hacked and I ended up losing months of hard work due to no back up. Do you have any methods to stop hackers?
Good site! I truly love how it is simple on my eyes and the data are well written. I’m wondering how I could be notified whenever a new post has been made. I have subscribed to your RSS feed which must do the trick! Have a great day!
magnificent points altogether, you simply gained a brand new reader. What would you suggest in regards to your post that you made some days ago? Any positive?
Hi my friend! I want to say that this post is amazing, nice written and include almost all important infos. I’d like to see more posts like this.
Hi , I do believe this is an excellent blog. I stumbled upon it on Yahoo , i will come back once again. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and help other people.
Hi there very cool site!! Guy .. Beautiful .. Superb .. I will bookmark your web site and take the feeds also…I am glad to seek out a lot of helpful information right here within the put up, we want work out more strategies on this regard, thanks for sharing.
Whats Happening i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I have found It absolutely useful and it has helped me out loads. I’m hoping to give a contribution & help other customers like its helped me. Great job.
I haven¦t checked in here for a while since I thought it was getting boring, but the last few posts are great quality so I guess I¦ll add you back to my daily bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
Im no longer sure the place you’re getting your information, however good topic. I needs to spend some time finding out more or figuring out more. Thank you for fantastic information I was searching for this info for my mission.
The Salt Trick is a natural technique that involves using specific salts, such as Blue Salt, to enhance male performance
Howdy this is kind of of off topic but I was wanting to know if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding expertise so I wanted to get guidance from someone with experience. Any help would be enormously appreciated!
I do not even know how I ended up here, but I thought this post was great. I do not know who you are but certainly you are going to a famous blogger if you aren’t already 😉 Cheers!
The Natural Mounjaro Recipe is more than just a diet—it’s a sustainable and natural approach to weight management and overall health.
The Natural Mounjaro Recipe is more than just a diet—it’s a sustainable and natural approach to weight management and overall health.
F*ckin’ tremendous things here. I’m very glad to see your post. Thanks a lot and i am looking forward to contact you. Will you kindly drop me a mail?
Mitolyn is a cutting-edge natural dietary supplement designed to support effective weight loss and improve overall wellness.
I appreciate, cause I found just what I was looking for. You’ve ended my 4 day long hunt! God Bless you man. Have a great day. Bye
You actually make it seem so easy together with your presentation but I to find this topic to be actually something which I think I would by no means understand. It kind of feels too complex and extremely extensive for me. I am having a look ahead for your next publish, I¦ll attempt to get the hold of it!
I always was concerned in this topic and stock still am, regards for posting.
PrimeBiome is a dietary supplement designed to support gut health by promoting a balanced microbiome, enhancing digestion, and boosting overall well-being.
I don’t commonly comment but I gotta tell appreciate it for the post on this great one : D.
Youre so cool! I dont suppose Ive learn something like this before. So nice to find any person with some authentic thoughts on this subject. realy thanks for beginning this up. this web site is one thing that is needed on the internet, someone with a little originality. useful job for bringing one thing new to the web!
I like this web blog very much so much wonderful info .
Wow! This can be one particular of the most useful blogs We’ve ever arrive across on this subject. Actually Magnificent. I am also a specialist in this topic therefore I can understand your hard work.
Magnificent website. Plenty of helpful info here. I am sending it to a few friends ans additionally sharing in delicious. And obviously, thanks in your effort!
Wow, awesome weblog structure! How lengthy have you ever been running a blog for? you make blogging glance easy. The entire look of your site is fantastic, let alone the content!
I was wondering if you ever thought of changing the page layout of your website? Its very well written; I love what youve got to say. But maybe you could a little more in the way of content so people could connect with it better. Youve got an awful lot of text for only having one or 2 pictures. Maybe you could space it out better?
WONDERFUL Post.thanks for share..more wait .. …
I’d have to examine with you here. Which is not one thing I usually do! I take pleasure in reading a post that may make folks think. Additionally, thanks for permitting me to comment!
Thanks for the auspicious writeup. It in fact was a enjoyment account it. Look advanced to more delivered agreeable from you! However, how could we communicate?
Well I sincerely enjoyed reading it. This information procured by you is very helpful for proper planning.
Hi there! This is kind of off topic but I need some help from an established blog. Is it very difficult to set up your own blog? I’m not very techincal but I can figure things out pretty quick. I’m thinking about creating my own but I’m not sure where to start. Do you have any tips or suggestions? Appreciate it
Some genuinely wonderful info , Sword lily I noticed this.
I precisely had to thank you very much all over again. I do not know the things that I would have implemented without these recommendations discussed by you over my theme. It actually was a fearsome matter in my opinion, however , witnessing the skilled strategy you handled the issue took me to leap for delight. I will be grateful for this information and even pray you realize what a great job you have been providing educating most people using your web blog. More than likely you’ve never got to know all of us.
I like this website its a master peace ! Glad I discovered this on google .
Appreciate it for helping out, good info .
Compre visualizações e espectadores reais para suas lives no YouTube, Instagram, Twitch, TikTok e Facebook. Aumente seu engajamento e credibilidade online com serviços seguros e confiáveis. Impulsione suas transmissões ao vivo hoje!
You really make it seem so easy with your presentation but I find this matter to be actually something which I think I would never understand. It seems too complex and extremely broad for me. I am looking forward for your next post, I will try to get the hang of it!
Good day! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with SEO? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good results. If you know of any please share. Many thanks!
I have been exploring for a little for any high-quality articles or blog posts in this kind of house . Exploring in Yahoo I finally stumbled upon this website. Reading this info So i¦m satisfied to express that I’ve an incredibly excellent uncanny feeling I came upon just what I needed. I so much surely will make sure to do not forget this website and give it a glance regularly.
Merely a smiling visitor here to share the love (:, btw outstanding style and design. “Everything should be made as simple as possible, but not one bit simpler.” by Albert Einstein.
Your place is valueble for me. Thanks!…
At Nursing Professionals Certifications Online, we are dedicated to providing accessible, convenient, and high-quality medical certification courses to healthcare professionals worldwide. Our platform is designed to meet the evolving needs of medical professionals seeking to enhance their skills, expand their knowledge, and advance their careers. Do you have problems passing your exam? We provide medical students with certificates, licenses, questions, and answers and upgrade previous scores for Prometric exams. #ECFMG #MCAT #SCFHS #MSNCB #OET #DHA #NLCEX #HAAD #MOH #MRCGP #MCAT #OMSB #SMLE #USMLE #QCHP #NHRA #DHCC #AMC #MRCS #MRCOG. You can obtain the above certificate and license online without attending the exam. Provide leaked questions bank and answers before the exam date. You can also upgrade your previous results. Study materials and tips are available for your upcoming exam dates. Chat on WhatsApp with +971 56 954 4538
I really wanted to make a brief remark in order to thank you for these remarkable secrets you are placing here. My prolonged internet investigation has now been honored with wonderful content to exchange with my relatives. I ‘d repeat that we website visitors are unquestionably blessed to exist in a wonderful website with many outstanding people with great pointers. I feel quite happy to have seen your entire weblog and look forward to plenty of more excellent moments reading here. Thanks a lot once more for a lot of things.
My spouse and I absolutely love your blog and find many of your post’s to be what precisely I’m looking for. Does one offer guest writers to write content to suit your needs? I wouldn’t mind publishing a post or elaborating on a number of the subjects you write related to here. Again, awesome web log!
You are a very capable person!
Very efficiently written article. It will be beneficial to anyone who utilizes it, including me. Keep up the good work – i will definitely read more posts.
Wow, marvelous blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you made blogging look easy. The overall look of your site is magnificent, let alone the content!
Deference to website author, some great entropy.
I used to be more than happy to search out this web-site.I needed to thanks in your time for this excellent learn!! I positively having fun with every little little bit of it and I’ve you bookmarked to check out new stuff you blog post.
Rattling wonderful visual appeal on this site, I’d value it 10 10.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
Excellent read, I just passed this onto a colleague who was doing a little research on that. And he actually bought me lunch because I found it for him smile So let me rephrase that: Thank you for lunch! “Never let inexperience get in the way of ambition.” by Terry Josephson.
The Salt Trick is a natural technique that involves using specific salts, such as Blue Salt, to enhance male performance
That is the right blog for anyone who desires to seek out out about this topic. You notice a lot its nearly laborious to argue with you (not that I truly would need…HaHa). You undoubtedly put a brand new spin on a topic thats been written about for years. Great stuff, just great!
certainly like your web site however you have to take a look at the spelling on quite a few of your posts. Several of them are rife with spelling issues and I find it very troublesome to tell the reality nevertheless I’ll definitely come again again.
My partner and I absolutely love your blog and find most of your post’s to be exactly what I’m looking for. Does one offer guest writers to write content for you? I wouldn’t mind creating a post or elaborating on a number of the subjects you write with regards to here. Again, awesome website!
Mitolyn is a cutting-edge natural dietary supplement designed to support effective weight loss and improve overall wellness.
Really enjoyed this update, how can I make is so that I receive an email sent to me whenever you make a fresh post?
Mitolyn is a cutting-edge natural dietary supplement designed to support effective weight loss and improve overall wellness.
Your style is so unique compared to many other people. Thank you for publishing when you have the opportunity,Guess I will just make this bookmarked.2
I am so happy to read this. This is the kind of manual that needs to be given and not the accidental misinformation that is at the other blogs. Appreciate your sharing this greatest doc.
The other day, while I was at work, my sister stole my iPad and tested to see if it can survive a thirty foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My apple ipad is now broken and she has 83 views. I know this is entirely off topic but I had to share it with someone!
Great post. I was checking continuously this blog and I’m impressed! Very useful info specially the last part 🙂 I care for such info much. I was looking for this certain information for a very long time. Thank you and good luck.
I have been examinating out a few of your stories and i can claim pretty good stuff. I will make sure to bookmark your blog.
If you’ve been looking for a way to unlock your full mental potential and attract wealth effortlessly, Billionaire Brain Wave might just be the breakthrough you’ve been waiting for!
I really like looking at and I think this website got some truly useful stuff on it! .
Very interesting topic, thanks for putting up.
This really answered my problem, thank you!
I?¦ve learn several excellent stuff here. Definitely value bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how so much attempt you put to create one of these fantastic informative web site.
This web site is really a walk-through for all of the info you wanted about this and didn’t know who to ask. Glimpse here, and you’ll definitely discover it.
What i don’t understood is in reality how you are now not really much more well-preferred than you might be now. You are so intelligent. You know therefore significantly in relation to this topic, made me in my opinion believe it from so many varied angles. Its like men and women don’t seem to be involved unless it is one thing to accomplish with Woman gaga! Your own stuffs outstanding. At all times deal with it up!
obviously like your web-site but you have to check the spelling on several of your posts. A number of them are rife with spelling issues and I to find it very troublesome to tell the truth nevertheless I will surely come back again.
After study a few of the blog posts on your website now, and I truly like your way of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back soon. Pls check out my web site as well and let me know what you think.
I would like to show thanks to the writer for rescuing me from this particular problem. Because of searching through the internet and finding methods that were not productive, I figured my entire life was well over. Existing without the approaches to the difficulties you have sorted out all through your main short article is a serious case, as well as the kind which might have negatively affected my career if I hadn’t discovered your site. Your own personal skills and kindness in dealing with a lot of things was vital. I’m not sure what I would have done if I hadn’t discovered such a solution like this. I can at this point look forward to my future. Thanks for your time very much for your professional and results-oriented help. I won’t hesitate to suggest the website to anyone who ought to have recommendations about this area.
Hi! This is kind of off topic but I need some guidance from an established blog. Is it hard to set up your own blog? I’m not very techincal but I can figure things out pretty fast. I’m thinking about setting up my own but I’m not sure where to begin. Do you have any tips or suggestions? Many thanks
Great blog right here! Additionally your web site so much up very fast! What host are you using? Can I get your affiliate link in your host? I wish my website loaded up as fast as yours lol
Hello! I know this is kind of off topic but I was wondering which blog platform are you using for this site? I’m getting fed up of WordPress because I’ve had issues with hackers and I’m looking at alternatives for another platform. I would be great if you could point me in the direction of a good platform.
I am extremely impressed with your writing skills as well as with the layout on your blog. Is this a paid theme or did you modify it yourself? Anyway keep up the excellent quality writing, it’s rare to see a nice blog like this one nowadays..
I saw a lot of website but I conceive this one has got something special in it in it
I am impressed with this website , very I am a big fan .
This is really interesting, You are a very skilled blogger. I have joined your rss feed and look forward to seeking more of your great post. Also, I’ve shared your website in my social networks!
Hi, Neat post. There’s a problem with your site in internet explorer, would test this… IE still is the market leader and a good portion of people will miss your magnificent writing due to this problem.
Thank you for the sensible critique. Me and my neighbor were just preparing to do a little research about this. We got a grab a book from our local library but I think I learned more clear from this post. I am very glad to see such fantastic information being shared freely out there.
There is noticeably a bundle to know about this. I assume you made certain nice points in features also.
But wanna remark on few general things, The website layout is perfect, the subject material is really wonderful. “In business school classrooms they construct wonderful models of a nonworld.” by Peter Drucker.
You should take part in a contest for one of the best blogs on the web. I will recommend this site!
Greetings from Colorado! I’m bored to death at work so I decided to browse your blog on my iphone during lunch break. I love the info you present here and can’t wait to take a look when I get home. I’m surprised at how fast your blog loaded on my cell phone .. I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyhow, excellent blog!
I am continuously browsing online for ideas that can help me. Thx!
Thanx for the effort, keep up the good work Great work, I am going to start a small Blog Engine course work using your site I hope you enjoy blogging with the popular BlogEngine.net.Thethoughts you express are really awesome. Hope you will right some more posts.
You made some nice points there. I did a search on the theme and found nearly all people will have the same opinion with your blog.
There are actually a number of details like that to take into consideration. That could be a great point to bring up. I offer the thoughts above as common inspiration but clearly there are questions like the one you bring up where an important factor will be working in honest good faith. I don?t know if finest practices have emerged round issues like that, but I’m sure that your job is clearly recognized as a fair game. Each girls and boys really feel the influence of only a moment’s pleasure, for the rest of their lives.
Good day! Would you mind if I share your blog with my myspace group? There’s a lot of folks that I think would really appreciate your content. Please let me know. Cheers
Simply wish to say your article is as amazing. The clarity in your post is just cool and i can assume you are an expert on this subject. Fine with your permission allow me to grab your RSS feed to keep updated with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please continue the enjoyable work.
I must show some thanks to this writer for rescuing me from this type of instance. Just after looking throughout the the net and getting strategies which were not pleasant, I figured my entire life was done. Existing minus the approaches to the difficulties you have resolved through this report is a critical case, as well as those that would have in a wrong way affected my entire career if I had not come across your site. The mastery and kindness in maneuvering all areas was priceless. I’m not sure what I would have done if I had not discovered such a stuff like this. I am able to now relish my future. Thank you so much for this high quality and effective help. I won’t be reluctant to propose your web blog to anyone who needs to have support on this area.
WONDERFUL Post.thanks for share..extra wait .. …
Whoa! This blog looks exactly like my old one! It’s on a totally different topic but it has pretty much the same layout and design. Outstanding choice of colors!
Thank you for the good writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it. Look advanced to far added agreeable from you! By the way, how can we communicate?
Hey there! Someone in my Facebook group shared this site with us so I came to look it over. I’m definitely loving the information. I’m bookmarking and will be tweeting this to my followers! Great blog and wonderful design.
Wow! Thank you! I continually needed to write on my website something like that. Can I include a fragment of your post to my site?
You can definitely see your expertise within the work you write. The world hopes for even more passionate writers such as you who are not afraid to mention how they believe. All the time follow your heart.
In the great pattern of things you secure a B+ just for effort and hard work. Where exactly you actually lost me was first in all the particulars. You know, as the maxim goes, details make or break the argument.. And that couldn’t be much more accurate here. Having said that, allow me inform you just what did deliver the results. Your text is certainly quite persuasive and this is probably the reason why I am making an effort in order to comment. I do not make it a regular habit of doing that. 2nd, even though I can easily notice the leaps in logic you make, I am not really confident of just how you appear to unite the ideas which inturn make the conclusion. For now I shall yield to your issue however hope in the near future you actually link the facts better.
When I initially commented I clicked the -Notify me when new feedback are added- checkbox and now every time a comment is added I get four emails with the identical comment. Is there any way you may remove me from that service? Thanks!
I love what you guys are usually up too. Such clever work and reporting! Keep up the good works guys I’ve incorporated you guys to blogroll.
I am always browsing online for articles that can assist me. Thx!
You really make it seem so easy with your presentation however I in finding this topic to be actually something which I believe I might never understand. It seems too complicated and very extensive for me. I am taking a look ahead in your subsequent post, I’ll attempt to get the grasp of it!
I like this web blog very much, Its a real nice situation to read and receive info .
Hello.This article was extremely fascinating, especially because I was looking for thoughts on this topic last week.
I am so happy to read this. This is the kind of manual that needs to be given and not the accidental misinformation that’s at the other blogs. Appreciate your sharing this greatest doc.
Very nice post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wished to say that I’ve really enjoyed browsing your blog posts. After all I’ll be subscribing to your rss feed and I hope you write again very soon!
Perfectly pent content, thank you for information. “The bravest thing you can do when you are not brave is to profess courage and act accordingly.” by Corra Harris.
Very interesting topic, appreciate it for posting.
I don’t even know how I finished up here, however I assumed this put up used to be good. I do not recognise who you are however definitely you’re going to a well-known blogger if you happen to are not already 😉 Cheers!
You could certainly see your expertise in the work you write. The arena hopes for more passionate writers such as you who aren’t afraid to say how they believe. All the time go after your heart. “Until you’ve lost your reputation, you never realize what a burden it was.” by Margaret Mitchell.
Thanks for sharing excellent informations. Your website is so cool. I am impressed by the details that you’ve on this website. It reveals how nicely you understand this subject. Bookmarked this web page, will come back for extra articles. You, my friend, ROCK! I found just the information I already searched everywhere and simply couldn’t come across. What a great web-site.
I visited a lot of website but I conceive this one contains something extra in it in it
This blog is definitely rather handy since I’m at the moment creating an internet floral website – although I am only starting out therefore it’s really fairly small, nothing like this site. Can link to a few of the posts here as they are quite. Thanks much. Zoey Olsen
You have remarked very interesting details! ps decent web site.
We absolutely love your blog and find a lot of your post’s to be just what I’m looking for. can you offer guest writers to write content for you? I wouldn’t mind publishing a post or elaborating on a lot of the subjects you write related to here. Again, awesome web site!
Wow, wonderful blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you made blogging look easy. The overall look of your website is great, let alone the content!
I was looking at some of your articles on this site and I believe this internet site is rattling instructive! Continue putting up.
This is the suitable blog for anybody who wants to search out out about this topic. You understand so much its nearly onerous to argue with you (not that I actually would want…HaHa). You undoubtedly put a brand new spin on a topic thats been written about for years. Great stuff, simply great!
I’m not that much of a internet reader to be honest but your blogs really nice, keep it up! I’ll go ahead and bookmark your website to come back later. All the best
Magnificent goods from you, man. I’ve understand your stuff previous to and you’re just too wonderful. I actually like what you’ve acquired here, certainly like what you are stating and the way in which you say it. You make it entertaining and you still care for to keep it sensible. I can’t wait to read far more from you. This is actually a terrific website.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
I like this web blog very much so much fantastic information.
This is the right blog for anyone who wants to find out about this topic. You realize so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I actually would want…HaHa). You definitely put a new spin on a topic thats been written about for years. Great stuff, just great!
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself? Plz reply back as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to know wheere u got this from. thanks
Its like you read my mind! You seem to know a lot about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you could do with some pics to drive the message home a little bit, but instead of that, this is great blog. A fantastic read. I’ll certainly be back.
Wow! Thank you! I continuously needed to write on my site something like that. Can I take a portion of your post to my site?
Its wonderful as your other posts : D, regards for putting up. “The art of love … is largely the art of persistence.” by Albert Ellis.
Thank you for the auspicious writeup. It in truth was a entertainment account it. Glance complex to more delivered agreeable from you! By the way, how could we communicate?
hello there and thanks for your info – I’ve certainly picked up anything new from right here. I did alternatively expertise several technical points the usage of this web site, since I skilled to reload the web site lots of instances previous to I may just get it to load correctly. I have been pondering if your web host is OK? Not that I’m complaining, but slow loading cases instances will sometimes have an effect on your placement in google and could injury your quality rating if advertising and ***********|advertising|advertising|advertising and *********** with Adwords. Anyway I am adding this RSS to my e-mail and could look out for a lot more of your respective fascinating content. Make sure you update this again very soon..
Hello just wanted to give you a quick heads up. The words in your article seem to be running off the screen in Ie. I’m not sure if this is a formatting issue or something to do with browser compatibility but I figured I’d post to let you know. The layout look great though! Hope you get the problem fixed soon. Kudos
I love it when people come together and share opinions, great blog, keep it up.
You really make it appear really easy together with your presentation but I find this matter to be actually one thing that I believe I’d by no means understand. It seems too complicated and extremely huge for me. I am having a look forward for your subsequent submit, I?¦ll try to get the cling of it!
Some truly wonderful posts on this site, thank you for contribution. “Give me the splendid silent sun with all his beams full-dazzling.” by Walt Whitman.
I would like to thank you for the efforts you have put in writing this website. I am hoping the same high-grade website post from you in the upcoming also. In fact your creative writing skills has inspired me to get my own site now. Really the blogging is spreading its wings quickly. Your write up is a great example of it.
I’d have to examine with you here. Which is not one thing I usually do! I take pleasure in reading a post that may make folks think. Additionally, thanks for permitting me to comment!
Some genuinely interesting details you have written.Aided me a lot, just what I was looking for : D.
Very nice post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wished to say that I’ve really enjoyed surfing around your blog posts. After all I’ll be subscribing to your rss feed and I hope you write again soon!
I just wanted to develop a simple remark to appreciate you for these superb facts you are showing on this site. My prolonged internet look up has at the end been rewarded with incredibly good information to talk about with my friends. I ‘d assert that we site visitors are undoubtedly fortunate to live in a decent community with very many brilliant individuals with interesting techniques. I feel very blessed to have seen your website page and look forward to plenty of more cool moments reading here. Thanks a lot once again for a lot of things.
Mitolyn is a cutting-edge natural dietary supplement designed to support effective weight loss and improve overall wellness.
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself? Plz reply back as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to know wheere u got this from. thanks
Loving the info on this web site, you have done great job on the content.
Mitolyn is a cutting-edge natural dietary supplement designed to support effective weight loss and improve overall wellness.
You actually make it seem so easy with your presentation but I find this topic to be actually something that I think I would never understand. It seems too complex and very broad for me. I am looking forward for your next post, I will try to get the hang of it!
I will right away grab your rss feed as I can’t find your email subscription link or newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Please let me know so that I could subscribe. Thanks.
F*ckin¦ remarkable things here. I am very satisfied to see your article. Thanks a lot and i am taking a look forward to touch you. Will you please drop me a mail?
The Natural Mounjaro Recipe is more than just a diet—it’s a sustainable and natural approach to weight management and overall health.
The Natural Mounjaro Recipe is more than just a diet—it’s a sustainable and natural approach to weight management and overall health.
Hey, I think your website might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your website in Firefox, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, great blog!
It’s really a great and helpful piece of info. I’m happy that you just shared this helpful info with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
so much excellent information on here, : D.
The Natural Mounjaro Recipe is more than just a diet—it’s a sustainable and natural approach to weight management and overall health.
Some really excellent posts on this website , appreciate it for contribution.
You made some decent factors there. I appeared on the web for the difficulty and found most people will associate with with your website.
Aqua Sculpt is an advanced body contouring treatment that uses hydrating active ingredients, cooling technology, and sometimes ultrasound or RF-based devices (depending on the version) to target fat cells and tighten the skin.
Hi I am so glad I found your website, I really found you by error, while I was looking on Digg for something else, Anyways I am here now and would just like to say thanks a lot for a tremendous post and a all round interesting blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to go through it all at the minute but I have saved it and also added in your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read much more, Please do keep up the great job.
I am extremely impressed with your writing skills and also with the layout on your weblog. Is this a paid theme or did you customize it yourself? Either way keep up the nice quality writing, it is rare to see a nice blog like this one nowadays..
You made various fine points there. I did a search on the subject matter and found the majority of persons will go along with with your blog.
PrimeBiome is a dietary supplement designed to support gut health by promoting a balanced microbiome, enhancing digestion, and boosting overall well-being.
Wow! This could be one particular of the most beneficial blogs We’ve ever arrive across on this subject. Basically Fantastic. I’m also a specialist in this topic therefore I can understand your hard work.
You are my aspiration, I own few web logs and rarely run out from to post .
I savor, lead to I found exactly what I used to be looking for. You have ended my 4 day long hunt! God Bless you man. Have a great day. Bye
My partner and I stumbled over here coming from a different website and thought I might check things out. I like what I see so i am just following you. Look forward to finding out about your web page yet again.
Its like you read my mind! You seem to know a lot about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you can do with a few pics to drive the message home a little bit, but instead of that, this is magnificent blog. A fantastic read. I will definitely be back.
I like this blog so much, saved to my bookmarks. “Respect for the fragility and importance of an individual life is still the mark of an educated man.” by Norman Cousins.
You are my inhalation, I have few web logs and occasionally run out from to post .
Heya i’m for the first time here. I found this board and I in finding It truly useful & it helped me out a lot. I hope to offer one thing back and aid others like you aided me.
This site is my aspiration, very wonderful style and design and perfect subject material.
Have you ever considered creating an e-book or guest authoring on other sites? I have a blog based on the same information you discuss and would love to have you share some stories/information. I know my readers would enjoy your work. If you are even remotely interested, feel free to send me an email.
What i do not realize is in reality how you are now not actually much more well-appreciated than you might be now. You are very intelligent. You realize thus significantly in relation to this matter, produced me in my view consider it from numerous various angles. Its like women and men don’t seem to be interested until it is something to do with Girl gaga! Your own stuffs excellent. All the time care for it up!
Simply wanna say that this is invaluable, Thanks for taking your time to write this.
There may be noticeably a bundle to find out about this. I assume you made certain good factors in features also.
I dugg some of you post as I thought they were very helpful extremely helpful
As soon as I noticed this web site I went on reddit to share some of the love with them.
What i don’t understood is actually how you are not really much more well-liked than you may be right now. You are very intelligent. You realize thus significantly relating to this subject, produced me personally consider it from a lot of varied angles. Its like men and women aren’t fascinated unless it is one thing to do with Lady gaga! Your own stuffs outstanding. Always maintain it up!
You completed a number of nice points there. I did a search on the theme and found a good number of persons will consent with your blog.
You really make it seem so easy with your presentation but I to find this matter to be really something which I feel I’d by no means understand. It kind of feels too complicated and extremely wide for me. I’m looking forward for your subsequent publish, I will attempt to get the cling of it!
Hello, Neat post. There is an issue with your website in web explorer, would check thisK IE nonetheless is the marketplace leader and a big part of folks will omit your great writing because of this problem.
Hey, you used to write wonderful, but the last few posts have been kinda boring… I miss your super writings. Past several posts are just a little bit out of track! come on!
It is actually a great and useful piece of info. I’m happy that you simply shared this helpful info with us. Please stay us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.
I like this web site very much so much good info .
Wow! Thank you! I continually wanted to write on my website something like that. Can I implement a part of your post to my site?
I dugg some of you post as I cogitated they were very beneficial very helpful
I’ve been absent for a while, but now I remember why I used to love this website. Thank you, I’ll try and check back more often. How frequently you update your site?
Attractive section of content. I just stumbled upon your weblog and in accession capital to say that I acquire in fact enjoyed account your weblog posts. Any way I will be subscribing for your augment or even I fulfillment you access consistently quickly.
Very interesting information!Perfect just what I was looking for!
Only wanna say that this is very helpful, Thanks for taking your time to write this.
As I web site possessor I believe the content material here is rattling fantastic , appreciate it for your efforts. You should keep it up forever! Best of luck.
I am no longer sure where you’re getting your information, however good topic. I needs to spend some time finding out much more or working out more. Thank you for magnificent information I used to be in search of this info for my mission.
obviously like your web-site however you have to take a look at the spelling on quite a few of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling issues and I to find it very bothersome to inform the reality on the other hand I¦ll surely come back again.
I was wondering if you ever considered changing the structure of your website? Its very well written; I love what youve got to say. But maybe you could a little more in the way of content so people could connect with it better. Youve got an awful lot of text for only having 1 or 2 pictures. Maybe you could space it out better?
I like this web site very much, Its a rattling nice berth to read and obtain info . “Practice, the master of all things.” by Augustus Octavius.
You made certain fine points there. I did a search on the subject matter and found the majority of persons will have the same opinion with your blog.
You made some clear points there. I did a search on the issue and found most individuals will consent with your site.
Hello! This post could not be written any better! Reading this post reminds me of my old room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this write-up to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
I love the efforts you have put in this, regards for all the great posts.
Hi, Neat post. There’s a problem with your web site in internet explorer, would check this… IE still is the market leader and a large portion of people will miss your fantastic writing due to this problem.
This blog is definitely rather handy since I’m at the moment creating an internet floral website – although I am only starting out therefore it’s really fairly small, nothing like this site. Can link to a few of the posts here as they are quite. Thanks much. Zoey Olsen
I am impressed with this web site, really I am a big fan .
It is actually a great and helpful piece of info. I am glad that you simply shared this helpful information with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
Some genuinely good articles on this website , thankyou for contribution.
excellent post, very informative. I wonder why the other specialists of this sector don’t notice this. You must continue your writing. I am sure, you’ve a huge readers’ base already!
I?¦ve recently started a web site, the information you offer on this website has helped me tremendously. Thanks for all of your time & work.
I got what you mean ,saved to fav, very decent web site.
Have you ever thought about creating an e-book or guest authoring on other blogs? I have a blog based upon on the same topics you discuss and would really like to have you share some stories/information. I know my visitors would appreciate your work. If you’re even remotely interested, feel free to shoot me an e mail.
I feel this is one of the such a lot significant info for me. And i’m happy studying your article. But want to commentary on few basic issues, The web site taste is great, the articles is in reality nice : D. Excellent activity, cheers
This blog is definitely rather handy since I’m at the moment creating an internet floral website – although I am only starting out therefore it’s really fairly small, nothing like this site. Can link to a few of the posts here as they are quite. Thanks much. Zoey Olsen
Thank you for sharing superb informations. Your website is very cool. I am impressed by the details that you?¦ve on this web site. It reveals how nicely you understand this subject. Bookmarked this web page, will come back for extra articles. You, my friend, ROCK! I found just the information I already searched all over the place and just could not come across. What a great web-site.
Explore Latina Plus Size to find out these Latinas doing his thing. They’re not just posing; they’re indulging in their wildest fantasies. From sucking dick to getting cum on their faces, these Latinas are always ready to do. Their passion and eagerness to please are usually evident in every image.
After study a few of the blog posts on your website now, and I truly like your way of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back soon. Pls check out my web site as well and let me know what you think.
certainly like your website however you have to take a look at the spelling on several of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling problems and I to find it very bothersome to tell the reality nevertheless I’ll surely come again again.
I have learn a few excellent stuff here. Certainly value bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how a lot attempt you set to make any such magnificent informative website.
I like this web site because so much useful material on here : D.
It¦s really a great and helpful piece of information. I¦m glad that you just shared this helpful information with us. Please stay us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.
This is a topic close to my heart cheers, where are your contact details though?
I think you have mentioned some very interesting details , thanks for the post.
whoah this blog is wonderful i love reading your articles. Keep up the good work! You know, a lot of people are hunting around for this info, you can aid them greatly.
you’re really a good webmaster. The web site loading speed is amazing. It seems that you’re doing any unique trick. In addition, The contents are masterpiece. you have done a wonderful job on this topic!
Respect to website author, some excellent selective information.
Very efficiently written article. It will be beneficial to anybody who usess it, as well as yours truly :). Keep up the good work – for sure i will check out more posts.
Attractive section of content. I just stumbled upon your web site and in accession capital to assert that I acquire actually enjoyed account your blog posts. Anyway I will be subscribing to your feeds and even I achievement you access consistently quickly.
Great post. I was checking continuously this blog and I’m impressed! Extremely helpful info specifically the last part 🙂 I care for such info much. I was looking for this certain info for a very long time. Thank you and best of luck.
I like what you guys are up too. Such intelligent work and reporting! Carry on the excellent works guys I¦ve incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it will improve the value of my web site 🙂
I?¦ve recently started a site, the information you provide on this site has helped me greatly. Thank you for all of your time & work.
Good V I should certainly pronounce, impressed with your web site. I had no trouble navigating through all tabs and related info ended up being truly simple to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it at all. Quite unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or something, website theme . a tones way for your client to communicate. Excellent task..
I have been absent for a while, but now I remember why I used to love this site. Thanks, I will try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your website?
Enjoyed reading this, very good stuff, thanks. “What the United States does best is to understand itself. What it does worst is understand others.” by Carlos Fuentes.
My brother recommended I would possibly like this web site. He used to be totally right. This post truly made my day. You cann’t imagine simply how much time I had spent for this info! Thanks!
I’ve been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this blog. Thanks , I’ll try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your website?
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
This is a very good tips especially to those new to blogosphere, brief and accurate information… Thanks for sharing this one. A must read article.
What i don’t realize is in truth how you’re no longer really a lot more smartly-appreciated than you might be right now. You’re very intelligent. You already know therefore considerably in terms of this matter, produced me in my view consider it from a lot of various angles. Its like women and men don’t seem to be interested except it is one thing to do with Girl gaga! Your personal stuffs excellent. Always handle it up!
I like what you guys are up too. Such clever work and reporting! Carry on the excellent works guys I?¦ve incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it’ll improve the value of my web site 🙂
Wow, wonderful blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you make blogging look easy. The overall look of your site is magnificent, let alone the content!
Some really good posts on this web site, thank you for contribution. “When he has ceased to hear the many, he may discern the One – the inner sound which kills the outer.” by H Hahn Blavatsky.
Yeah bookmaking this wasn’t a risky determination outstanding post! .
Loving the info on this site, you have done outstanding job on the blog posts.
Wonderful blog! Do you have any suggestions for aspiring writers? I’m planning to start my own website soon but I’m a little lost on everything. Would you propose starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There are so many options out there that I’m totally confused .. Any suggestions? Many thanks!
My brother recommended I might like this blog. He was entirely right. This post actually made my day. You can not imagine just how much time I had spent for this info! Thanks!
Thanks , I’ve recently been looking for info about this topic for ages and yours is the best I’ve discovered so far. But, what about the bottom line? Are you sure about the source?
Hi, Neat post. There is a problem with your web site in internet explorer, would check this… IE still is the market leader and a large portion of people will miss your wonderful writing due to this problem.
Sweet internet site, super layout, very clean and utilize genial.
A large percentage of of whatever you claim is supprisingly legitimate and it makes me ponder why I had not looked at this with this light previously. This article truly did turn the light on for me as far as this specific subject goes. However there is just one issue I am not necessarily too comfortable with and whilst I make an effort to reconcile that with the actual core idea of your point, allow me observe just what the rest of your subscribers have to say.Very well done.
I enjoy the efforts you have put in this, regards for all the great articles.
Hey there, You have performed an incredible job. I’ll definitely digg it and for my part recommend to my friends. I am confident they’ll be benefited from this site.
I have not checked in here for a while as I thought it was getting boring, but the last several posts are good quality so I guess I?¦ll add you back to my everyday bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
Hey there just wanted to give you a brief heads up and let you know a few of the pictures aren’t loading correctly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different browsers and both show the same outcome.
I was very pleased to find this web-site.I wanted to thanks for your time for this wonderful read!! I definitely enjoying every little bit of it and I have you bookmarked to check out new stuff you blog post.
You could certainly see your expertise in the work you write. The world hopes for more passionate writers like you who are not afraid to say how they believe. Always go after your heart.
I got what you mean , regards for posting.Woh I am happy to find this website through google. “Spare no expense to make everything as economical as possible.” by Samuel Goldwyn.
Hey very nice web site!! Man .. Beautiful .. Amazing .. I’ll bookmark your website and take the feeds also…I am happy to find so many useful information here in the post, we need develop more strategies in this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
Exactly what I was looking for, appreciate it for posting.
Super-Duper site! I am loving it!! Will be back later to read some more. I am bookmarking your feeds also.
My husband and i felt quite joyful Jordan could round up his preliminary research because of the ideas he received from your own site. It is now and again perplexing to simply find yourself offering guidance which often men and women could have been trying to sell. We consider we’ve got the blog owner to give thanks to for that. The entire illustrations you’ve made, the simple site navigation, the friendships you can help promote – it is mostly remarkable, and it is letting our son in addition to us know that that topic is fun, and that is rather pressing. Many thanks for all!
I always was concerned in this topic and still am, thankyou for posting.
You need to participate in a contest for probably the greatest blogs on the web. I will recommend this website!
Hey! Someone in my Myspace group shared this site with us so I came to check it out. I’m definitely loving the information. I’m book-marking and will be tweeting this to my followers! Excellent blog and excellent style and design.
I got what you intend,saved to fav, very decent web site.
Excellent blog here! Also your web site loads up very fast! What host are you using? Can I get your affiliate link to your host? I wish my web site loaded up as quickly as yours lol
The next time I read a blog, I hope that it doesnt disappoint me as much as this one. I mean, I know it was my choice to read, but I actually thought youd have something interesting to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something that you could fix if you werent too busy looking for attention.
I¦ve recently started a site, the information you offer on this site has helped me tremendously. Thank you for all of your time & work.
Good write-up, I am normal visitor of one¦s site, maintain up the nice operate, and It is going to be a regular visitor for a lengthy time.
Lovely just what I was searching for.Thanks to the author for taking his clock time on this one.
I am not real wonderful with English but I find this very easygoing to understand.
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself? Plz reply back as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to know wheere u got this from. thanks
Greetings! Quick question that’s entirely off topic. Do you know how to make your site mobile friendly? My website looks weird when viewing from my iphone4. I’m trying to find a theme or plugin that might be able to fix this problem. If you have any recommendations, please share. Thanks!
Good write-up, I’m normal visitor of one’s blog, maintain up the nice operate, and It is going to be a regular visitor for a lengthy time.
You are a very intelligent person!
What i do not understood is in truth how you’re not really much more smartly-favored than you might be right now. You are very intelligent. You recognize therefore considerably with regards to this matter, produced me in my view imagine it from a lot of numerous angles. Its like men and women aren’t fascinated until it’s something to do with Girl gaga! Your own stuffs excellent. All the time handle it up!
Thank you for the good writeup. It in fact was once a amusement account it. Look complicated to more brought agreeable from you! By the way, how can we communicate?
I’m not certain the place you’re getting your information, but good topic. I needs to spend a while studying much more or working out more. Thanks for excellent info I was in search of this info for my mission.
Very interesting info !Perfect just what I was searching for!
Nice blog right here! Also your web site so much up very fast! What host are you using? Can I get your associate hyperlink in your host? I wish my web site loaded up as quickly as yours lol
I am impressed with this website , very I am a fan.
Throughout the great scheme of things you actually get a B+ with regard to hard work. Where you actually misplaced us ended up being on all the specifics. You know, as the maxim goes, details make or break the argument.. And it couldn’t be much more correct right here. Having said that, permit me tell you what did work. The text is certainly extremely persuasive which is possibly the reason why I am making an effort to opine. I do not make it a regular habit of doing that. Second, while I can see the jumps in reasoning you make, I am not necessarily certain of just how you appear to connect your points which produce the final result. For right now I will subscribe to your issue but trust in the near future you actually link the dots much better.
Would you be interested by exchanging links?
Hi! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading this post reminds me of my good old room mate! He always kept chatting about this. I will forward this page to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Many thanks for sharing!
I am always invstigating online for posts that can facilitate me. Thanks!
As soon as I observed this website I went on reddit to share some of the love with them.
But wanna state that this is very useful, Thanks for taking your time to write this.
Hello There. I found your blog using msn. This is an extremely well written article. I’ll make sure to bookmark it and return to read more of your useful info. Thanks for the post. I will definitely return.
Hi, Neat post. There is an issue together with your site in internet explorer, might check this?K IE nonetheless is the marketplace leader and a large component to folks will omit your excellent writing because of this problem.
I was suggested this web site by my cousin. I’m not sure whether or not this submit is written via him as nobody else know such targeted approximately my difficulty. You’re incredible! Thank you!
I am really enjoying the theme/design of your web site. Do you ever run into any web browser compatibility problems? A small number of my blog readers have complained about my website not operating correctly in Explorer but looks great in Chrome. Do you have any solutions to help fix this problem?
Very good blog you have here but I was curious if you knew of any forums that cover the same topics discussed here? I’d really love to be a part of community where I can get advice from other experienced individuals that share the same interest. If you have any recommendations, please let me know. Thanks!
What i don’t realize is in reality how you’re not actually much more neatly-liked than you might be right now. You are so intelligent. You realize therefore significantly in relation to this subject, produced me individually imagine it from numerous varied angles. Its like women and men are not interested except it is one thing to accomplish with Woman gaga! Your personal stuffs excellent. At all times take care of it up!
F*ckin’ remarkable issues here. I am very glad to peer your article. Thanks a lot and i’m having a look forward to touch you. Will you please drop me a e-mail?
What i do not understood is in truth how you’re not actually much more well-appreciated than you might be right now. You are so intelligent. You recognize therefore significantly with regards to this subject, produced me personally consider it from a lot of varied angles. Its like women and men are not fascinated unless it’s one thing to accomplish with Girl gaga! Your own stuffs nice. All the time handle it up!
I haven?¦t checked in here for some time because I thought it was getting boring, but the last few posts are good quality so I guess I will add you back to my everyday bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
Howdy! Would you mind if I share your blog with my twitter group? There’s a lot of folks that I think would really enjoy your content. Please let me know. Thank you
Some really good blog posts on this internet site, appreciate it for contribution.
Hi there, I found your site via Google while searching for a related topic, your site came up, it looks great. I’ve bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
Greetings from Florida! I’m bored to tears at work so I decided to check out your site on my iphone during lunch break. I really like the info you present here and can’t wait to take a look when I get home. I’m amazed at how fast your blog loaded on my mobile .. I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyways, wonderful site!
Some genuinely grand work on behalf of the owner of this site, dead outstanding content.
You made some nice points there. I looked on the internet for the issue and found most persons will go along with with your site.
Outstanding post, you have pointed out some great details , I too conceive this s a very great website.
Very efficiently written article. It will be supportive to everyone who usess it, as well as myself. Keep doing what you are doing – for sure i will check out more posts.
I happen to be writing to let you know what a excellent discovery our princess encountered reading through your web site. She figured out several things, with the inclusion of what it’s like to have a very effective coaching mindset to have other individuals completely learn certain tricky things. You actually exceeded our expectations. Thanks for giving such precious, trustworthy, edifying and also fun thoughts on your topic to Kate.
Hey! Quick question that’s completely off topic. Do you know how to make your site mobile friendly? My site looks weird when viewing from my iphone 4. I’m trying to find a template or plugin that might be able to fix this problem. If you have any suggestions, please share. Thanks!
I was very pleased to find this web-site.I wanted to thanks for your time for this wonderful read!! I definitely enjoying every little bit of it and I have you bookmarked to check out new stuff you blog post.
It?¦s really a great and useful piece of information. I am satisfied that you shared this helpful info with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
Mitolyn is a cutting-edge natural dietary supplement designed to support effective weight loss and improve overall wellness.
It¦s really a great and helpful piece of info. I¦m glad that you shared this useful info with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
Hiya very cool blog!! Guy .. Beautiful .. Superb .. I will bookmark your site and take the feeds additionally…I am happy to seek out so many useful information here within the submit, we need work out extra strategies on this regard, thank you for sharing.
Do you have a spam issue on this site; I also am a blogger, and I was wanting to know your situation; many of us have developed some nice procedures and we are looking to exchange solutions with others, why not shoot me an email if interested.
Thanks for sharing excellent informations. Your web-site is so cool. I am impressed by the details that you’ve on this website. It reveals how nicely you understand this subject. Bookmarked this web page, will come back for more articles. You, my pal, ROCK! I found simply the info I already searched everywhere and just couldn’t come across. What an ideal site.
The Natural Mounjaro Recipe is more than just a diet—it’s a sustainable and natural approach to weight management and overall health.
I am incessantly thought about this, appreciate it for putting up.
I regard something really special in this site.
hi!,I really like your writing very so much! share we keep up a correspondence more approximately your post on AOL? I require a specialist in this area to unravel my problem. Maybe that’s you! Looking ahead to peer you.
Prostadine is a liquid supplement made from a blend of natural plant-based ingredients, minerals, and antioxidants. Its primary goal is to help
I know this if off topic but I’m looking into starting my own weblog and was curious what all is required to get set up? I’m assuming having a blog like yours would cost a pretty penny? I’m not very internet smart so I’m not 100 certain. Any recommendations or advice would be greatly appreciated. Thanks
Hi! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be ok. I’m undoubtedly enjoying your blog and look forward to new posts.
Regards for helping out, great information.
I like this blog so much, saved to my bookmarks. “American soldiers must be turned into lambs and eating them is tolerated.” by Muammar Qaddafi.
What i do not understood is actually how you are now not really a lot more well-favored than you might be right now. You are very intelligent. You already know therefore significantly relating to this matter, produced me for my part consider it from so many various angles. Its like women and men aren’t fascinated except it is something to accomplish with Lady gaga! Your personal stuffs nice. All the time take care of it up!
Some really excellent blog posts on this website, regards for contribution. “Such evil deeds could religion prompt.” by Lucretius.
I’m truly enjoying the design and layout of your blog. It’s a very easy on the eyes which makes it much more enjoyable for me to come here and visit more often. Did you hire out a designer to create your theme? Exceptional work!
Wonderful blog! I found it while browsing on Yahoo News. Do you have any tips on how to get listed in Yahoo News? I’ve been trying for a while but I never seem to get there! Appreciate it
Have you ever considered creating an e-book or guest authoring on other sites? I have a blog based on the same ideas you discuss and would love to have you share some stories/information. I know my audience would value your work. If you are even remotely interested, feel free to shoot me an email.
Keep functioning ,great job!
This is very attention-grabbing, You’re a very professional blogger. I have joined your feed and stay up for in the hunt for more of your wonderful post. Additionally, I have shared your site in my social networks!
After study a few of the blog posts on your website now, and I truly like your way of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back soon. Pls check out my web site as well and let me know what you think.
Great wordpress blog here.. It’s hard to find quality writing like yours these days. I really appreciate people like you! take care
Hello my friend! I wish to say that this article is amazing, nice written and include almost all important infos. I would like to see more posts like this.
Thank you for another excellent article. Where else may just anybody get that kind of info in such a perfect way of writing? I’ve a presentation next week, and I’m at the search for such info.
Whats Happening i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I have discovered It positively useful and it has aided me out loads. I’m hoping to give a contribution & aid other customers like its aided me. Great job.
I just couldn’t go away your site prior to suggesting that I extremely loved the usual info an individual provide to your guests? Is gonna be again often to check up on new posts
Hello there, just became aware of your blog through Google, and found that it is really informative. I am going to watch out for brussels. I’ll appreciate if you continue this in future. Many people will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
I will right away take hold of your rss as I can’t in finding your email subscription link or newsletter service. Do you have any? Kindly permit me recognize in order that I may subscribe. Thanks.