“8D” Methodology basically uses eight disciplines or principles of “Problem Solving“. This Problem Solving Technique is widely used by quality engineers and managers of automotive industries.
This approach is also commonly used by other professionals working in Manufacturing, Government, Construction, Healthcare, IT/BPO, and other service sectors.
The objective/purpose of the 8D Methodology is to identify and define the problem statement effectively for necessary Corrective and Preventive actions – CAPA to stop/prevent the recurrence and occurrence of the problem.
The corrective actions are basically taken on the identified root cause to prevent the recurrence of the problem whereas preventive actions are taken in advance on potential causes of failure to prevent the occurrence of the problem.
The horizontal deployment of corrective action i.e. corrective actions implementations in other products, machines, or services sometimes referred to as preventive actions also.
The basic 7 QC Tools are commonly used in 8D Report generation and problem-solving methodology/approach/steps.
And apart from 8D, there are various Problem-Solving techniques or methodologies like PDCA Deming Cycle, Quality Circle, and Six Sigma – DMAIC, etc. that are commonly applied in a variety of organizations to identify and solve work-related quality problems.
8D CAPA Report is mainly demanded by all OEMs and IATF 16949 certified companies from their suppliers ( at least ISO 9001 certified) to solve customer complaints or quality-related issues.
Table of Contents
8D Approach | 8D Problem-Solving Steps
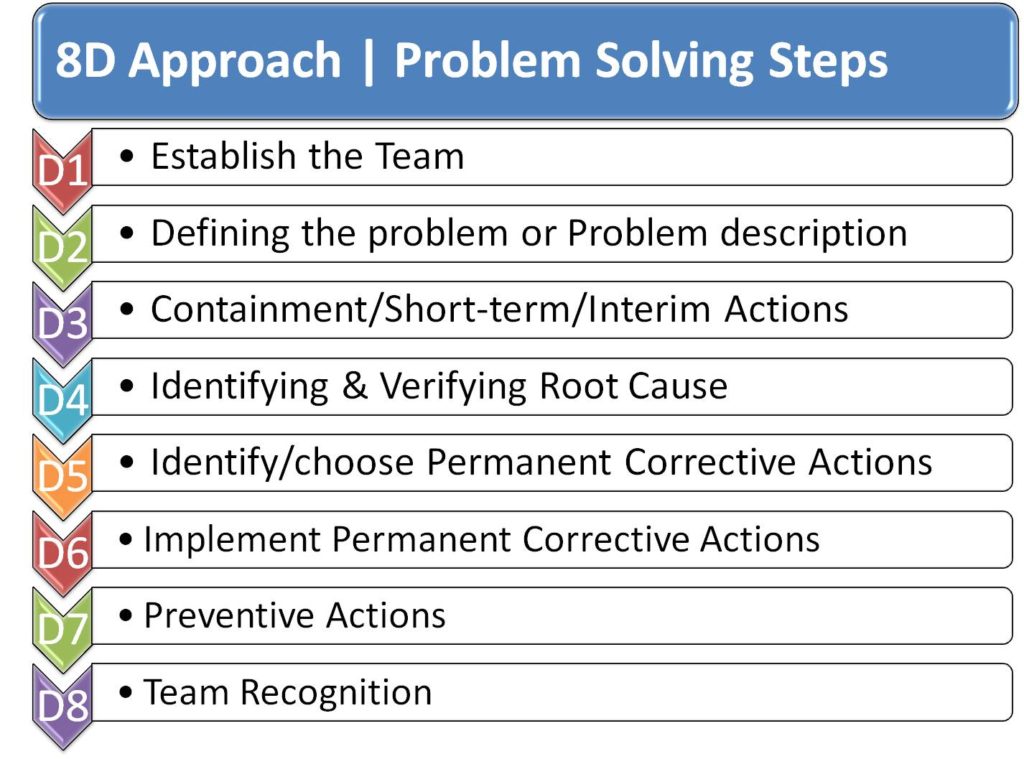
The eight disciplines for process improvement or problem-solving are as follows:
8D Step – D1: Establish the Team
- Identify team leader and team members.
- Establish a team of competent people with product/process knowledge.
- Cross-functional team-CFT members must be related to the concerned problem.
- Identify the team’s goals and objectives.
D2: Defining the problem
- Define the problem clearly using the 5W2H approach and Process flow diagram-PFD.
- Problem definition shall be based on facts, not opinions.
D3: Containment or Interim Actions
- Containment action is also known as Interim action or Short term action.
- Interim actions are immediate actions/first aid taken against the problem to stop defects/suspected material outflow at the customer end.
- Interim actions protect the customer’s production line from the arisen quality problem until we define the root cause and implement necessary countermeasures.
- Examples of containment actions are: Displaying of QAN-Quality Alert Note, customer complaint awareness training to all concerned, defective or suspected material/parts segregation at the WIP stage, store location, ready for the dispatch-RFD stage, supplier end, transit, and customer end.
D4: Identifying & Verifying Root Cause
Root Cause Analysis-RCA is a systematic approach to determining and identifying the Root Cause of the problem. We can use 7 QC tools,5 Whys, 4M or 6M factors, and a Fishbone diagram for RCA.
Steps for Root Cause Identification:
- Use the Brainstorm technique and Fishbone diagram to identify all possible potential causes related to your problem. Consider all 4M or 6M factors in potential cause identification.
- Verify/Validate the identified potential causes.
- Now, Select the best potential cause that contributes to the problem/effect.
- Drill down the selected potential cause using the 5-Why approach to arrive at the root cause of the problem.
- Identify the root cause on both the Occurrence and Detection or Inspection side.
- Verify the root cause for necessary measures.
Note: Don’t end the root cause with the operator’s negligence, lack of training, etc. while identifying the root cause using the 5Why tool. The problem always occurred when there is a gap in the system/procedure/standards.
D5: Identify Permanent Corrective Actions-PCA
- Identify and Select the permanent corrective actions that address and correct the root cause. In other words, the selected PCA will resolve the problem of the customer.
- Solutions/PCA determined to be the best of all the alternatives.
- Document and verify the Permanent Corrective Action (PCA).
D6: Implementing the Permanent Corrective Action
- Implement the best permanent corrective actions (PCA) and ensure effective monitoring of implemented actions.
- Detect any undesirable side effects of implemented corrective actions.
- Return to root cause analysis, if necessary. In other words, if a still problem exists, you may need to fine-tune your actions or re-analyze the problem to identify a new root cause.
D7: Preventive Actions
- Ensure horizontal deployment of corrective actions, i.e. Ensure similar types of problems will not occur in other machines, products, and services.
- Update the Systems, Processes, Procedures, and Documents like PFC, control and FMEA to prevent a recurrence.
- Implement Poka-Yoke (mistake-proofing or error-proofing) to make the system or processes safer and more reliable.
- Ensure effectiveness/sustenance monitoring of permanent corrective actions.
8D Step – D8: Team Recognition
- Congratulations to your team.
- Celebrate the successful conclusion of the problem-solving effort.
- Organization to express thanks to the team.
- Document lesson learned card-LLC and display at all respective areas.
