Accuracy and Precision are the two important term that often comes into picture during the measurement, testing, and calibration process. The effectiveness of the decisions is based on the measurement data’s accuracy and precision.
Equipment with high accuracy and high precision will always lead to better decisions, improve quality of measurement data, low variations, and fewer errors.
Table of Contents
Accuracy and Precision Definition | Meaning
Accuracy is measuring near the target/true value while Precision is getting consistent results of repeated measurements.
In other words, accuracy is the difference between the observations/measurements and the true/actual value of the part, while precision is the variation in measurements obtained when measuring the same part several times with the same instrument.

Accuracy can be measured easily through bias study while Precision can be determined easily through gage repeatability and reproducibility study (Gage R&R study) performed in measurement system analysis–MSA.
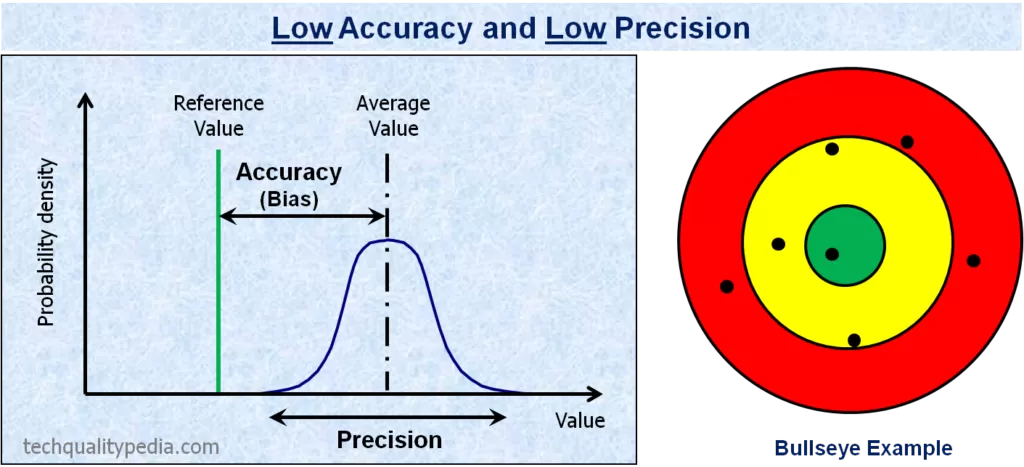
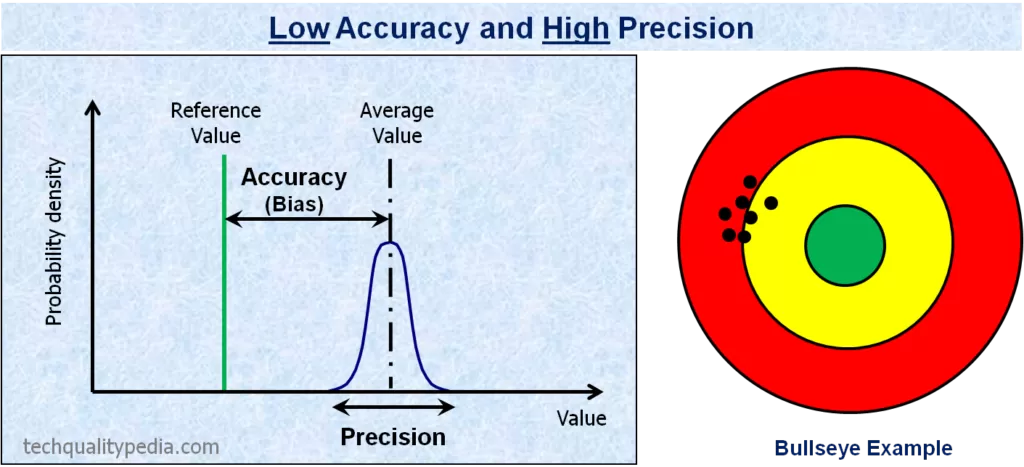
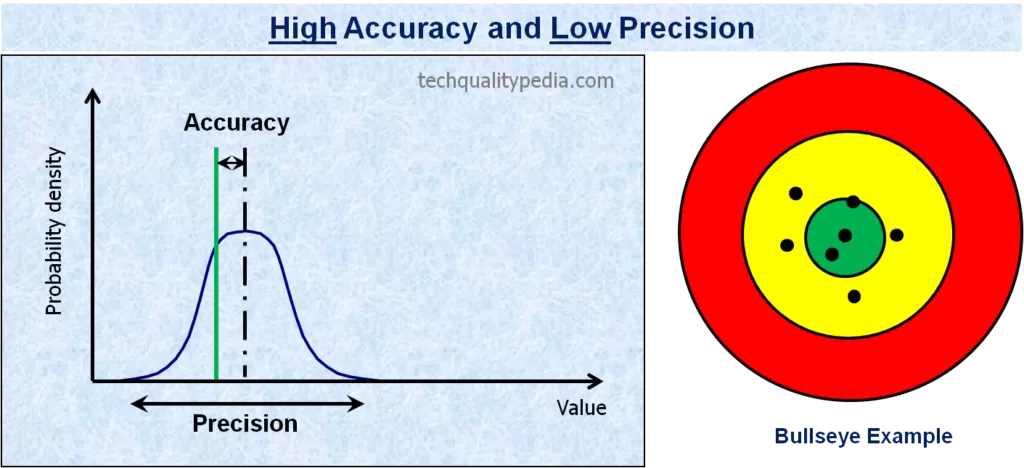
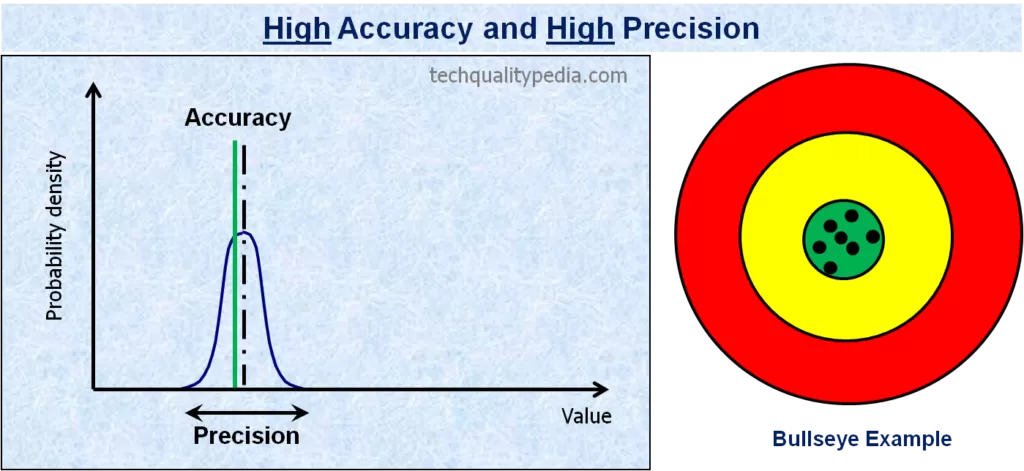
Accuracy is the difference between the observed average value and a standard/target value
Precision is the consistent results of repeated measurements regardless of closeness to standard/target value.
Precisionis autonomous or free ofaccuracy.
Accuracy provides us the measure of the Bias and Precision provides us the measure of the Repeatability and Reproducibility errors.
What is precision in measurement?
A measurement system is said to be valid if a set of measurement data points or measured values falls very close to each other and near to target/reference/true value i.e. both precise and accurate.
In MSA, measurement system variations or errors are classified into five categories – Bias, Stability, Linearity, Repeatability, and Reproducibility.
Bias often referred to as ‘Accuracy’ while Repeatability and Reproducibility errors are referred to as Precision.
Bias is the difference between the observed average value and the true or reference value.
Repeatability is the variation in measurements when the same appraiser/person measuring the same part repeatedly with the same instrument.
Reproducibility is the variation in measurements when different appraisers/persons measuring the same part using the same instrument.
A gage should have adequate accuracy and precision. If these two conditions are not met, the gage may be inadequate and measurement data obtained from the gage maybe have no value.
Accuracy and Precision examples
Below examples of graphs and bullseye will help us to visualize the difference between accuracy and precision concepts:
>Explore Precision meaning with examples.
Related articles
- Explore MSA objective, application, and measurement system.
- Explore measurement system variation.
- Explore Gage Repeatability and Reproducibility study.
