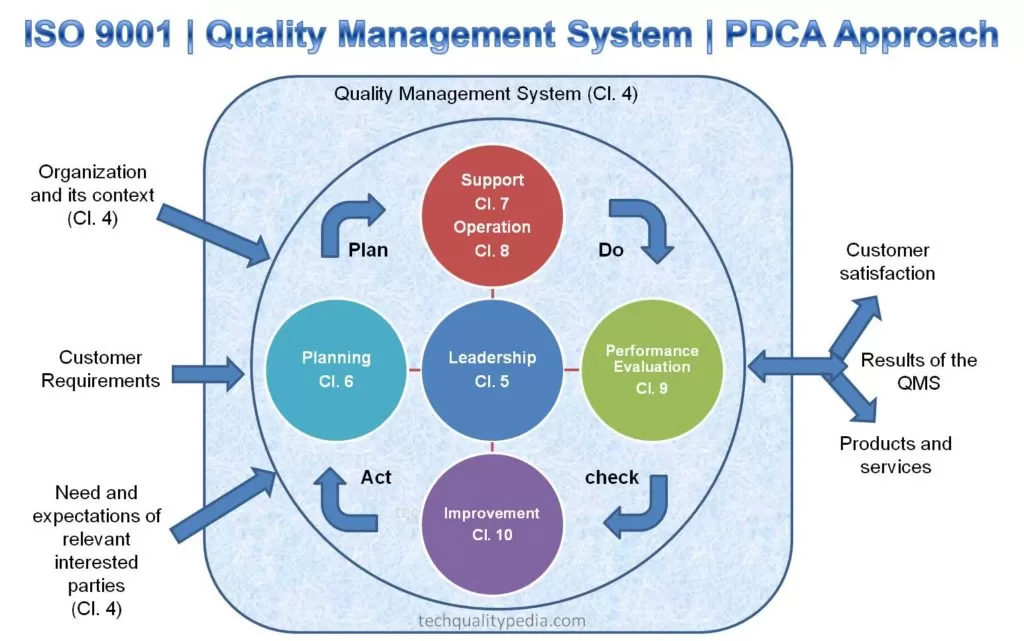
The audit process follows the PDCA approach( Plan – Do – Check – Act ).
The work of the audit process can be divided into the following stages:
- Audit planning & Preparation
- Audit execution
- Audit reporting
- Follow-up

Table of Contents
Audit process – Audit planning & Preparation
The audit planning and preparation steps include:
- Appointing and audit co-ordinator
- Defining the scope of the audit
- Deciding frequency
- Preparing audit programme
- Making audit schedule/plan
- Document review
- Preparation of audit checklists
Audit Means | Audit Definition
Auditing is a systematic, independent, and documented method/process for gathering audit information and objectively analyzing it to determine the extent to which the audit criteria are met.
Types of Audit
Audits are classified into major two categories:
First Classification
- Adequacy Audit
- compliance Audit
Second Classification
- Internal Audit
- External Audit
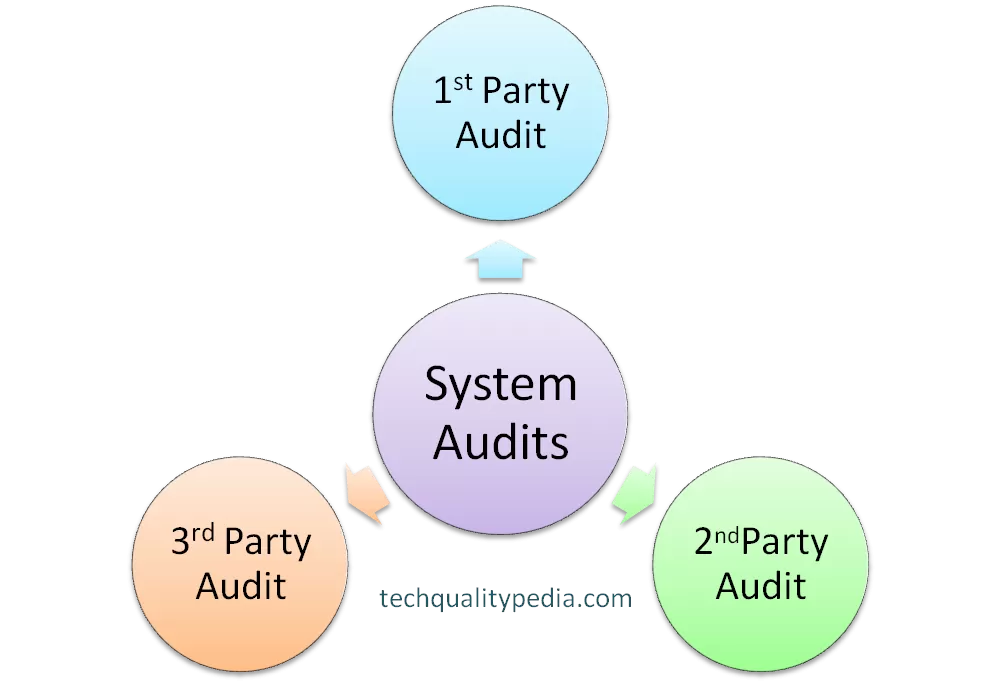
Internal Audit
- First Party Audit (Us on Us) – e.g. Product and Process audit, System audit by internal qualified auditors.
External Audit
- Second Part Audit (Us on them or them on us) – e.g. Customer audit at supplier end, an audit by the consultant.
- Third-Party Audit – Registration audit by third party e.g. Re-certification and Surveillance audit by certification bodies like BSI, DNV, UL, BVQI, TUV, etc.
Audit objectives
General objectives of an audit include:
- To determine conformity/Non-conformity of management system elements.
- To determine the effectiveness of the implemented management system in meeting the system objectives.
- To improve the management system.
- To permit registration/certification of a company’s management system.
Specific objectives of an audit include:
- To evaluate a supplier before establishing a contractual relationship.
- To verify a supplier for continued conformance to a management system under contractual relationship.
- To evaluate an organization’s own management system.
Who qualifies to be an internal auditor ?
- Trained personnel (Own staff or hired professional).
- Independent.
- May not be a specialist, but has a general understanding of the area of audit.
- Knowledge of the relevant standard.
Auditor’s Seven Friends
- What?
- Why?
- When?
- Where?
- Who?
- How?
- Show me?
Audit Samples
- Documents
- Equipment
- Personnel
- Products
- Activities
- Records etc.
Information sources for selection of samples are-
- History or findings of previous audits.
- Customer complaints reported.
- Internal customers.
- Management concerns.
Audit standards
There are various management standards used for auditing the organization’s management system.
Some of the widely used audit standards are listed below:
- ISO 9001: Quality Management Standard – for any kind of industry/sector.
- IATF 16949: Quality Management Standard – for automotive industries.
- AS9100: Quality Management Standard – for aerospace industries.
- ISO 14001: Environmental Management Standard – for environment safety.
- ISO 45001: Occupational Health and Safety standard – for worker’s safety.
- SA8000: Social Accountability Standard.
Audit Report format
Audit report format generally consists of following details:
- Audit ref. no.
- Audit date
- Client name
- NC no.
- NC description with objective evidence
- Correction and Corrective action plan with responsibility and target date
- CAP review and verification with date
- CAP closure status.
Download Audit report format and NC report format
You’ll also like: