ISO 9001:2015 is one of the most recognized standard that defines the quality management system requirements.
The revised ISO 9001 standard is based on the high-level structure and integrates with other management systems such as IATF 16949, ISO 14001, and ISO 45001 standards.
Table of Contents
What is ISO?
ISO stands for International Organization for Standardization. The dictionary meaning of the ‘ISO’ word is ‘Similar’.
It is ISO & not IOS – why?
‘Iso’ is a word derived from the Greek word ‘Isos’ meaning ‘equal’.
Remember ‘isometric’ ‘Equal’ relates to ‘standard’.
Translation of the organization’s name in different languages may result in different acronyms, hence the common name “ISO”
What is ISO 9001?
ISO 9001 means a standard that defines the QMS(Quality Management System) requirements, aims to produce quality products and services, and ultimately to meets customer needs and expectations.
ISO 9001 Quality Management Systems – Requirements
Revised ISO 9001 standard specifies requirements for a QMS when an organization:
- Needs to demonstrate its ability to consistently deliver goods and services that meet customer and all applicable legal requirements.
- Aims to increase customer satisfaction by implementing the system effectively, including processes for system improvement and ensuring to meets all applicable legal compliance and customer requirements.
All the requirements of ISO 9001:2015 quality management standard are generic and can be applied to any company or organization, regardless of its size, type, or products and services it provides.
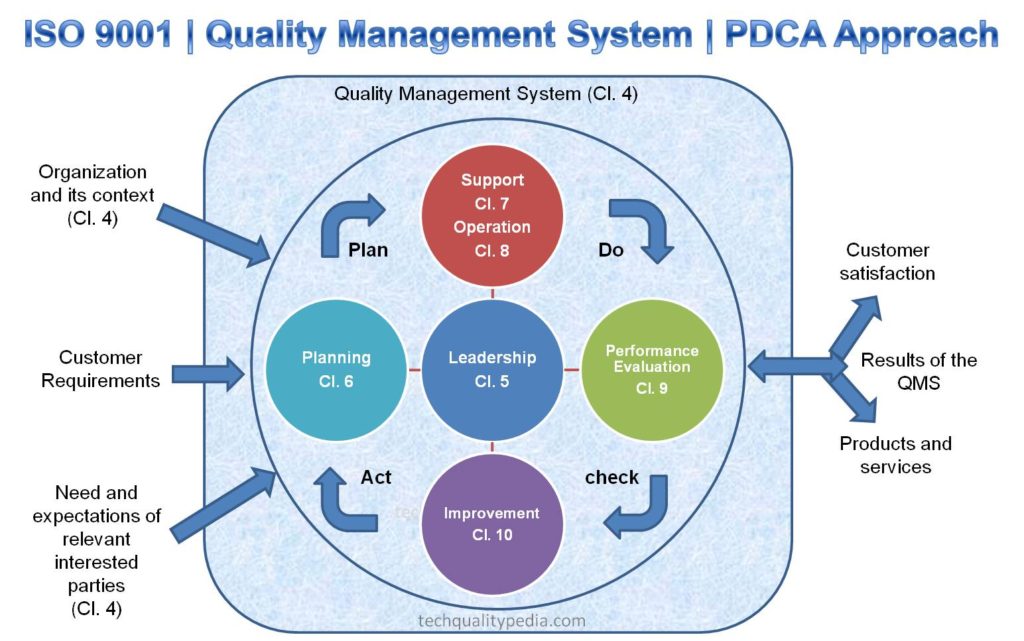
ISO 9001:2015 Approach
The revised ISO 9001:2015 standard is based on the following three approaches:
- Process approach
- PDCA Approach
- Risk-based thinking
The old ISO 9001:2008 standard was based on the Process approach and PDCA approach only.
Risk-based thinking is the new approach that is added in the revised ISO 9001:2015 standard to address the risk opportunities that could cause its processes and quality management system to deviate from the planned results.
Risk is the effect of uncertainty on expected/desired results.
Quality Management System ISO 9001 | Fast facts
The fast facts about the Quality Management System ISO 9001:2015 are:
- ISO 9001:2015 replaced ISO 9001:2008 standard.
- The revised ISO 9001 was published in September 2015.
- The revised standard consists of 10 clauses. Earlier there were 8 clauses in ISO 9001:2008.
- The changes were managed by the ISO committee ISO/TC 176.
- ISO 9001:2015 is more compatible with other management systems, such as ISO 14001, and ISO 45001, making it more effective and efficient to integrate management systems.
- IATF 16949 standard will be used in conjunction with ISO 9001:2015. i.e. Organizations looking for IATF certification will have to follow the ISO 9001:2015 standard separately.
ISO 9001 Principles | Quality Management System Principles
The 7 Quality Mgmt. Principles as per the latest standard are:
- Customer focus
- Leadership
- Engagement of People
- Process Approach
- Improvement
- Evidence-Based Decision Making
- Relationship Management
QMS Principles – ISO 9001:2015 Vs ISO 9001:2008
The major changes incorporated in ISO 9001 quality management principles are:
- Involvement of people changed to Engagement of people.
- Factual approach to decision-making changed to Evidence-Based decision-making.
- System approach to management changed to Improvement.
- Continual Improvement and Mutually Beneficial Supplier Relationship changed to Relationship Management.
The new standard is based on the seven quality management principles whereas the old standard was based on the eight quality management system principles.
Seven Quality Management Principles (As per ISO 9001:2015 new version)
- Customer focus
- Leadership
- Engagement of People
- Process Approach
- Improvement
- Evidence-Based Decision Making
- Relationship Management
Eight Quality Management Principles (As per ISO 9001:2008 old version)
- Customer focus
- Leadership
- Involvement of People
- Process Approach
- System Approach to Management
- Factual Approach to Decision Making
- Continual Improvement
- Mutually Beneficial Supplier Relationship
ISO 9001 Clauses
- Clause 1 – Scope
- Clause 2 – Normative References
- Clause 3 – Terms and Definitions
- Clause 4 – Context of the organization
- Clause 5 – Leadership
- Clause 6 – Planning
- Clause 7 – Support
- Clause 8 – Operation
- Clause 9 – Performance evaluation
- Clause10 – Improvement

The mandatory seven clauses of ISO 9001 are clauses 4 to clause 10. All these clauses are arranged according to the PDCA cycle.
Difference in clauses – ISO 9001:2008 and ISO 9001:2015
There is no change in the first three clauses of the revised ISO 9001:2015 standard and are the same as those in ISO 9001:2008, but there is a considerable difference from the fourth clause onwards.
| Clause | As per ISO 9001:2008 old version | Clause | As per ISO 9001:2015 new version | Remarks |
| Cl. 0 | Introduction | Cl. 0 | Introduction | |
| Cl. 1 | Scope | Cl. 1 | Scope | Same |
| Cl. 2 | Normative References | Cl. 2 | Normative References | Same |
| Cl. 3 | Terms and Definitions | Cl. 3 | Terms and Definitions | Same |
| Cl. 4 | Quality Management System | Cl. 4 | Context of the organization | Change |
| Cl. 5 | Management Responsibility | Cl. 5 Cl. 6 | Leadership Planning | Change |
| Cl. 6 | Resource Management | Cl. 7 | Support | Change |
| Cl. 7 | Product realization | Cl. 8 | Operation | Change |
| Cl. 8 | Measurement, analysis, and improvement | Cl. 9 Cl. 10 | Performance evaluation Improvement | Change |
When to Implement ISO 9001?
When a company wants to improve its QMS to enhance its goods or services, and eventually customer satisfaction. The ISO 9001 standard is most commonly used when:
- Customers specify this need in their contracts.
- Countries need certification to trade with them.
- Businesses aim to increase the quality of their goods and the level of customer satisfaction.
- Organizations want to meet all legal and statutory compliance.
Benefits of ISO 9001
The potential benefits of implementing QMS standard based on ISO 9001 requirements are:
- Improved customer satisfaction.
- Enhanced Quality, Productivity, and Work Efficiency.
- Reduced Costs of Poor Quality and Waste
- Increased Business Opportunities
- Better Risk Management-addressing risks and opportunities, and effective planning of actions to mitigate them.
- Provide the products and services consistently that meet all legal compliance and customer requirements.
- Provide the right direction to achieve organizational objectives and goals.
- Engaging employees for continual improvement in products, processes, and services.
- Global Recognition and Credibility.
- Better Supplier Relationships.
- Compliance with Regulatory Requirements.
- Employee Satisfaction and Engagement.
- Stronger Internal Communication.
- Continuous Improvement in the Product, Processes, and Services.
