KPIs stand for Key Performance Indicators. KPIs are the metrics that monitor the performance of business objectives against the set target/goal (desired result). In other words, KPIs measure a company’s performance/output against set objectives and targets.
Key Performance Indicators are generally used to measure performance on a daily, weekly, and monthly basis against a defined target or goal, but some others focus on achieving long-term goals.
KPIs vary from company to company and help every area of the business like Sales and Marketing, Finance, Production, Quality, and HR.
KPIs provide the targets for teams to measure progress to achieve desired results and help in better decision-making.
The Key Performance Indicator is one of the important tools of the Lean Manufacturing process and also fulfills the quality management system requirements.
Table of Contents
KPI Definition
A Key Performance Indicator is a measurable value that demonstrates how effectively an organization is achieving its desired key business objectives/goals.
KPIs Types
Key Performance Indicators are to be made in a company at multiple levels to evaluate their success and to achieve the desired target/goal effectively.
Key Performance Indicators are broadly classified as Higher Level and Lower Level KPIs.
- Higher Level KPIs – focus on the overall performance of an organization. These are generally CEO and director-level indicators. Also known as business-level KPIs.
- Lower Level KPIs – focus on the functional or departmental processes such as Production, Quality, HR, Purchase, Finance, Sales and Marketing. Also known as functional or departmental-level Key Performance Indicators.
The lower-level key performance indicators should be aligned with the higher-level key performance indicators.
Key Performance Indicators are also categorized as:
- Quantitative KPIs- that can be presented with numbers.
- Qualitative KPIs- that cannot be presented as a number.
- Leading Indicators- that can used to predict the outcome of a process. In simple, leading indicators Influence future performance.
- Lagging Indicators- that show/present the success or failure post hoc. In simple, lagging indicators analyze past performance.
- Process Indicators- that represent the process efficiency and productivity
SMART KPIs
Key performance indicators (KPIs) of a company should be SMART to achieve desired results for business success.
SMART KPIs means:
- S – Specific
- M – Measurable
- A – Attainable
- R – Relevant
- T – Time-bound
KPIs Examples | PQCDSM KPIs
In most organizations, Key Performance Indicators are generally monitored according to the PQCDSM approach, especially in the automotive and manufacturing industries.
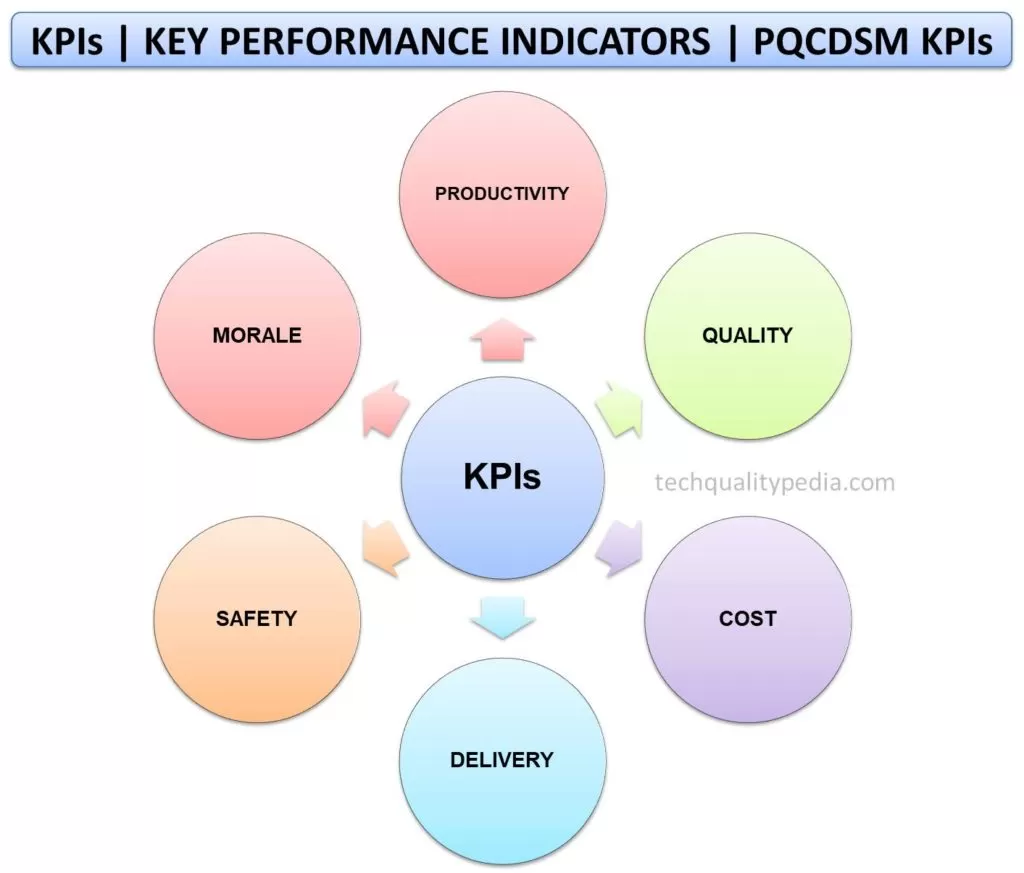
Some of the important Manufacturing or PQCDSM or Functional KPIs are as follows:
PRODUCTIVITY KPIs
Focus: Productivity key performance indicators focus on process efficiency improvement.
- Production Plan Adherence
- OEE (Overall Equipment Efficiency)
- Capacity Utilization
- SMED ( Single Minute exchange of dies )- SMED performance is measured in total no. of setups in various time slots.
QUALITY KPIs
Focus: Product and process quality improvement, rejection, and customer complaints reduction.
- In-house Rejection/Scrap (unit of measurement in %age or PPM)
- In-house Rework (unit of measurement in %age or PPM)
- Customer Returns (unit of measurement in %age or PPM)
- Customer Complaints (unit of measurement in numbers)
- Cost of Poor Quality (unit of measurement in %age, and value)
- Vendor / Supplier rejection (unit of measurement in % or PPM)
- Warranty Return (unit of measurement in % or PPM)
- Straight Pass final quality gate (unit of measurement in % )
COST Key Performance Indicators
Focus: Process improvement cost reduction.
- Tooling cost
- Raw Material cost
- Consumable cost
- Energy/Electricity cost
- Fuel cost
- Labor cost
- Machine Breakdown cost
DELIVERY Key Performance Indicators
Focus: Reduction in delivery time, delivery of the right quantity at the right time.
- Customer Schedule Adherence
- On-Time Delivery- adherence to customer’s delivery commitments.
- Supplier/Vendor delivery performance monitoring.
SAFETY Key Performance Indicators
Focus: Reduction in human injury or accidents and better safety at the workplace.
- Accident severity– major or minor
- Accident frequency or reported
- Safety training hours
MORALE KPIs | HR Key Performance Indicators
Focus: To increase employee morale and competence level.
- Total Employee Involvement (TEI) – Encourage involvement of the employees through Suggestion schemes (e.g. suggestion /employee, Suggestion/month).
- Enhance the Competence & Skill of employees (e.g. Training plan adherence, Training hours/ employee, Training effectiveness)
- Employee Absenteeism
- Employee Attrition Rate
Some other Functional or Departmental KPIs are:
STORE Key Performance Indicators
- Inventory Turnover Ratio (ITR)
- Red Inventory (Direct/Indirect)
- Gray Inventory (Direct/Indirect)
- Green Inventory (Direct/Indirect)
MAINTENANCE Key Performance Indicators
- PM Plan adherence
- Mean Time To Repair (MTTR)
- Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF)
- Breakdowns Hours
KPI for Sales | Marketing
- Customer Schedule vs Actual
- Customer Satisfaction Index (CSI)
- Customer Rating
- Customer Retention
- Sales Growth Rate
Financial Key Performance Indicators
- EBITDA
- Net Profit
- Gross Profit
- Profit Margin
- Revenues Growth
- Revenue Per Client (RPC)
Continual Improvement Key Performance Indicators
QMS | EHS KPIs
- Internal Audit Plan adherence
- MRM Plan adherence
- Non-conformance closure-100% adherence
You’ll also like: