Lean production manufacturing is a management philosophy and operational strategy that was developed in Japan following World War II.
Lean Production Manufacturing is a standardized approach for the identification and elimination of waste (non-value-added process/activities) for achieving perfection.
A systematic approach for maximization of value and elimination of waste.
“A systematic/standardized approach that reduces the time-frame between the customer’s order and delivery of product through waste elimination.
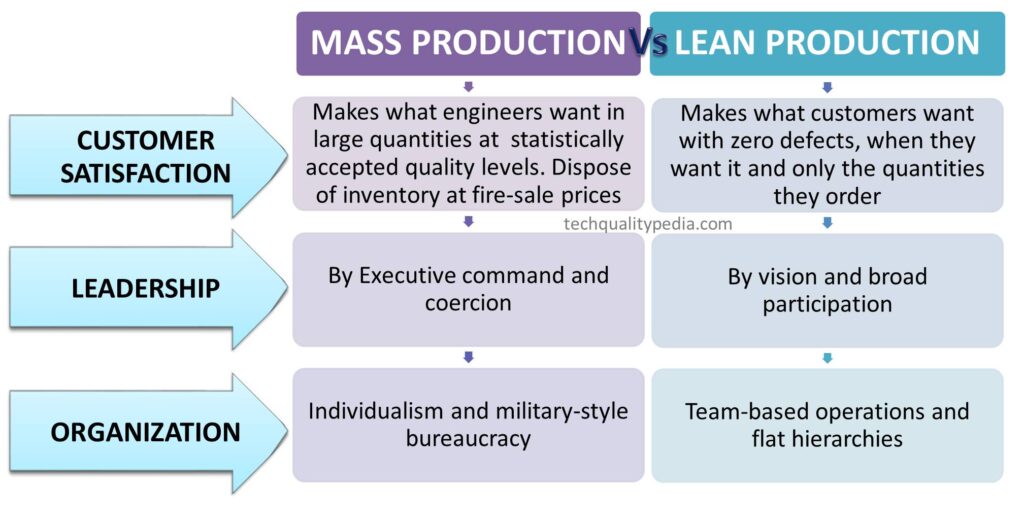
Table of Contents
Mass Production Vs Lean Production
| Mass Production | Lean Production | |
| Customer Satisfaction |
Makes what engineers want in large quantities at statistically accepted quality levels. Dispose of inventory at fire-sale prices |
Makes what customers want with zero defects, when they want it and only the quantities they order |
| Leadership | By Executive command and coercion |
By vision and broad participation |
| Organization | Individualism and military-style bureaucracy | Team-based operations and flat hierarchies |
| External Relations |
Based on price | Based on long-term relations |
| Information Management
|
Poor management based on abstract reports generated by and for managers |
Rich management based on visual control systems maintained by all employees |
| Culture | Of Loyalty & obedience; sub-culture of alienation and labor strife |
Harmonious culture of involvement based on human resources & long term relations |
| Production | Large-scale machines, functional layout, minimal skills, long production runs, massive inventories |
Human scale machines, cell-type layout, multi-skill, one-piece flow, zero inventories |
| Design & Engineering |
Isolated genius model with little input from customers and little respect for production realities |
Team-based model, with input from customers & concurrent development of product and process design |
| Maintenance & Quality |
By Specialists | Equipment management by production & engineering |
Principles of Lean Production Manufacturing
The core principles of lean production manufacturing are to eliminate waste and optimize efficiency. These principles include:
- VSM – Value Stream Mapping: Identifying the value-added and non-value-added activities in a manufacturing process.
- JIT – Just-in-Time: Producing and delivering products when needed by customers.
- Continuous Improvement through Kaizen: Promoting an improvement-oriented culture at all levels.
- Autonomation (Jidoka): Building self-monitoring and self-regulating processes to eliminate quality defects.
- Workforce Empowerment: Total Employee Involvement-TEI in decision-making and quality problem-solving.
The primary objective of lean manufacturing is the elimination of the supply chain. The eight recognized types of waste in lean production manufacturing are:
- Overproduction
- Inventory
- Transportation
- Waiting
- Motion
- Defects
- Overprocessing
- Underutilized Talent
Lean Production Manufacturing Tools and Techniques
Lean production manufacturing utilizes various quality and productivity improvement tools and techniques to achieve its desired objectives, such as:
- Lean 5S: To organize the workplace.
- Kanban: A visual signaling system for inventory control.
- Poka-Yoke: Error-proofing system to prevent quality defects.
- Value Stream Mapping: VSM visualizes processes to identify values and inefficiencies.
- Total Productive Maintenance: Ensuring zero machine breakdowns.
- Andon: Visual management to alert production problems.
- Six Sigma-DMAIC
- Single Minute Exchange of Die-SMED
- Just In Time-JIT
- Continuous Improvement/PDCA
- Cellular Manufacturing
- And many more Lean Manufacturing Tools…
