MSA-Measurement System Analysis primarily deals with investigating/studying the effect of the Measurement System on the measured value.
The measurement system analysis primarily focused on finding the effect of Equipment Variation and Appraiser/Personnel variation.
It is a statistical tool that is used to assess whether the measurement system is capable or not.
We test the system to find out the numerical values of its statistical properties and compare them to accepted standards.
MSAis one of the important quality tools among the below-mentioned five core tools ofthe IATF 16949:2016standard.
- Advanced Product Quality Planning-APQP
- Production Part Approval Process-PPAP
- Failure Mode and Effect Analysis-FMEA
- Measurement System Analysis-MSA
- Statistical Process Control-SPC
Table of Contents
Measurement System
Measurement System is defined as the complete process used to obtain measurement.
In other words, a Measurement System is a combination of –
- Operations
- Procedures and methods
- Personnel
- Environment
- Equipment/Gage/Instrument
- Software and
- Assumptions etc.
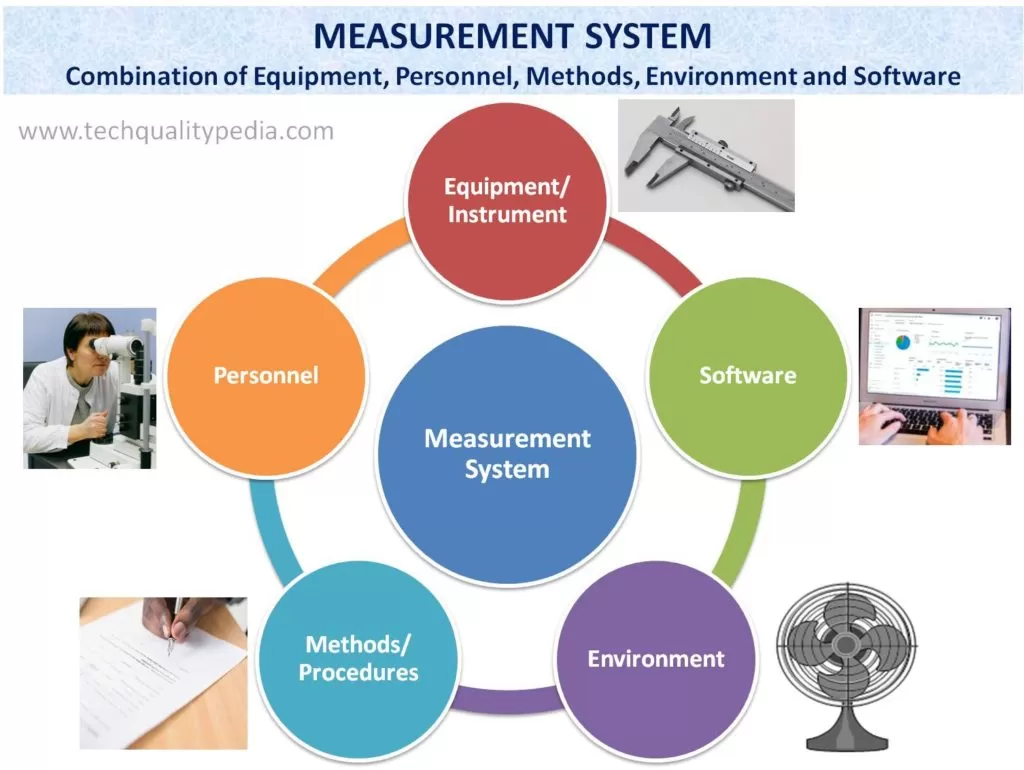
A measurement system is a process by which we assign a number to a characteristic of a product or service. The first step in assessing a system is to understand this process and determine if it will satisfy our requirements.
MSA Types
- Variable MSA study – based on the variable data collection e.g. Length, width, dia, etc.
- Attribute MSA study – based on the attribute data collection e.g. Go and No Go, OK and Not OK
Purpose of MSA:
- To better understand the sources of variation that can influence the result produced by the system.
- To find the equipment variation (within system variation) and appraiser variation (between system variation).
- To Minimize the variation in the measurement system.
- To assess the quality of the measurement system.
MSA Applications:
- To assess(accept/reject/improve) new measuring equipment/measuring process.
- A comparison of one measuring device with another.
- To compare measuring instruments/gage/device before and after repair.
Why MSA is required?
Effectiveness of decisions making process purely based on the quality and accuracy of collected data. The quality of the measured data decreases due to measurement system errors and that leads to poor decision making. MSA here is used to analyze and reduce the measurement system errors and helps in effective decision making.
In other words, the decision to adjust a manufacturing process based on measurement data. If the quality of the measured data is low then chances of wrong judgment can be made.
During product inspection, an operator or appraiser can accept bad parts as good parts and good parts as bad parts, resulting in higher costs, higher rejection, and customer complaints. Therefore, MSA is used to avoid the probability of such mistakes assure accurate inspection, and help to stop defective part outflow at the customer end.
Measurement Issues
Three fundamental issues need to be addressed in evaluating a measurement system:
- Adequate discrimination.
- Statistical stability over time.
- Statistical properties to be:
- Consistent over the expected range, and
- acceptable for process control.
Measurement System Errors
Five categories of measurement system errors/variations are:
- Bias – often referred to as “Accuracy”.
- Stability
- Linearity
- Repeatability
- Reproducibility
Repeatability and Reproducibility errors are referred to as “Precision”.
Bias, Stability, and Linearity fall under Location Errors.
Repeatability and Reproducibility fall under Width Errors
Measurement System Variation
The sources of variations present in the measurement system are:
- Method – variation due to inspection and testing method.
- Man – inspector/operator skills, and training.
- Machine/Equipment/Tools – Jig/fixtures, gages, measuring and testing equipment used.
- Part to be measured.
- Environment – temperature, humidity, etc.
All the above-mentioned possible sources of variation must be considered during the Measurement System Analysis study.
Measurement system analysis activities generally examine the two primary sources of variation, the first is the parts variation and the second is the measurement of those parts i.e. equipment and appraiser variation. The total variation of the measurement system is the sum of these two values.
GRR Acceptance Criteria
Gage R&Racceptance criteria based on the estimated value of repeatability and reproducibility (%R&R) of the measurement system. Click to see GRR Acceptance Criteria.
You may also like:
- Accuracy and Precision | What is precision in measurement?
- Accuracy definition | Accuracy Vs Precision | Accuracy meaning
- Precision meaning | Precision synonyms | Precision definition
- MSA | MSA meaning | MSA full form | MSA in Quality
- Gage R & R | GRR | Gage repeatability and reproducibility
- Variation Meaning | Process Variation | Common Causes Vs Special Causes
- What is Six Sigma? Six Sigma Levels | Methodology | Tools
- What is Process Capability? Process Capability Indices | Cp and Cpk
- Quality Assurance and Quality Control | Difference and Meaning
