Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is a performance metric used in the manufacturing process to measure how effectively a machine or process is being utilized.
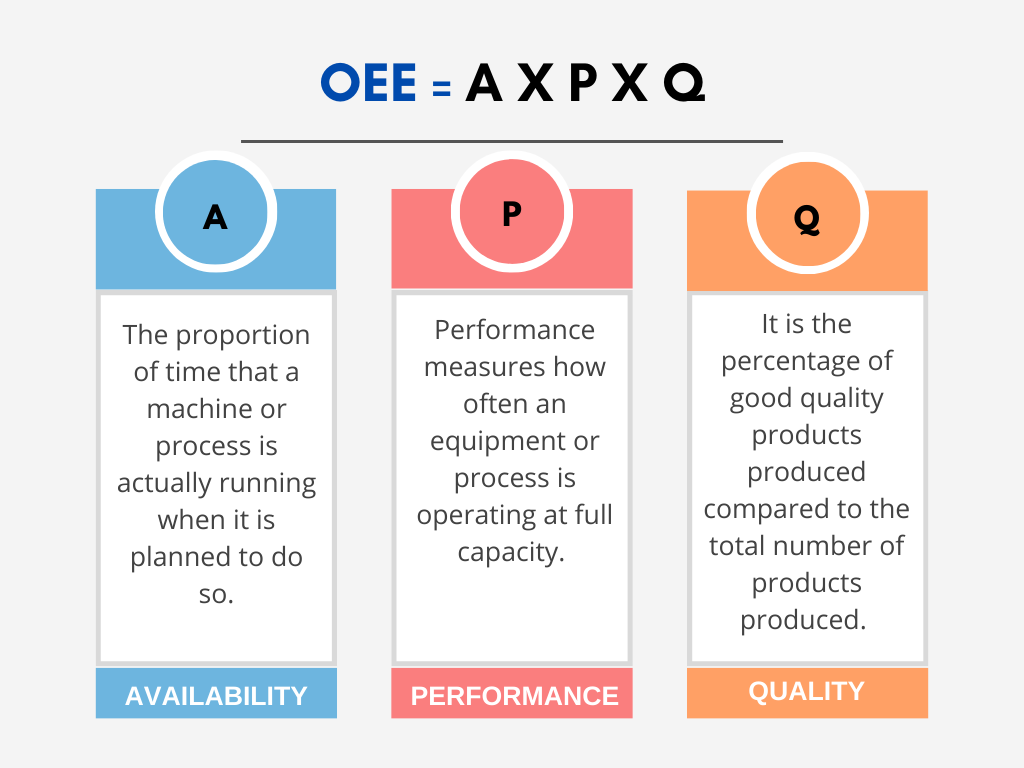
OEE is calculated by multiplying three factors (Availability X Performance X Quality).
Table of Contents
AVAILABILITY
The percentage of time that the equipment/machine or process is scheduled to run and is actually running. In other words, the proportion of time that a machine or process is actually running when it is planned to do so.
PERFORMANCE
Performance measures how often an equipment or process is operating at full capacity. In other words, the percentage of time that the equipment/machine or process is running at its full/maximum speed.
QUALITY
It is the percentage of good quality products produced compared to the total number of products produced. In other words, Quality is the ratio of the quantity of high-quality items to all products produced.
OEE is a useful KPI (Key Performance Indicator) for the manufacturers since it can help the organizations/manufacturers to identify the areas for improvement. When a manufacturer is tracking the OEE at defined interval & initiating continual improvement actions, then their process quality, productivity & efficiency is increased.
QUALITY FORMULA
The OEE formula is:
OEE = Availability x Performance x Quality
OEE CALCULATION I EXAMPLE
A machine is scheduled to run for 8 hours per day. During that time, it is down for maintenance for 30 minutes and produces 1000 units. The machine’s maximum production rate is 150 units per hour.
To calculate the OEE, we first need to calculate the availability, performance, and quality.
Availability: Operating Time / Scheduled Time
Operating Time = (Scheduled Time – Downtime) = (8 hours – 0.5 hours) = 7.5 hrs
Here Scheduled time is 8 hours & downtime is ½ hours
Now,
Availability = Operating Time / Scheduled runtime
Availability = 7.5 hours / 8 hours = 93.75%
Performance = (Actual output / Theoretical output) x 100%
Performance = (1000 units / (150 units/hour * 8 hours)) x 100%
= ( 1000 / 1200) x 100%
= 83.33%
Quality = (Good units produced / Total units produced) x 100%
Quality = (1000 units / 1000 units) x 100% = 100%
Now, we can calculate the OEE:
OEE = Availability x Performance x Quality
OEE = 93.75% x 83.33% x 100% = 78.12%
This means that the machine is being used 78.12% of its potential.
OEE DOWNTIME LOSSES
The major contributors to OEE losses are downtime losses. Downtime losses refer to any period when equipment/machine is stopped or not available to run due to planned or unplanned events.
Planned downtime: Includes Scheduled maintenance, changeover, breaks, etc.
Unplanned downtime: Includes Equipment breakdowns, material shortages, power outages, etc.
According to a National Institute of Standards and Technology research, industrial facilities’ average OEE is just 60–70%. This indicates that 30–40% of each hour of production time is wasted due to downtime.
Downtime losses can take many different forms, including:
- Equipment failure
- Material shortage
- Power failure/outage
- Setup and changeovers
- Minor stops
Equipment failure: The most frequent cause of downtime loss is equipment failure. Wear and tear, inadequate maintenance, human mistakes, and other causes can all lead to equipment failure.
Material shortage: This happens when there aren’t enough Raw Materials & supplies available to keep the machinery/equipment running. It can be caused due to poor inventory management, supplier delays, and quality problems.
Power outages: When there is a power outage, the equipment is unable to function. It can be caused due to bad weather conditions, equipment failures, and human mistakes.
Setup and changeovers: Setup and changeovers: This is the time it takes to switch the equipment from producing one type of item to another. Changeovers and setup can be time-consuming, especially for complicated items.
Minor stops: These are small interruptions or pauses in the production process, such as when a worker needs to adjust the equipment or clear a jam. Small interruptions can add up over time, leading to large downtime losses.
How to reduce OEE downtime?
Manufacturers can take a number of actions to decrease downtime losses, including:
- Preventive maintenance
- Just-in-time (JIT)
- Single-minute exchange of dies (SMED)
- Total productive maintenance (TPM)
- Uninterruptible power supplies (UPSs)
- Lean 5s
Preventive maintenance: Routine equipment inspections and maintenance can help to prevent or reduce unplanned equipment breakdowns.
JIT (Just-in-time) inventory management: By ensuring that there is always enough material on hand to satisfy production demands, JIT inventory management can assist to prevent material shortages.
SMED (Single-minute exchange of dies): is a procedure for speeding up setup and changeover times. It stands for a single-minute exchange of dies.
Total productive maintenance (TPM): is a program that aims to increase the performance and dependability of equipment.
Uninterruptible power supplies (UPSs): In the case of a power outage, UPSs may supply backup power to keep equipment functioning and minimize downtime losses.
Organizations can improve their OEE and productivity by taking action to decrease downtime losses.
