Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION
Financial markets are the backbone of the world economy, which act as marketplaces where buyers and sellers trade financial securities. Understanding the different kinds of markets is very crucial for anyone who seeking to invest in the financial world. The primary and secondary markets are two of the most important types. Understanding the distinctions between these markets can aid investors in making better-informed decisions.
WHAT IS SECURITY?
Investors invest their funds in buying shares, bonds, etc., called Securities.
Securities are tradable financial instruments (such as shares/stock, bonds, derivatives, etc.) used to raise capital in public and private markets.
SECURITIES MARKET
The securities market or Financial market is a critical component of the global financial system, serving as the bedrock for investment, economic growth, and wealth creation. Understanding the securities market is essential for anyone looking to invest or participate in the stock or share markets.
Definition: A broad term that refers to any marketplace where various financial instruments/securities such as stocks, bonds, and derivatives, are bought and sold.
Instruments: The securities market includes both Equity (stocks) and Debt (bonds) securities.
Time Horizon: Include both short-term (money market) and long-term (capital market) securities.
Participants: Involves a wide range of investors, including individuals retailers, governments, and institutions like banks and insurance companies.
Purpose: Facilitates the trading of securities, ensuring liquidity, price discovery, and allocation of resources efficiently.
TYPES OF SECURITIES
Some major types of Securities are listed below:
- Equity Shares commonly called Shares or Stocks
- Debt Securities
- Derivatives (Futures and Options)
- Mutual Funds
- Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs)
Equity Securities
Equity securities, commonly known as stocks/shares, represent ownership in a company. When you buy a share of stock in the stated company, you become an owner or part-owner and thus are entitled to its profits (in the form of dividends). Investing in an equity security is generally seen as a high-risk, high-reward proposition.
Debt Securities
Debt securities can include bonds, debentures, and notes, representing a loan made by an investor to a borrower (in most cases corporate or governmental). In exchange, the borrower promises to repay the original principal amount with interest. Debt securities are generally considered safer than Equity securities but provide lower returns than equity.
Derivatives (Futures and Options)
Derivatives are financial instruments or contracts that derive their value from an underlying asset, such as stocks, bonds, and commodities. Options, Futures, and Swaps are the common types of derivatives. Derivatives are often used for hedging risks or speculative purposes.
Mutual Funds
Mutual funds are a well-liked and popular investment that pool/combine the funds of several individuals to buy stocks, bonds, and other assets.
Varioustypes of Mutual Fundsare classified as follows:
- Mutual Funds by Investment Objective
- Mutual Funds by Structure
- Solution-Oriented Mutual Funds
ETFs | Exchange Traded Funds
ETFs combine elements of Mutual Funds and Stocks, providing liquidity and diversified exposure.
TYPES OF SECURITIES MARKETS
The Securities Market has two interdependent and inseparable segments viz.:
1. Primary Market
2. Secondary Market
THE PRIMARY MARKET | Primary Markets Meaning
The primary market is where new securities are issued and sold to investors for the first time. In this market, companies, public sector institutions, and governments raise funds(capital) by issuing new securities (shares, debentures, bonds, etc.) directly to investors through initial public offerings (IPOs).
The primary market is also called a New Issues Market.
The funds raised in the primary market are typically used for business expansion, debt repayment, or other corporate purposes.
Primary Markets Example | Primary Markets Issues
Following are the primary market examples or Issues for retail investors:
1. Initial Public Offerings (IPO)
2. Follow on Public Offerings (FPO)
3. Rights Issue
IPO (Initial Public Offer)
–IPO is the primary market example. Fresh issue of securities, where new shares are issued by the Company for the First time.
–Enables a company to get listed on the stock exchange and be publicly traded.
FPO (Follow on Public Offer)
–Fresh Issue of shares by a company who has already done IPO.
–Already listed company issues shares to the public.
–Different from IPO as the company is already listed in the case of FPO.
–Help in raising additional capital.
–On issuance of fresh shares in FPO, the number of shares of the company increases but the value of the company remains the same which may cause a decrease in the market price of the shares.
Rights Issues
-Fresh Issue of shares by the company to its existing shareholders.
-The purpose is to raise additional capital without further expanding its shareholding among new shareholders.
-A Rights Issue is a way to raise additional capital by offering existing shareholders the opportunity to purchase more shares at a discounted price before offering them to the general public.
-This is a common method used to raise funds quickly, often for expansion, debt repayment, or other strategic objectives.
Who can apply for an IPO/FPO?
- Anyone with a PAN card and a valid demat account.
- Trading account – Not mandatory for IPOs and FPO.
- To sell shares allotted during an IPO trading account is needed.
- Trading & Demat Account- Enables investors to subscribe to shares in an IPO and also trade in these shares afterward. Investor has the choice to open only a Demat Account without a Trading Account.
SECONDARY MARKET
Once securities are issued in the primary market by the company, these shares get listed on Stock Exchanges and investors can buy/ sell these listed securities through those Stock Exchanges (such as the New York Stock Exchange- NYSE, NASDAQ, BSE, and NSE, etc).
The secondary market involves trading between investors. Unlike the primary market, it does not involve the issuer directly.
How to Invest in a Secondary Market?
Trading on the Stock Exchange occurs on all days of the week (except Saturdays, Sundays, and holidays declared by the Stock Exchanges).
After a trading/ broking account is opened with a Stock Broker of a recognized Stock Exchange, investors can buy and sell company shares through the Stock Broker at the Stock Exchange.
The order for the purchase or sale of securities can be placed through a Stock Broker using the online trading account by:
1. Visiting broker’s website
2. Mobile trading app of broker
3. Through the phone using the Call and Trade facility
4. Physically visiting the Broker’s office
5. Through Authorized Persons of Stock Broker
What is needed to trade on the stock market?
You must have the accounts listed below to invest and trade in the stock market.
- Trading Account
- Demat Account
- Linked Bank Account
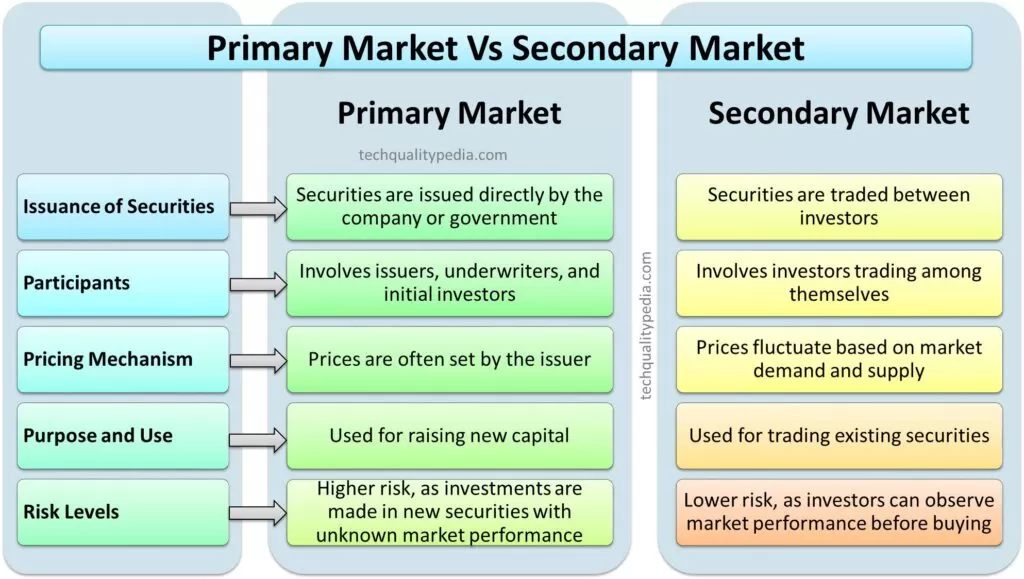
PRIMARY MARKET AND SECONDARY MARKET | DIFFERENCE
The Primary and Secondary Market differences are:
| Primary Market | Secondary Market | |
Issuance of Securities | Securities are issued directly by the company or government | Securities are traded between investors |
Participants | Involves issuers, underwriters, and initial investors | Involves investors trading among themselves |
Pricing Mechanism | Prices are often set by the issuer | Prices fluctuate based on market demand and supply |
Purpose and Use | Used for raising new capital | Used for trading existing securities |
Risk Levels | Higher risk, as investments are made in new securities with unknown market performance | Lower risk, as investors can observe market performance before buying |
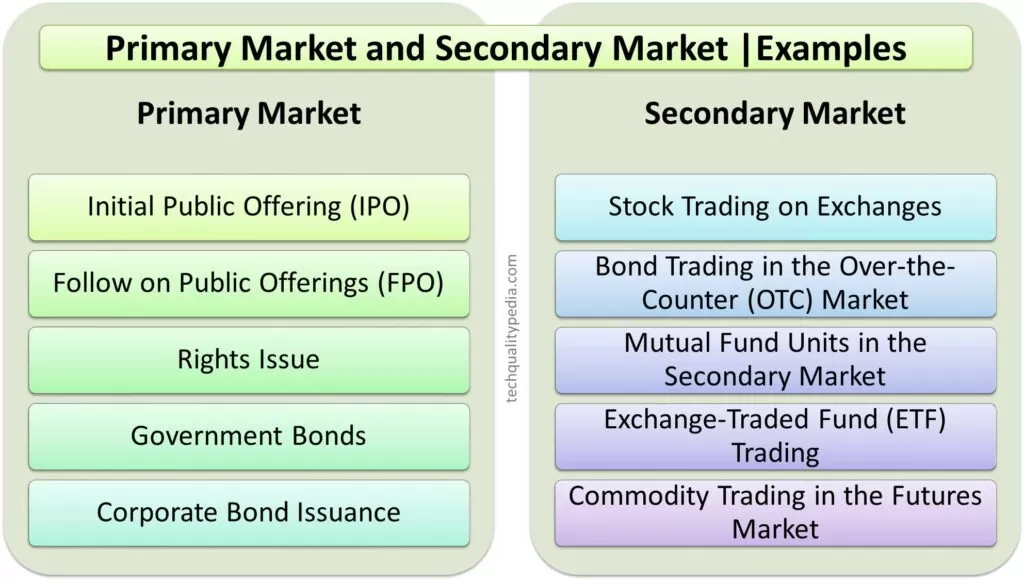
PRIMARY MARKET AND SECONDARY MARKET | EXAMPLE
The primary market examples are:
- Initial Public Offering (IPO)
- Follow on Public Offerings (FPO)
- Rights Issue
- Government Bonds
- Corporate Bond Issuance
The secondary market examples are:
- Stock Trading on Exchanges,
- Bond Trading in the Over-the-Counter (OTC) Market,
- Mutual Fund Units in the Secondary Market,
- Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF) Trading,
- Commodity Trading in the Futures Market
Primary Market Versus Secondary Market | Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages and disadvantages of Primary Market Vs Secondary Market are listed below:
Advantages of Primary Market
- Capital Raising for Companies
- Direct Investment Opportunities
- Price Stabilization
Disadvantages of Primary Market
- Limited Access for Small Investors
- High Risk for New Issues
Advantages of Secondary Market
- Liquidity and Marketability of Securities
- Access to Investment for the Public
Disadvantages of the Secondary Market
- Market Volatility
- Speculative Risks
Security Market vs. Capital and Money Markets
- Security Market is a broader term including the Capital Market and Money Market
- Capital and Money Markets are subcategories of the Security Market.
You may also like:
- Share market terminologies | Share market terms for beginners
- Candlestick Patterns Bullish | Candlestick Patterns Bearish
- Candlestick Patterns Hammer | Bullish Hammer candlestick pattern
- TYPES OF MUTUAL FUNDS | MUTUAL FUND INDIA
