Problem solving tools are widely applied in various industries, especially Manufacturing and Automotive Industries. Manufacturers deal with challenges on a regular basis, which include equipment breakdowns to quality concerns. It is not only beneficial but also necessary to have the appropriate tools to address these issues. This article will examine the best problem-solving techniques utilized in manufacturing, their operation, and the reasons they are essential to business success.
Table of Contents
Challenges in Manufacturing Industries
Manufacturers often deal with machine and equipment breakdowns/malfunctions, product and process quality defects, and inefficiencies in production processes. If these problems are not resolved quickly, they may become more serious, resulting in lost time and higher expenses due to lower productivity, higher rejection, and the cost of poor quality.
Importance of Systematic Problem-Solving
A systematic problem-solving approach ensures problems are identified, analyzed, and resolved effectively and efficiently. This isn’t about interim/containment/quick actions; it’s about long-term permanent solutions that prevent the recurrence of problems.
Problem Solving Tools
The problem-solving tools are broadly classified into 3 categories:
- Analytical Tools for Problem-Solving
- Continuous Improvement Tools for Problem-Solving
- Collaborative Tools for Problem-Solving

Analytical Tools
Analytical tools help break down quality problems into manageable parts for better clarity and understanding. Some widely applied Analytical Tools in manufacturing, automotive, and services industries are:
- 7QC Tools
- Statistical Process Control
- 8D Methodology
- Failure Mode Effect Analysis
- Pareto Analysis
- Cause and Effect Diagram/Fishbone Diagram
- Process Flow Chart/Process Mapping
7QC Tools
7QC Toolsare also known as7 Basic Quality Toolsfor Problem Solving.These graphical and statistical tools are used to analyze and solve product and process-related problems effectively. The7 Quality Control tools are generally used byquality controlandquality assuranceengineers and managers to solve quality problems and avoid re-occurrence.
Statistical Process Control
SPC studyis used to measure, record, analyze, and control theProcess Variabilityto improve product and process quality. In a statistical process control study, product measurement data are obtained in real-time, and then data is plotted on the SPC Control Chartwith predetermined upper and lower control limits.
8D Methodology
8D Methodology uses 8 Disciplines or principles of Problem Solving. The main purpose of the 8D technique is to identify and define the problem statement systematically for necessarycorrective measures to prevent the recurrence and occurrence of the quality problem.
Failure Mode Effect Analysis
An FMEA is a systemized study or set of activities designed to recognize and assess a possible failure in advance and its negative effects on product and process quality. FMEA is classified as – Design FMEA and Process FMEA.
Pareto Analysis
The Pareto charthelps to Narrow down problem areas or prioritize the major problems for corrective actions. It is based on the Pareto 80-20 rule which means that 80 percent of the problems are caused by 20 percent of the few major causes which are often referred to asVital Few.
Cause and Effect Diagram | Fishbone Diagram
The Fishbone Diagramalso known as the Cause and Effect Diagram and Ishikawa diagram. It helps to Identify all potential causes and select the best one that contributes to the problem. This is a very important basic seven QC Tool and is widely applied in Problem-Solving techniques like PDCA, 8D, andSix Sigma.
Process Flow Chart | Process Mapping
AProcess Flow Chart (PFC) in manufacturing is a diagram of the separate steps of operations/processes in sequential order. PFC also known asprocess flow diagram(PFD), and Process Map. Process flow chart in manufacturingis one of the basic seven quality control tools or7 QC toolsand is widely used in quality problem-solving methodologies like8DandSix Sigma.
Continuous Improvement Tools
Continuous improvement tools focus on long-term efficiency and quality improvements on products, processes, and services. Some widely applied Continuous Improvement Tools in manufacturing, automotive, and services industries are:
- Poka-Yoke (Error Proofing)
- Kaizen
- Six Sigma Methodology
- 5S Methodology
- TPM (Total Productive Maintenance)
- Lean Manufacturing Tools
- PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) Cycle
Poka-Yoke (Error Proofing) Technique
Poka Yokeis a Japanese term that meansMistake- ProofingorError-Proofing. The essential idea ofPoka Yokeis to design your process in such a way that chances of error or mistakes are eliminated at source or at least easily detected.
Kaizen
Kaizen meanscontinuous improvements in the daily working life, home life, personal life, and social life. It is a Japanese word made by the combination of two words:
- Kai– means toModifyorChange
- Zen– meansGood( for theBetter)
Therefore,Kaizencan be defined as the “change for the better”.
Six Sigma Methodology
Six Sigmais a quality improvement programme with a prime goal to reduce the number of defects to as low as 3.4 parts per million(PPM) by process variation reduction. Six Sigma focuses on reducing process variability and improving quality using the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) methodology. WhenSix Sigma Methodologyis used, variance is reduced and process capability and performance are simultaneously increased.
5S Methodology
5Sis an improvement tool or process to eliminate the seven type of waste that originates from a poorly organized workplace/area. It is the first basic tool and foundation stone of Lean manufacturing and an organization cannot succeed without it. 5Sisn’t just a one-time activity, it’s a continualQuality Improvement Process.
Total Productive Maintenance
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) consists of eight supporting activities or 8 pillars. TPM aims for “ZERO MACHINE TROUBLE” or “ZERO BREAKDOWN”
TPM is a method for continuously improving the effectiveness of the production equipment or manufacturing processes through thepeople’s involvement within the organization.
Lean Manufacturing Tools
Lean manufacturingis a systematic approach toward business success, and it utilizes various lean tools to maximize value and eliminate waste from a manufacturing process and services to achieve perfection. Lean manufacturing uses variousLean Manufacturing Toolsto enhance quality, productivity, and operational efficiency.
PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) | PDCA Deming Cycle
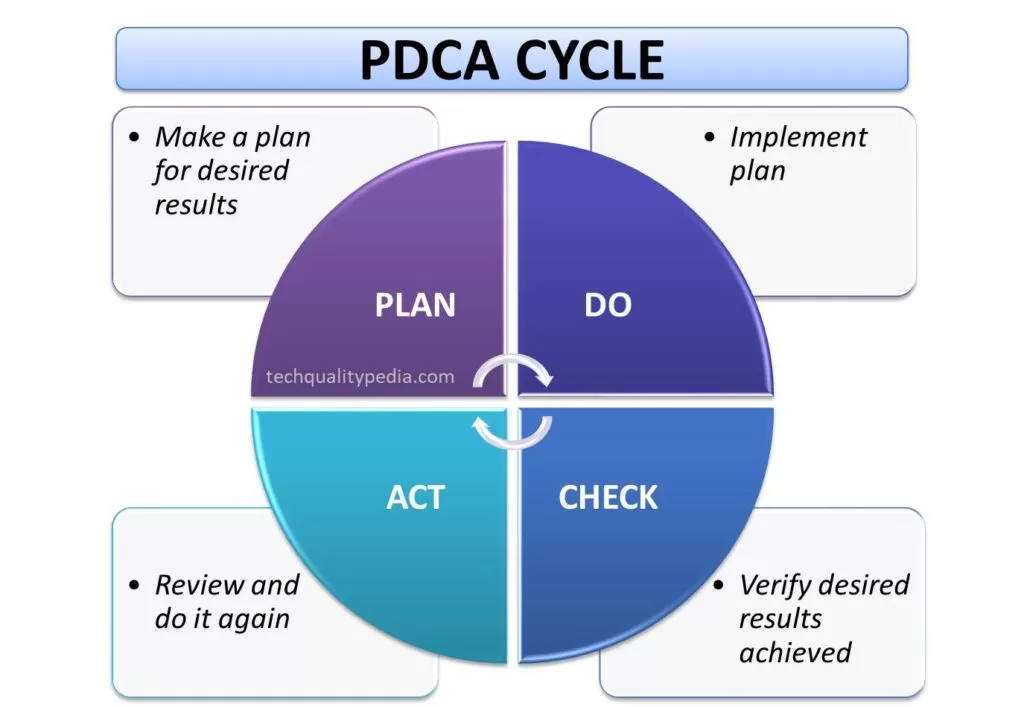
Deming’s PDCA approach is a very effective problem-solving tool for continuous improvements. You can achieve desired results through effective and systematic planning, implementation, evaluation, reviewing, and refining processes.
- Plan(Make a plan for desired results)
- Do(Implement a plan)
- Check(Verify expected results achieved)
- Act(Review and repeat)
Collaborative Tools
Collaborative tools encourage teamwork and diverse perspectives to identify innovative solutions/ideas about a particular quality problem.
Brainstorming Technique | Brainstorming Session
Team members use the brainstorming technique to solve a problem. It involves bringing teams together to identify/generate all potential causes/ideas related to the 6M factors (Man, Machine, Method, Material, Measurement, and Mother nature). All the identified potential causes are further validated to find the best potential causes that contribute to a problem/defect. The best potential causes are further drilled down using the 5-Why approach to arrive at the root cause of the problem. Team members generally use the Fishbone diagram(Ishikawa diagram) tool to identify the 4M or 6M related potential causes.
5 Whys Analysis | RCA (Root Cause Analysis)
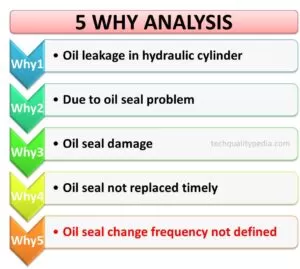
The 5Why Analysis or RCA is a simple and very effective tool/technique for finding the real root cause of a problem by repeatedly asking “Why?” until the underlying problem is revealed. This simple yet effective tool involves asking “Why” 5 times to find the root cause of a problem. The 5 Why Analysis or RCA technique is generally applied after a brainstorming session.
Benefits of Using Problem-Solving Tools
The key benefits of Problem-Solving Tools used in manufacturing industries are:
- Enhanced Productivity: Problems are resolved faster, minimizing downtime.
- Reduced Waste: Tools like Lean eliminate unnecessary processes or non value added activities, saving time and resources.
- Improved Quality: Analytical and continuous improvement tools ensure better quality products and servces.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Customer satifaction level increased through improved product and process quality, timely delivery, meeting customer demand, zero customer complaints.
