A process capability study is carried out to measure the ability of a process to meet the specifications (Customer Voice).
SPC–Statistical Process Control is used to measure and control theProcess Capabilityand controlling quality during the production process.
The frequency distribution diagram called Histogram and Control Charts are the basic 7 QC Tools that are used to measure, analyze, and control Process Variations and Process Capability.

Table of Contents
Process
The process is a set of interrelated activities that convert the inputs such as equipment, materials, people, methods, and environment into desirable output.
The quality of the process is measured by the output of product quality characteristics. If product characteristics/specifications conform to engineering/customer requirements, then the process is considered stable/capable and performing well as per set standards.
A process is considered stable if there are onlyCommon Causes of Variationpresent in the process.
Process Capability Meaning and Definition
Minimum spread of process variation present in a manufacturing process.
Process capability means how likely a product is going to meet the design specification.
It is the 6 Sigma range of processInherent variation.
In SPC, Control limits are one of the most basic requirements of aprocess capabilitystudy, So it is very important to ensure the condition of the 4M input while calculating trial control limits.
Process Capability= +/- 3 Sigma = Total spread of 6 Sigma
Need for process capability (PC)
- For meeting customer requirements/specifications.
- To measure and control the spread of the process.
- To provide more realistic tolerances for product dimensions.
- Improve the process performance capability
Factors influencing PC
- Condition of machine and equipment.
- Operation type and operational conditions.
- Type of Raw Materials.
- The Skill of Operators and Inspectors.
- Measurement method.
- Gauge/Instruments condition.
Tools for PC estimation
- Histogram.
- Control charts.
- Analysis of Variances.
- Run chart.
Process Capability Indices: Cp and Cpk
Cp Process Capability
Process capability – Cp: It is defined as the tolerance width divided by the total spread of the process.
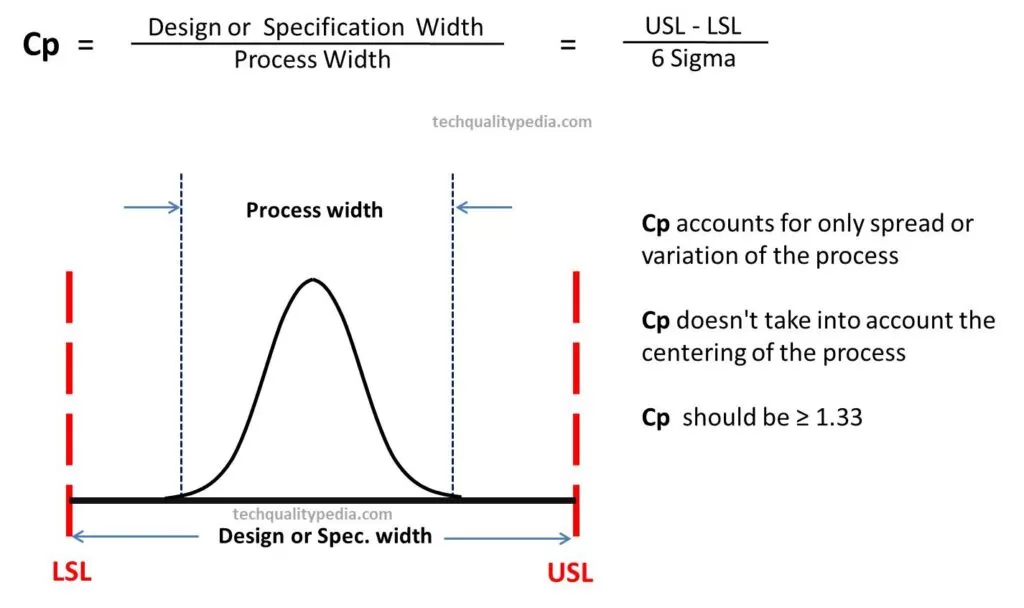
Cp indicates the spread of variation present in a process.

Cpk Process Capability Index | Cpk in Quality
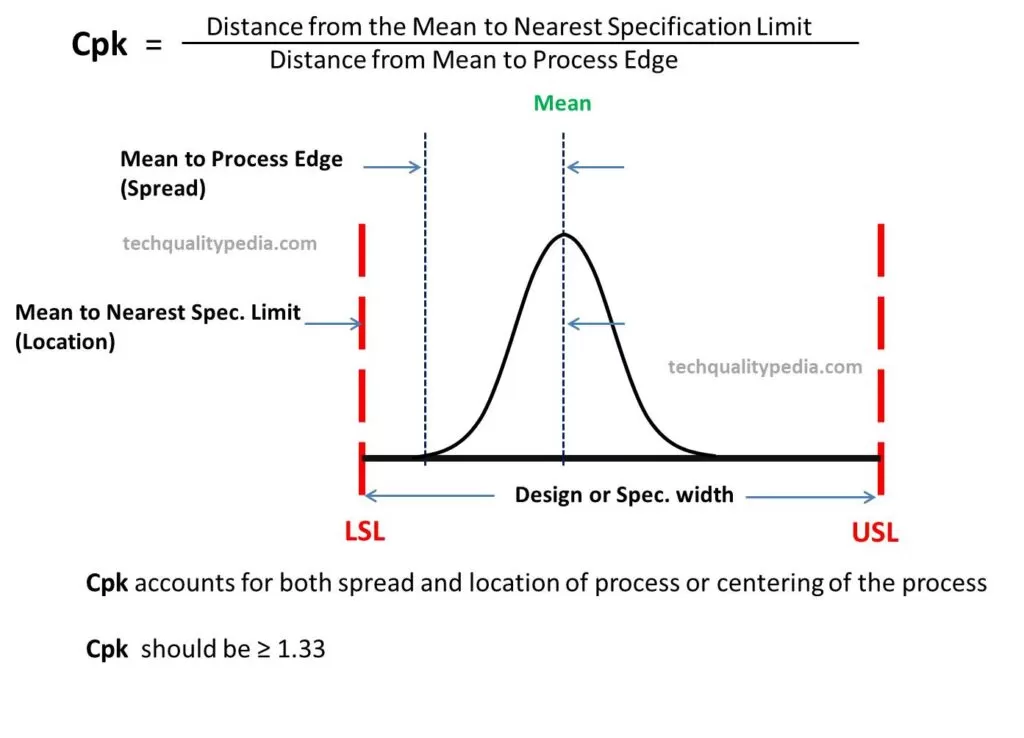
Cpk Process Capability Index: Cpk is the capability index that accounts for both the spread and location of the process or the centering of the process.
Cpk in quality is a measure of the process performance capability.
It measures how close your manufacturing process is to the center of the design specification limits.
Cpk Formula | Calculation
Cpk in the manufacturing process should be greater or equal to 1.33, and it is defined as the minimum of Cpu and Cpl.

Cp and Cpk Difference
| Cp | Cpk |
| Cpis the Process Capability and it is defined as the tolerance width divided by the process width(6Sigma). | Cpk is the Process Capability Index and measures how close your manufacturing process is to the center of the design specification limits. |
| Cp doesn’t take into account the centering of the process. Cp accounts for only spread or variation of the process | Cpk take into accounts for both spread and centering of the process |
| Formula: Cp = Design Tolerance/6Sigma = (USL-LSL)/6Sigma Where USL- Upper Specification Limit, LSL-Lower Specification Limit Sigma(σ) – Short-term Standard Deviation | Formula: Cpk is the minimum value of Cpu or Cpl denoted as Cpk = Min (Cpu, Cpl) Cpu = (USL – X Double Bar)/(3Sigma) Cpl = (X Double bar – LSL)/(3Sigma) Where Cpu – Upper Capability Index, Cpl – Lower Capability Index Sigma(σ) – Short-term Standard Deviation |
| Cpshould not looked into isolation, it is the only used to find out whether the process is capable or not i.e. Cp ≥1.33 | Cpk should always be looked into, it is used to find out whether the process is capable to meet the customer requirements or not i.e. Cpk ≥1.33 |
You may also like:
How to Calculate Process Capability? Example and Interpretation
What is Statistical Process Control (SPC)?
Process Variations | Common Causes Vs Special Causes
