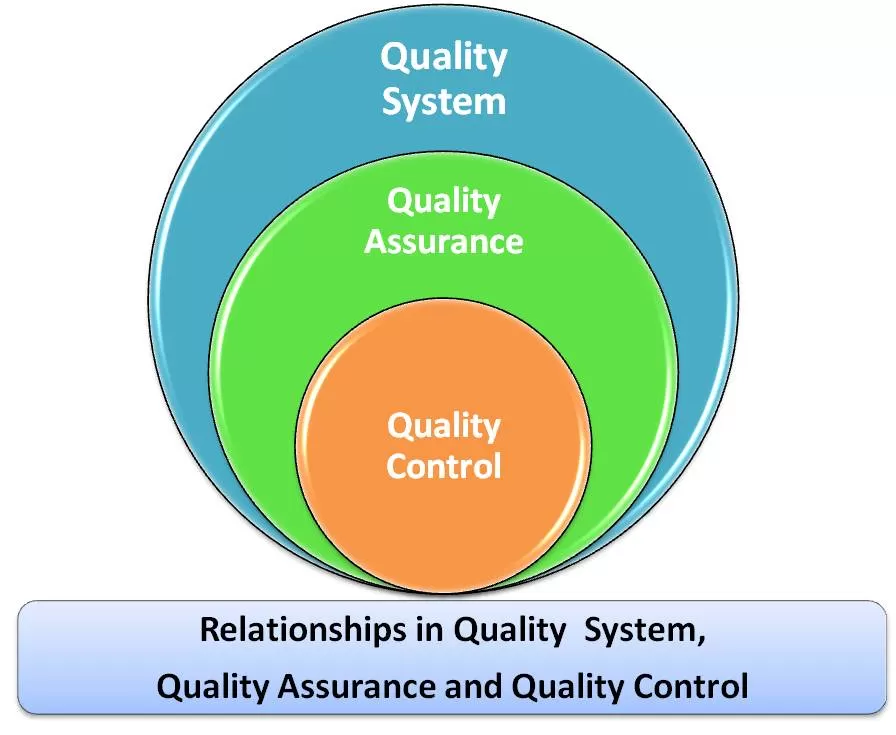
Quality Assurance and Quality Control activities are part of a Quality System or Quality Management System. QA includes QC.
QAcontains all those planned and systematic actions necessary to provide adequate confidence that a product or service will satisfy/fulfill given requirements forQuality.
Quality Controlis a set of activities for ensuring quality in theProducts.
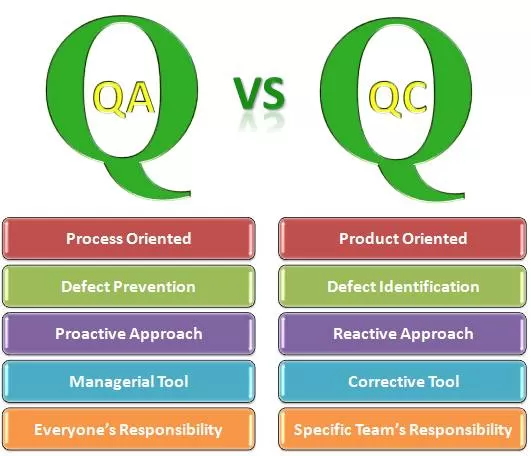
See Differences : Quality Assurance Vs Quality Control
| Quality Assurance | Quality Control | |
| Definitions | Quality Assurance is a set of activities for ensuring Quality in the Processes by which products are developed. | Quality Control is a set of activities for ensuring quality in the Products. The activities focus on identifying defects within the actual products produced. |
| Goal | Quality Assurance’s goal is to improve development and test processes so that defects do not arise when the product is being developed. | Quality Control’s goal is to identify defects after a product is developed and before it’s released. |
| Focus on | QA’s goal is to prevent defects with a focus on the processes used to make the product. Therefore, it is a Proactive quality process. | QC’s goal is to identify and correct defects in the final product. Therefore, it is a Reactive process. |
| How | To build a good quality management system and the assessment of its adequacy. Periodic conformance audits [System, Process, and Product audit] of the operations of the system. | Finding and eliminating sources of quality defects/issues through tools and equipments to meet the customer’s requirements. |
| What | Prevention of quality problems through planned and systematic activities including documentation [SOPs, FMEA, CP, and WIs, etc.] | The activities or techniques used to achieve and maintain the product quality, process, and service. |
| As a Tools | QA is a managerial tool | QC is a corrective tool |
| Responsibility | Everyone on the team i.e. all functions/departments are involved in developing the product is responsible for QA. | QC is usually the responsibility of a specific quality control team that tests the product for defects. |
| Statistical Techniques | Statistical tools and techniques can be applied in both QA and QC. When they are applied to processes [process inputs and operational parameters i.e. CTQs and CTPs], they are called Statistical Process Control-SPC and it becomes the part of QA. | When statistical tools and techniques applied to finished product [process output], they are called Statistical Quality Control-SQC and comes under QC |
| Orientation | Quality Assurance is Process-oriented | Quality Control is Product-oriented |
| Example | Verification/Audit is an example of QA | Validation/Software Testing is an example of QC |
See also the following topics :
QualityMeaning and Definitions by Quality Gurus
Quality AssuranceMeaning and Definition
Quality ControlMeaning and Definition
8D – Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving
