A Quality Circle or Quality Control Circle is a group of people from the same area, coming together voluntarily to identify, and analyze the work area problems, and find effective solutions.
The quality circle members present the solutions to management and implement them after approval. Review and follow-up of implementation are also the responsibility of the QC members.
Quality Circle projects provide better results when combined with Lean Manufacturing and TQM best practices.
Table of Contents
What is a Quality Circle? Quality Circle definition
- Quality Circle is a voluntary group of 4 to 6 members.
- Members are usually from one section or department.
- One senior member acts as a facilitator
- Identify a problem in the work area, meet and discuss the problem regularly, ideally once a week.
- Identify and implement solutions in a standardized methodology.
History of Quality Circle
Dr. Kaoru Ishikawa (1915-89) known as “Father of Quality Circle” for his role in starting Quality Control Circles(QCC) in Japan in the 1960s to improve Quality, Productivity, and the work environment.
QCC is known as Quality Circles in India and in many nations. Quality Circles term was most accessibly defined by Dr. K. Ishikawa in his book, ” What is Total Quality Control?
Toyota liked the quality circle idea and started this concept throughout their production system and other areas of the manufacturing process. Companies around the world realize the importance of this concept and began implementing this strategy. The quality circle concept got more popular in the 1960s, 1970s, 1980s and now being used worldwide in the industries along with TQM and Lean Manufacturing best practices to improve quality and productivity.
Why Quality Control Circle?
- Workforce knows best about the work area.
- With proper support, most of their problems will be solved by themselves.
- QC Circle raises morale and team spirit.
- Work becomes safer and easier.
- Improve quality and efficiency of work
How does the QC circle work?
Training on problem-solving tools and techniques like 7 QC tools, 8D, 5Whys, and Poka-Yoke, etc. must be given to the workforce for effective implementation of QC Circles projects in an organization. The quality circle steps include:
- Step 1: Training on 7 QC tools and Poka-Yoke
- Step 2: Forming and naming quality circles-
- QC circles are formed with 4 to 6 members.
- One member acts as a leader by rotation.
- One supervisor acts as a facilitator.
- Step 3: Identify Quality Circle themes
- Step 4: Select a project based on priority.
- Step 5: Find the best solution using a standardized methodology.
Quality Circle Structure
QC structure includes:
- QC Administrator
- Facilitator
- Leader
- Members
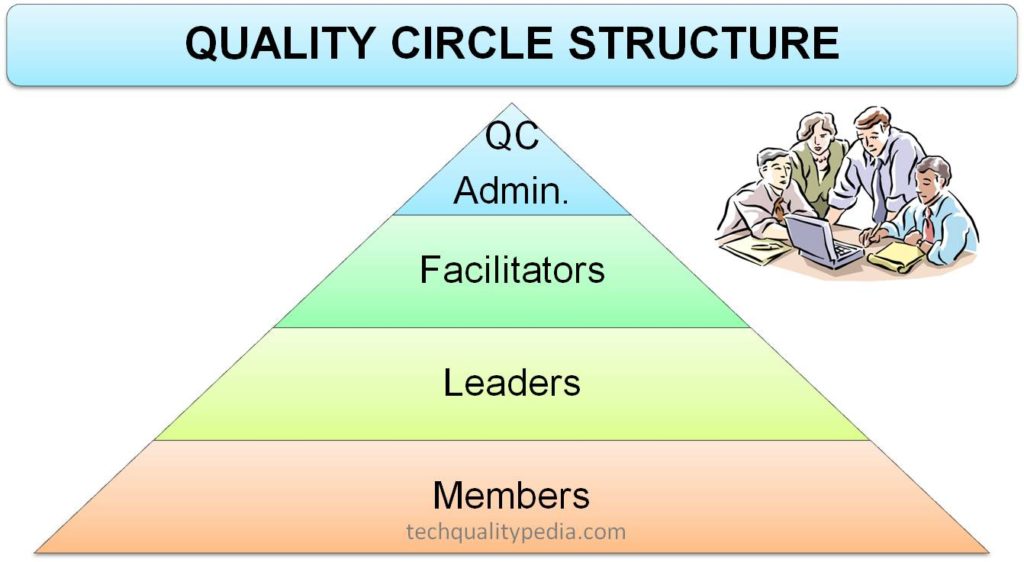
The main role and responsibilities of each one are:
QC Circle member
- Participate in the discussions.
- Weekly meeting adherence.
- Brainstorm and select problems.
- Discuss and sort out useful ideas.
- Implement and check the benefits.
- Present to the top management.
QC Circle leader
- Responsible for weekly meetings.
- Agenda for a weekly meeting.
- Lead roll-on presentation to top management
QC facilitator
- Generally the area supervisor.
- Key role in presenting the project- act as a teacher, Coach, Guide, & Motivator.
- Coordinate with the departments.
- Responsible for the effectiveness of the circle.
QC administrator
- A bridge between top management and the QCC members.
- Project planning – Annually/Monthly.
- Monitoring weekly meetings.
- Taking responsibility for QCC-related training.
- Arranging monthly management presentations
- Rewards / Recognition
Quality Circle Steps
- Defining the Problem
- Analyzing the Problem
- Identifying the Cause
- Finding out the Root Cause
- Data Analysis on Root Cause
- Developing Solution
- Foreseeing Possible Resistance
- Trail, Implement, and Checking Performance
- Regular Implementation
- Follow-up/Review
Quality Circle Tools | Quality Circle Techniques
The workers should be given in-depth exposure to the basic 7 QC tools of quality, Poka-Yoke, and Kaizen techniques.
The most common QC tools and techniques used in QC Circle projects to analyze the problem, discover the root causes, and help implement effective countermeasures are:
7 QC Tools
- Check sheet
- Fishbone diagram or Cause and effect diagram
- Pareto chart
- Control Chart
- Histogram or Frequency distribution chart
- Stratification of data
- Scatter diagram
There are some other potential quality tools used in quality circles techniques to analyze and solve quality problems effectively:
- Process flow diagram
- Bar graphs or charts
- Process mapping tools
- Run Chart
- Why-Why Analysis
- Poka-Yoke
- Kaizen
Guidelines for Quality Circles Success
Once the Quality Circles are initiated in any organization, it is the responsibility of the top management to nurture them and pay attention to all relevant aspects related to QC project.
- The QC member should attend the meeting regularly, and punctually, and work in groups in the desired manner.
- Circle members should participate actively in the discussions and learn the techniques and new things taught to them.
- Training on 7 QC tools and kaizen must be given to all circle members.
- The circle must select the leader from among its members.
- A circle must have one facilitator and QC administrator who guide and support QC projects.
- The Quality Circle meeting’s discussion points must be maintained in a record book and should be verified by the coordinator in the organization for correction and effectiveness.
- Circle follows the agenda without wasting time and listening to others while putting their points of view and suggestions.
- Quality circle members must maintain proper records of their activities.
The following points must be covered in the QC record book:
- QC Circle theme, section, department, and organization address.
- Meeting date, time, duration, and place of meeting.
- Quality Circle movement start date, when the circle was formed, and date of inauguration.
- The number of problems identified by them since functioning, their classification, and the number of problems solved so far.
