Table of Contents
What is Safety?
Safety is prevention of accidents which results personal injury and property damage.
Safety in a industrial establishment is required to avoid any interruptions into all the below factors:
Man, Machine, Material and Environment.
Safety Management Principle
- Safety is everyone’s responsibility
- Good result can not be obtained without unified safety consciousness.
- Safety takes priority over everything else i.e. Safety First
- First priority must always be given to safety to protect “Employees”.
- All industrial accidents are preventable
- Dangerous environment is the factor of the industrial accidents.
- Industrial accidents are preventable if we eliminate the danger.
Safety Audit Purpose
- To identify unsafe conditions/unsafe acts
- To find out ways and means to implement preventive actions
- To ensure employee participation in accident prevention
- To evaluate & compare the safety performance level within departments
- To register the upward communication on safety issues
- To create a safe work place
- To fulfill legal compliance
Who Secure Safety ?
Safety should be secured by all the members.
Safety Audit Methodology
- Prepare Safety Audit Checklist for conducting audit
- Identify key persons to conduct the conduct the audit
- Adequately train the identified key persons
- Select a department /Area /Section
- Conduct the audit once in month comprehensively
- Record the findings in the defined format
- If possible, take a photograph of the non-conformity as evidence
- Put a tag explaining the non-conformity
- Number the tag and category or criteria
- Present them in the Safety committee meeting
- Suggest countermeasure and preventive measure
- Send minutes of meeting to the concerned process owners (HODs)
- Follow the progress of action
- Re-audit the same if the non-conformities existing
Types of Safety Audit
The Safety Audit types in manufacturing industries are:
- Material Handling Equipments
- Machine Guarding
- Electrical Safety
- Fire Fighting Equipments
- Safety Switches
- Layout of Machines
- Training and knowledge of operators
- Chemical Handling
- Safety Communication
- Contractors Regulation
- Storage of Materials
- Work Environment Hazards
- ISO 14001 Environmental Management Standard
- OHSAS 18001/ISO 45001 Occupational Health & Safety Management Standard
Prepare Safety Audit checklist by addressing all above safety points.
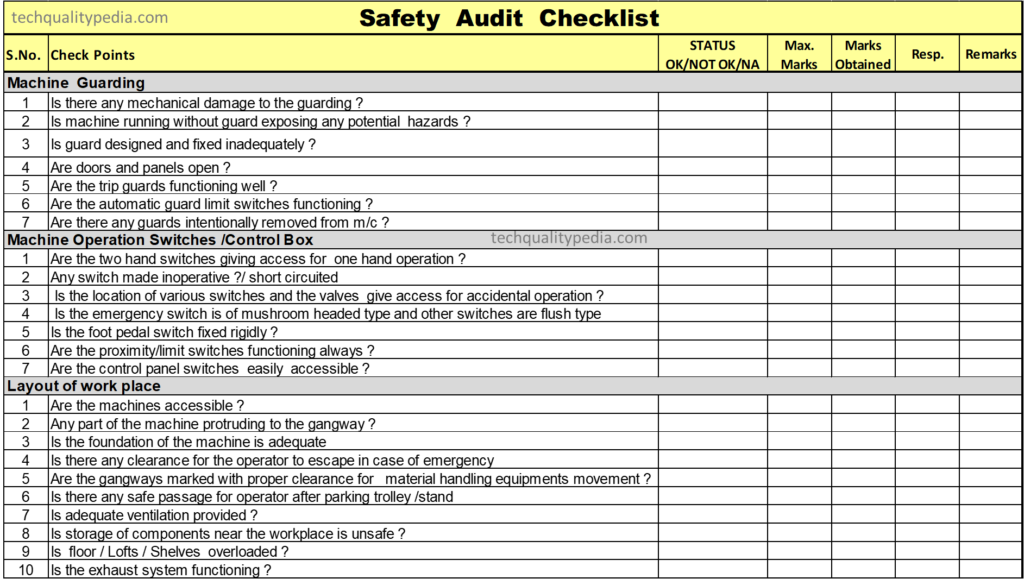
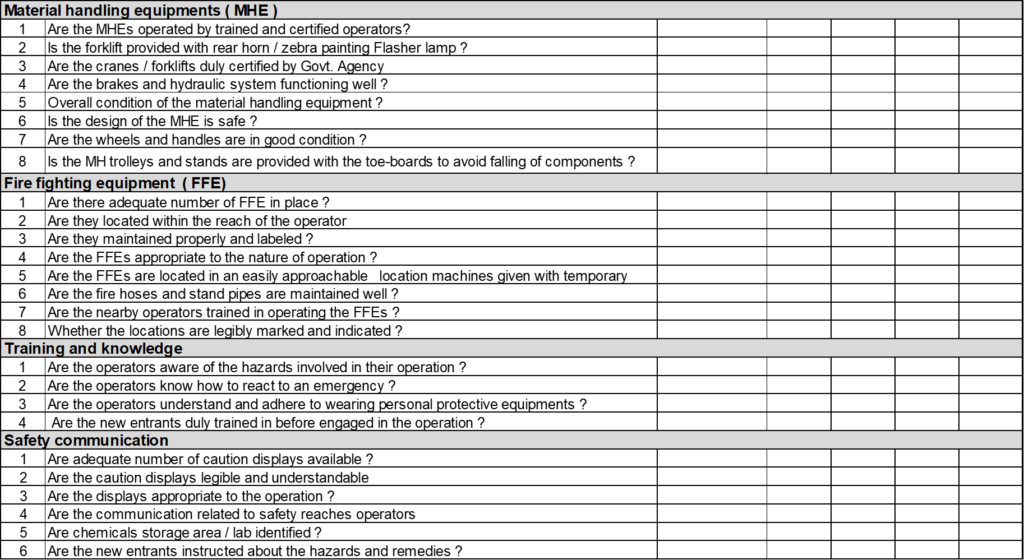
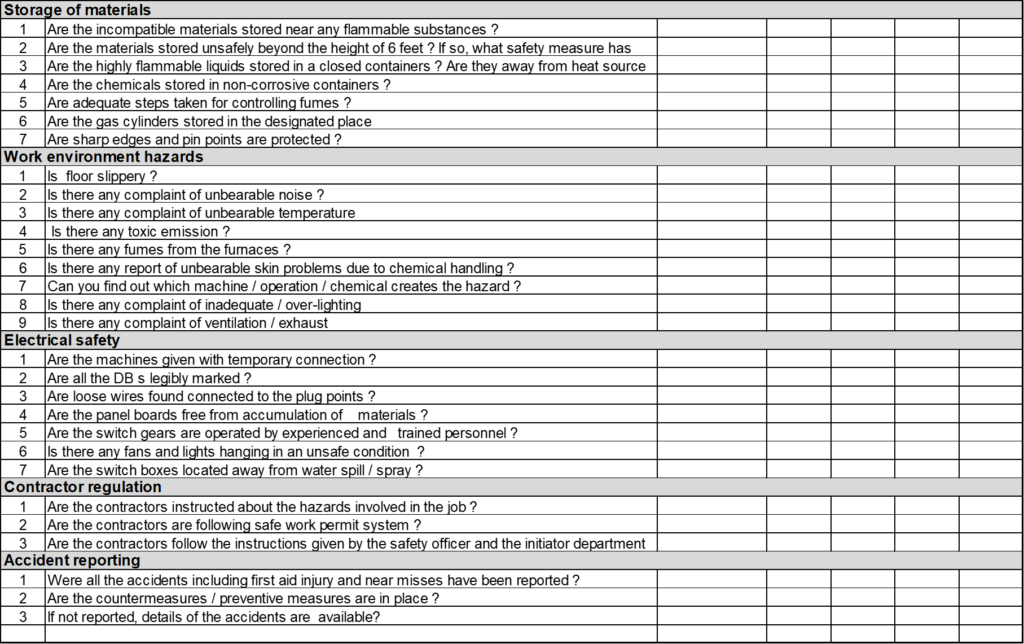
Marks Criteria:
For 100% Compliance :- 2 Marks
50% Compliance :- 1 Mark
Poor condition/Not follow :- 0 Mark
Not Applicable :- NA
-> No good work without safe working environment
-> No good quality without good work
-> No productivity improvement without good quality

