Table of Contents
STOCK MARKET MEANING | SHARE MARKET MEANING
-
A share market is also called a Stock Market.
-
The stock market is a set of marketplaces (called a stock exchange) where people buy and selling of shares in publicly traded companies. When someone buys stocks of any particular company, then the investor becomes a shareholder or gets partial ownership of that particular company. Examples of stock exchanges include the NSE, BSE, NASDAQ, and New York Stock Exchange (NYSE).
-
In simple words, a stock market is a place where stocks or shares are bought and sold by people including retail investors, institutions, banks, etc.
SHARE MARKET TERMINOLOGIES | STOCK MARKET TERMINOLOGIES
The share market terminologies for beginners are explained briefly for quick and easy understanding.
SHARE
A unit of stock representing ownership in a company. When you buy or own shares of a company, then you become a shareholder.
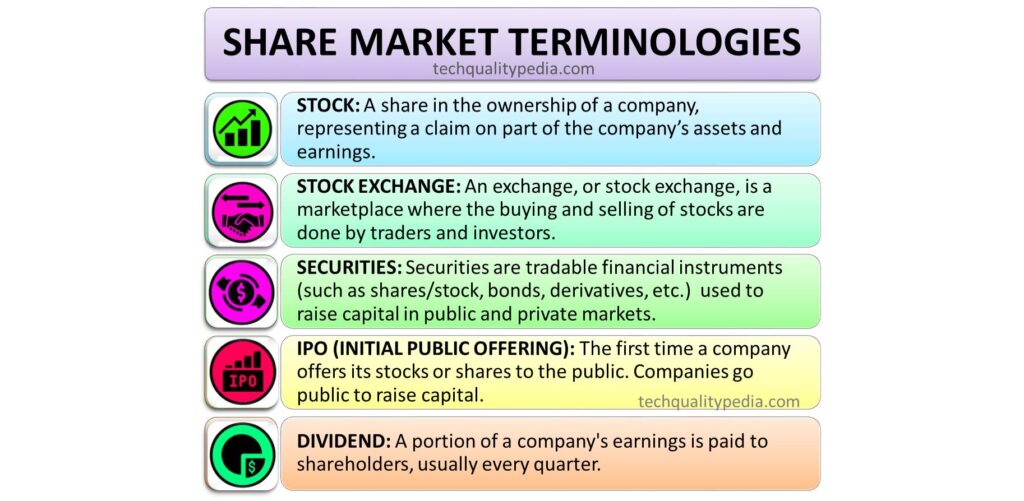
STOCK
A share in the ownership of a company, representing a claim on part of the company’s assets and earnings.
BULL MARKET
A market condition where stock prices are rising or are expected to rise, encouraging buying.
BEAR MARKET
A market condition where prices are falling or are expected to fall, encourages selling.
EXCHANGE
An exchange, or stock exchange, is a marketplace where the buying and selling of stocks are done by traders and investors. Examples of well-known stock exchanges in the US are – the NASDAQ and NYSE (New York Stock Exchange) and stock exchanges in India are- the NSE (National Stock Exchange) and BSE (Bombay Stock Exchange).
INDEX | INDICES
A statistical measure of the changes in a portfolio of equities/stocks representing a portion of the overall market.
Indices provide a snapshot of market trends and are used as benchmarks for performance.
Examples of Major Index | Indices
- NSE Nifty 50: Tracks the performance of the 50 largest Indian companies.
- BSE Sensex: Tracks the performance of 30 largest Indian companies.
- S&P 500: Tracks the performance of 500 largest US companies.
- Nasdaq Composite: Represents more than 3,000 stocks, primarily in the tech sector.
- Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA): Represents 30 companies in the US.
INDEX FUND
Index funds are mutual funds with a portfolio that tracks the components of a market index such as the BSE Sensex, the Nifty 50, Gift Nifty, S&P 500, and Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA).
SECURITIES
Investors invest their funds in buying shares, bonds, etc., called Securities.
Securities are tradable financial instruments (such as shares/stock, bonds, derivatives, etc.) used to raise capital in public and private markets.
BROKER
An individual or firm that acts as an intermediary between an investor and a stock exchange or securities exchange. Brokers buy and sell shares on behalf of investors.
DIVIDEND
A portion of a company’s earnings is paid to shareholders, usually every quarter. Not every company offers dividends.
DIVIDEND YIELD
A dividend yield is a dividend expressed as a percentage of its stock price.
IPO (INITIAL PUBLIC OFFERING)
The first time a company offers its stocks or shares to the public. Companies go public to raise capital.
PORTFOLIO
A collection of financial investments like bonds, stocks, commodities, and cash equivalents.
MARKET CAPITALIZATION (MARKET CAP)
The total market value of a company’s outstanding shares. It is calculated by multiplying the number of outstanding shares by the current market price of one share.
LIQUIDITY
Liquidity refers to how fast and easily a security or asset can be bought or sold in the market without affecting its price. Stocks that are easily bought and sold are considered liquid stocks.
BID PRICE
The highest price that a buyer is willing to pay for a stock.
ASK PRICE
The lowest price at which a seller is willing to sell a stock.
SPREAD
Spread is the difference between the bid price and the ask price. It represents the transaction cost for buying and selling a stock.
VOLUME
The number of shares of a security (Equity, Derivatives, ETFs, etc.) traded during a given period. Higher volume often signifies higher interest in that security.
VOLATILITY
A statistical measure of the dispersion of returns for a given security or market index. High volatility means that the price of the security can change dramatically over a short period in either direction.
DAY TRADING
The act of buying and selling a securities/financial instrument within the same trading day. Traders who participate in day trading are called Intraday or day traders.
LIMIT ORDER
An order to buy or sell a stock at a specific price. A buy limit order can only be executed at the limit price or lower, and a sell limit order can only be executed at the limit price or higher.
STOP-LOSS ORDER
An order is placed with a broker to buy or sell once the stock reaches a certain price. It is intended to limit an investor’s loss on a position.
SHORT SELLING
The practice of selling securities or other financial instruments that are not currently owned, and subsequently repurchasing them (“covering”). Usually in a falling market, the seller hopes to profit by the gap between the buy price and the sale price.
P/E RATIO (Price-to-Earnings Ratio)
A valuation ratio of a company’s current share price compared to its earnings per share. It provides an idea of what the market is willing to pay for the company’s earnings.
BLUE CHIP STOCKS
Stocks of large-cap, financially sound, and well-established companies with a track record of reliable growth and stable earnings. Examples include companies like Tata Motors, Reliance, Apple, Microsoft, and NVIDIA.
ETF (Exchange-Traded Fund)
A type of security that involves a collection of securities such as stocks and other securities that often follow an underlying index. ETFs are traded on the stock market, similar to individual equity/stocks.
MUTUAL FUND
A pool of funds collected from many investors and used to invest in securities such as bonds, stocks, and other financial instruments. Mutual funds are managed by professional fund managers.
The share market terminologies mentioned above should provide a solid foundation for understanding the basics of the stock market. As you become more familiar with share market terms and concepts, you will be more capable of making informed trading and investing decisions.
