Six Sigma is a quality improvement programme with a prime goal to reduce the number of defects to as low as 3.4 parts per million(PPM) by process variation reduction. It uses the Normal Distribution to predict failure/defective rates.
Six Sigma is a problem solving and best management strategy, which is developed by MOTOROLA USA in 1981.
When Six Sigma Methodology is used, variance is reduced and process capability and performance are simultaneously increased.
A product is said to be of 6sigma (6σ) quality if there are no more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities(DPMO) at the part and process step level.
6 Sigma has replaced Total Quality Management (TQM) and Business Process Reengineering (BPR) as the key strategy for product and process quality improvement.
For effective implementation of 6sigma project, the company should be:
- Open to change.
- Anxious to act quickly to good idea.
- Eagerness to learn.
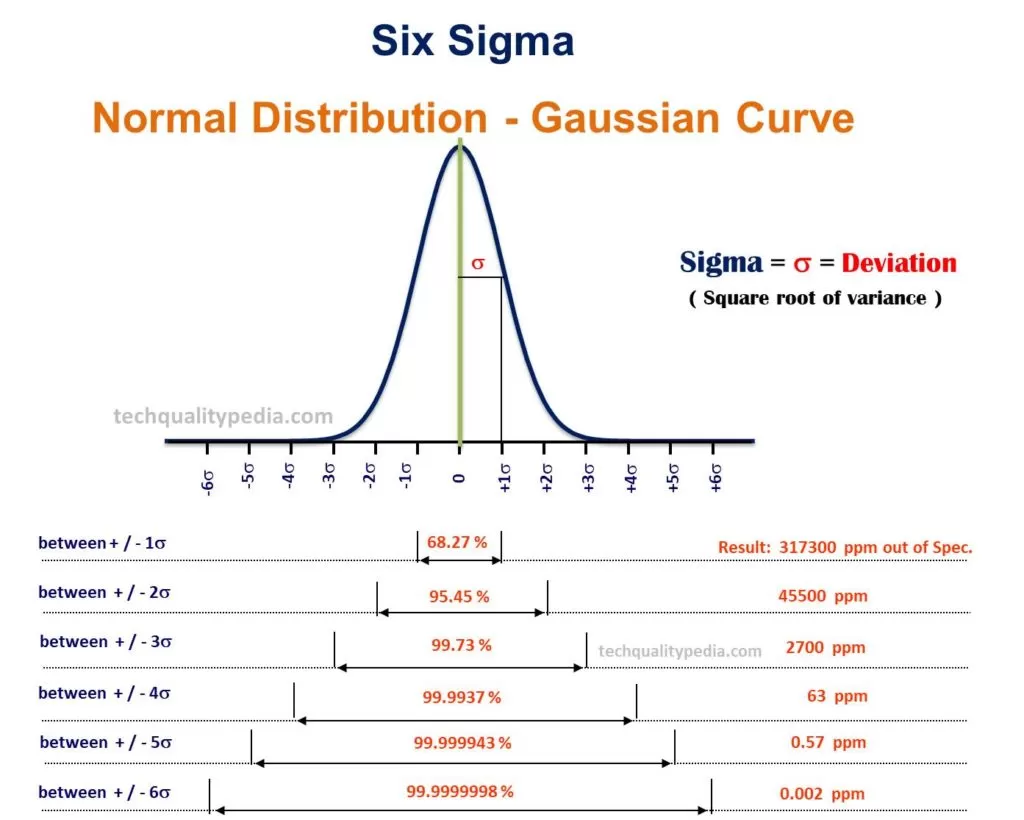
Table of Contents
Six Sigma Definition
- σ – is a Greek symbol that indicates Standard Deviation, a measure of variability.
- Six Sigma – A quality improvement strategy that focuses on eliminating defects through the reduction of process variations.
- Defect – A measurable outcome that is not within standard specification or acceptable specification limits.
6 Sigma is a quality management concept/philosophy and a methodology that emphasizes on variation reduction, defects elimination, and improving the process and product quality, and services. 6σ is also defined as a methodology for quality problem solving.
Six Sigma Metric
The 6σ metric uses Defects Per Million Opportunities(DPMO).
Six Sigma Objective
The main objective of 6σ strategy or approach is to eliminates defects/rejections through reduction of process variation.
Six Sigma Methodology
The six sigma uses two methodologies for completing projects or problem solving.
- DMAIC Methodology
- MADV Methodology
DMAIC Methodology
DMAIC methodology is used for existing process/system improvement. DMAIC stands for – Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control.
DMADV Methodology
DMADV methodology is used for new process/system development from scratch. DMADV stands for – Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, and Verify.
There is another methodology called Lean that widely adopted along with the 6sigma for product, process, and services improvement.
Lean and the six sigma methodologies combined to form a Lean Six Sigmathat aimed primarily to reduce cost and improve quality by eliminating waste (non-value added activities) and reducing process variations.
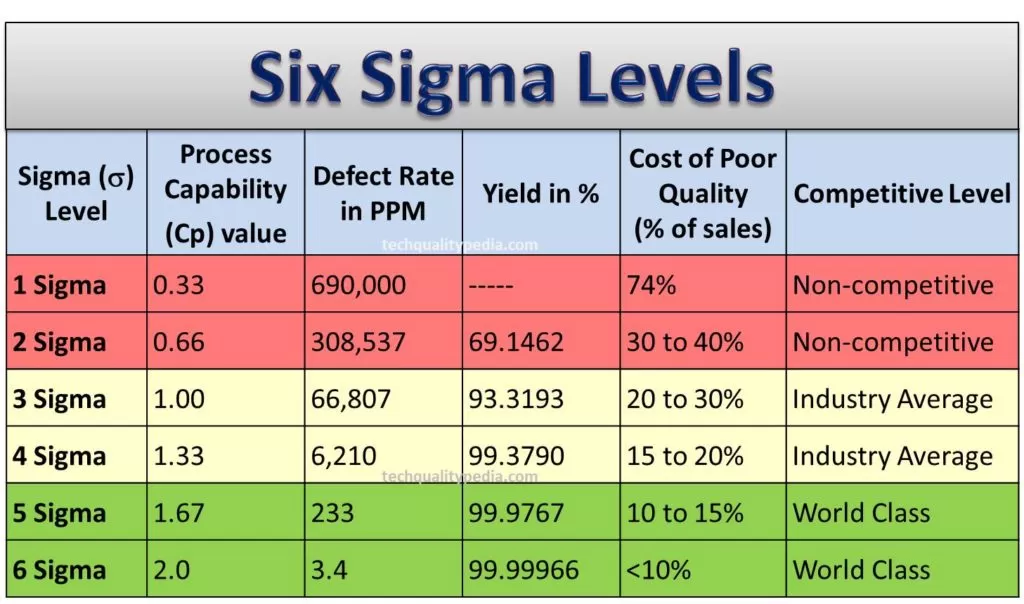
Six Sigma Levels
As the sigma level increases, the process capability (Cp) increases, and thereby the defects rate reduces.
Process capability and 6sigma scale of defects w.r.t sigma levels is shown below:
SIX SIGMA PROCESS | SIX SIGMA DMAIC
There are five phases of six sigma process. The DMAIC steps involved in the application of 6sigma process are summarized as below:

1. Define Phase
The objective of define or Identify phase is to:
Determine the important process/product characteristics that must be met in order to achieve 6sigma quality levels.
To identify the chances for defects or quality problems within each sub-process, which can be done by through the use of various statistical tools, like regression analysis, design of experiments and Chi-square testing.
2. Measure Phase
The objective of measure phase is to:
- Select CTQ characteristics
- Define performance standards
- Validate measurement systems
3. Analyze Phase
The objective of the analyze phase is to:
- Establish process/product capability
- Define performance objectives
- Identify variation sources
The various statistical quality tools as well as conventional quality techniques like Brainstorming, Root-Cause Analysis, Fishbone Diagram, Pareto Analysis etc., could also be used in analyze phase.
4. Improve Phase
The objective of the Improve phase is to:
- Screen potential causes
- Discover variables relationship
- Establish operating tolerances
- Improve continuously.
If the existing quality level is < 3σ, then efforts must be directed to improve the processes to achieve at least 3σ or 4σ quality level.
5. Control Phase
The objective of control phase is to:
- Validate measurement system
- Determine process capability
- Implement process controls
The final stage of 6sigma implementation process is to hold the improvements/gains made during the improve stage. During this phase the new process conditions are documented, and frozen into systems so that the improvements or gains are made permanent.
Six Sigma Belt Levels | Six Sigma Certification
Six Sigma Levels are differentiated by belt level. Almost like the belt levels used in martial arts, Six Sigma Certifications are awarded in levels employing a belt classification system.
Six Sigma Belts are:
- White Belt
- Yellow belt
- Green belt
- Black belt
- Master black belt
Six Sigma White Belt
White Belt is an entry level certification that provides the basic knowledge of 6sigma concepts or methodology. White belt work with local quality problem teams, but they’ll not be part of 6sigma project team.
Six Sigma Yellow Belt
Participate within the 6sigma project as a team member and reviews project-supporting process improvements.
Six Sigma Green Belt
Lead Green Belt project team and assist in the collecting and analyzing data for black Belt projects.
Six Sigma Black Belt
Lead projects for quality problem-solving. Trains and educate the 6sigma project teams.
Six Sigma Master Black Belt
6Sigma master black belt trains and coaches the Green and Black Belts. Serves as a 6Sigma expert and consultant for an organization.
Champion
An top level executive who translate the organization’s vision, mission, objectives, and targets/goals. Responsible to identify adequate resources and remove barrier for effective implementation of 6sigma projects across all functions/departments.
Six Sigma Tools
The 6sigma tools of statistical methods and quality management are listed below that are used in various phases of DMAIC and DMADV process.
Six Sigma Tools of Statistical methods:
- SPC
- MSA
- DOE
- ANOVA
- Control Charts
- Statistical Hypothesis Testing
- Regression Analysis
- Chi-square testing
Six Sigma Tools of Quality Management:
- Pareto Chart
- QFD
- FMEA
- Process Mapping
- Cause & Effect diagram
- 5 Why Analysis
Six Sigma Benefits
It helps employers businesses and employees in many ways that are listed below:
- Reduced process variation.
- Reduced process waste (non-value added activities).
- Increased process efficiency.
- Increased revenue, and lowering cost of capital.
- Reduced quality defects and errors/mistakes.
- Increased brand value.
- Enhanced customer satisfaction.
- Leadership opportunities.
- Higher pay and job security.
- Increase in opportunities for career growth.
