Stratification is a statistical technique of breaking down value/data into meaningful categories or classifications.
This is considered one of the basic 7 QC Tools and is extensively used in Problem Solving Techniques such as 8D, PDCA, and Six Sigma.
Table of Contents
Stratification Definition and Meaning
Stratification is a technique or method that can be defined in many ways:
A method for breaking down a universe of data into uniform groups known as strata.
Stratification is a technique or method used to separate and classify data into distinct classes or groups (called strata) to better understand patterns, variations, and root causes.
It involves observing data, splitting them into distinct classes or categories to see a different process for better analysis.
In Stratification, data recording/observation carried out from multiple sources like shifts, machines, days, people, etc.
In other words, it is a method to divide the data into sub-categories and obtain meaningful information to solve a quality problem.
A statistical technique or system of formation of layers or classes or categories to analyze the problem.
To put it simply: To identify the true problem, examine each group independently rather than combining them.
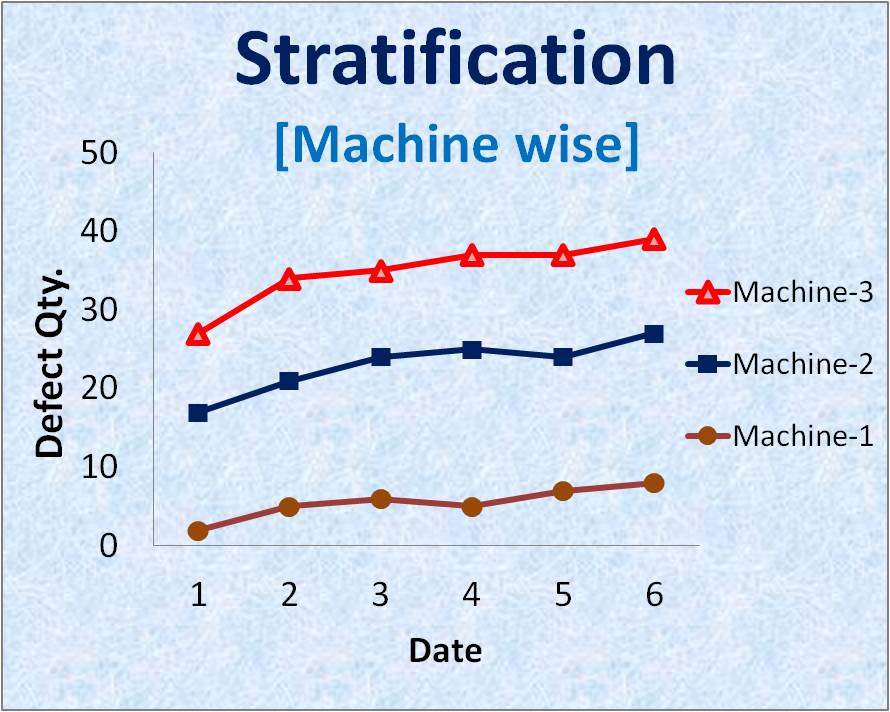
Example: Machine wise Stratification.
Rejection data collected from three different machines and date wise trend chart plotted. From the chart, we can see that machine-3 is contributing to high defects/rejection as compare to machine-1. Therefore, the main focus area/source is a machine no. 3 for necessary measures to reduce process variation and rejection level.
Purpose of Stratification
- To categorize the data into meaningful subcategories prior to analysis.
- To enhance the accuracy as well as reliability of results.
- To find hidden trends or patterns in gathered information that might be unnoticed.
When to use Stratification?
- When the information comes from several sources or circumstances, including information gathered from various machines, individuals, shifts, days, and suppliers, etc.
- Used extensively to control and improve the process. Is the process running OK and how long?
How it is carried out ?
It is carried out by splitting process data into distinct layers or sub-groups and understanding the different meaningful patterns to analyze and solve problems.

Benefits of Stratification
- Overall improvement in product and process quality.
- Unknown strands of data can be identified.
- Helps in root cause analysis.
- Identify hidden problems.
- Works in combination with other QC tools like histograms, check sheets, etc.
- Systematic reduction of Process Variation-common cause of variation.
- Focuses improvement efforts where required.
Stratification helps in analyzing “Quality Cost”.
- Internal Failure cost
- External Failure cost
- Prevention cost
- Appraisal cost
Summary
Stratification is a useful analytical method that helps pinpoint the actual causes of variance or flaws by dividing large, complicated data sets into distinct categories. Better data-driven judgments are supported, and it increases the effectiveness of other high-quality tools.
