The Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) approach is ” I OPERATE, and I FIX/MAINTAIN” i.e. the operators maintain their own machines and equipment condition proactively to enhance productivity and lower costs.
TPM is a culture that focuses on maximizing the OEE-overall equipment effectiveness (effectiveness of the plant, equipment, and processes) by involving all employees from top management to front line workers with aim of keeping all machines in top working conditions throughout life.
Involving all departments that plan, use, maintain equipment and promoting zero losses through self-directed small groups.
TPM is also known as “Medical Science of Machine”
Table of Contents
TPM Meaning
TPM is a combination of three words: Total+Productive+Maintenance=TPM.
Total: All employees from top to bottom to take part or all individuals working together.
Productive: To enhance productivity by reducing losses, wastes, and manufacturing costs through effective utilization of all resources.
Maintenance: Maintaining the machine and equipment so that its efficiency can be high to its entire life i.e. keeping old machines like brand new.
TPM Objective | Target | Goal
The main goal or objective of total productive maintenance is to maintain machine/equipment condition and to increase the OEE through:
- Zero Breakdowns or No Breakdowns
- Zero Accidents or No Accidents
- Zero Defects or No Defects
- No Small Stops or Slow Running
Total Productive Maintenance Philosophy
TPM philosophy is – Throughput enhancement (overall Equipment Effectiveness-OEE)
Total Productive Maintenance Focus
TPM focuses on Assets i.e. the efficient and effective utilization of production equipment.
TPM Application
Equipment-focused Measurement, Condition, and Improvement cycle.
TPM Assumptions
Equipment reliability and efficiencies will improve business performance. Many small improvements are better than system improvements
Total Productive Maintenance Pillars
There are eight pillars of TPM:
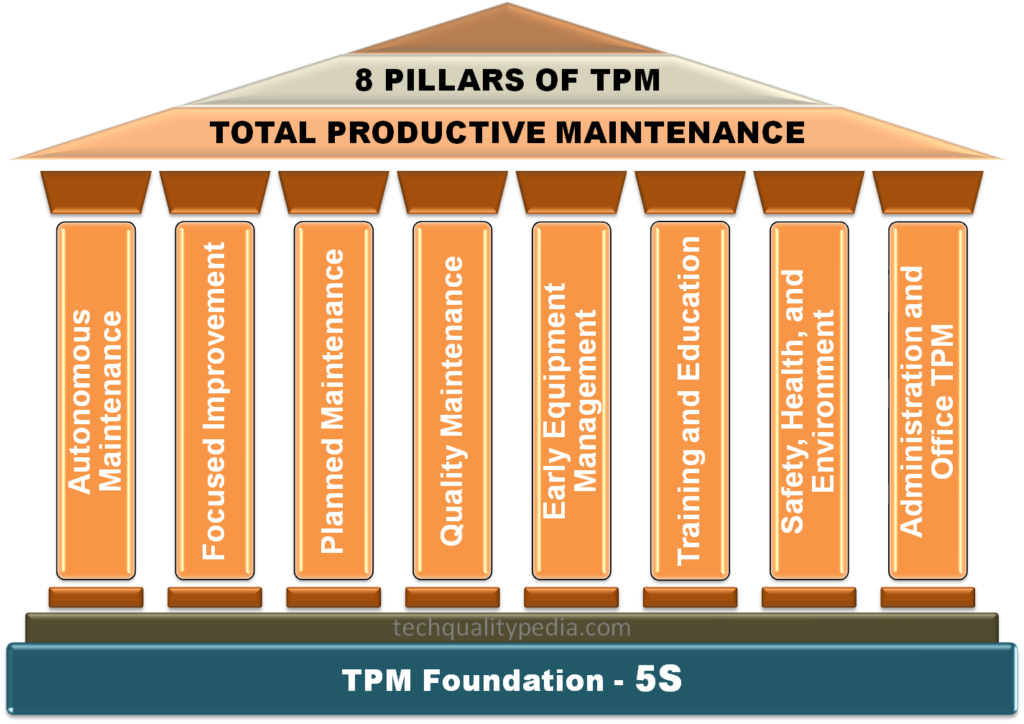
- Autonomous Maintenance ( JISHU HOZEN )
- Focused Improvement (KOBETSU – KAIZEN)
- Planned Maintenance
- Quality Maintenance
- Early Equipment Management
- Training and Education
- Safety, Health, and Environment
- Administration and Office TPM
TPM foundation | 5S TPM
5S is the foundation stone of TPM process, which is supported by 8 pillars of TPM. The first step in a TPM implementation program is to establish the 5S foundation within an organization and development of an autonomous maintenance plan.
TPM Implementation steps
A relationship between manufacturing, maintenance, and engineering is required to implement an effective TPM program. The key to an effective preventive maintenance component within the TPM initiative is the machine operators. Up to 75% of the breakdowns can be detected and prevented by well-trained operators. Therefore, machine operators or floor workers are given more importance and encouraged to get involved in the TPM implementation program.
There are 5 key steps for TPM program implementation:
- Identify a pilot Area
- Restore the Machine/Equipment to Prime Operating Condition
- Measure Overall Equipment Effectiveness-OEE
- Identify and Reduce Major Losses.
- Implement Planned Maintenance
TPM Improvement Measures
Overall Equipment Effectiveness-OEE measures how well a plant is performing relative to reducing the equipment losses and conditions. These conditions and losses are:
- Equipment breakdowns
- Scrap and rework caused due to poor performance of machine/equipment.
- Low productivity due to equipment
- running at reduced speed
- receiving unnecessary adjustment
- idling or stoppages which require the operator’s attention.
Forming small, interdisciplinary teams to address fundamental areas such as preventative and autonomous maintenance, training personnel who operate machines, and standardization of work processes are common ways to improve OEE using TPM.
Key Requirements for TPM improvement
There are three main requirements for effective TPM implementation and improvement within the organization:
- Increasing employee motivation and changing their mindset or attitude.
- Increasing employee competency and skill level.
- Improving the working culture or environment, so that it helps to support in establishment and effective implementation of a TPM program.
All these three requirements need to be fulfilled within the organization in order to follow the further steps for the implementation of any kind of improvement programs/techniques like TPM, TQM, Lean manufacturing, Six Sigma, etc.
Total Productive Maintenance Advantages
Many areas of a facility will improve when everyone in the organization is thinking about and contributing to maintenance. Effective TPM (Total Productive Maintenance) implementation provides the following advantages:
- No or fewer Breakdowns
- Reduced equipment/machine unplanned downtime
- Provide a safer workplace.
- Lower quality defects and rejection rate.
- Customer complaints reduction
- Increased OEE and plant capacity
- Process and product quality improvement.
- Lower manufacturing and maintenance cost.
- Increased Tool/Machine life.
- Increased ROI(Return On Investment).
- Enhanced job satisfaction Increase in employee morale, confidence level, and teamwork spirit.
