OVERVIEW OF MUTUAL FUNDS
Having a lot of alternatives might make investing seem like a challenging task. Among them, mutual funds are frequently the most well-liked option for both new and experienced investors. However, what precisely are mutual funds, and why is it so crucial to understand? Even if you are just beginning your investment journey, this article will simplify and make it easier for you to comprehend or understand the Types of Mutual Funds and what mutual funds represent.
Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION
Mutual funds are a well-liked and popular investment that pool/combine the funds of several individuals to buy stocks, bonds, and other assets. They provide a method of investing in a varied portfolio without requiring the selection and administration of individual securities. However, there are many types of mutual fund options available, making it difficult to select the best one. With this guide’s aid, you can choose which mutual fund type would be the greatest fit for your financial objectives/goals.
MUTUAL FUND TYPES | MUTUAL FUND INDIA
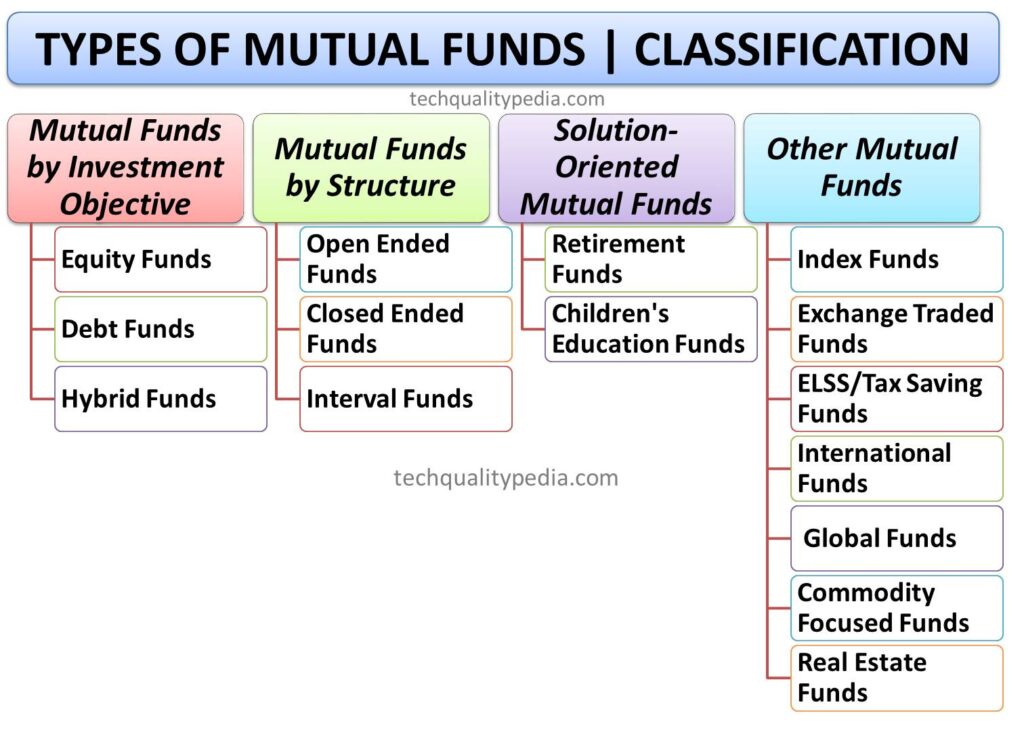
Various types of Mutual Funds are classified as follows:
- Mutual Funds by Investment Objective
- Mutual Funds by Structure
- Solution-Oriented Mutual Funds
- Other Mutual Funds
TYPES OF MUTUAL FUNDS BY INVESTMENT OBJECTIVE
- EQUITY FUNDS
- Large-Cap Funds
- Mid-Cap Funds
- Small-Cap Funds
- Multi-Cap Funds
- Flexi-Cap Funds
- Sectoral/Thematic Funds
- Dividend Yield Funds
- Focused Mutual Funds
- DEBT FUNDS
- Liquid Funds
- Income Funds
- Short-Term Funds
- Ultrashort Duration
- Medium Duration
- Long Duration
- Overnight Mutual Funds
- Dynamic Funds
- Gilt Funds
- Money Market Funds
- Banking and PSU Funds
- Corporate Bond
- Credit Risk
- HYBRID FUNDS
- Balanced Funds/Dynamic Asset Allocation Fund
- Aggressive Hybrid Funds
- Conservative Hybrid Funds
- Multi-Asset Allocation Funds
- Arbitrage Funds
TYPES OF MUTUAL FUNDS BY STRUCTURE
- Open Ended Funds
- Closed Ended Funds
- Interval Funds
SOLUTION-ORIENTED MUTUAL FUNDS
- Retirement Funds
- Children’s Education Funds
OTHER MUTUAL FUNDS
- Index Funds (BSE/NSE/S&P 500)
- ETF-Exchange Traded Mutual Funds
- ELSS (Equity Linked Savings Scheme)/Tax Saving Funds
- International Funds
- Global Funds
- Commodity Focused Stock Funds
- Real Estate Funds
MUTUAL FUNDS BY INVESTMENT OBJECTIVE
EQUITY FUNDS | MUTUAL FUND STOCKS
- Equity funds are designed for long-term growth and mostly invest in equities/stock markets.
- They have a greater risk but also greater profit potential.
- Equity funds are perfect for investors who have a longer investing horizon and a larger risk tolerance.
DEBT FUNDS
- Debt funds are designed to make investments in fixed-income securities such as government securities and bonds.
- They are a great option for conservative investors seeking stable income rather than significant returns.
- They are typically regarded as safer than equities funds but provide lower returns.
HYBRID FUNDS
- Hybrid funds provide a balanced strategy by investing in both debt and equity securities.
- They are appropriate for investors who seek exposure to the growth potential of equities/stocks while reducing risk with bonds.
MUTUAL FUNDS BY STRUCTURE
OPEN-ENDED FUNDS
- The most popular kind of mutual fund is an open-ended fund.
- They let investors purchase and sell shares whenever they choose, with the price determined by the net asset value (NAV) of the fund.
- They are perfect for investors seeking liquidity because of their flexibility.
CLOSE-ENDED FUNDS
- The Close-ended funds have a fixed quantity of stocks or shares issued through IPO (Initial public offering IPO) partnerships.
- After The IPO, these shares are traded on stock markets.
- Closed-ended funds are less liquid than open-ended funds since they do not permit the acquisition or redemption of shares after the initial offer period.
INTERVAL FUNDS
- Interval funds are a hybrid between open-ended and close-ended funds.
- They provide the option to buy or redeem shares on specific schedules, such as quarterly or yearly.
- This arrangement provides a balance between liquidity and the ability or opportunity to invest in less liquid assets.
SOLUTION-ORIENTED FUNDS
RETIREMENT FUNDS
- Retirement funds are long-term investment plans made to help investors to build a corpus for their retirement.
- These funds are designed to offer consistent returns over a long period and often include a lock-in period.
CHILDREN’S EDUCATION FUNDS
- Children’s education funds are solution-oriented plans designed to help parents save money for their children’s education.
- These funds provide the potential for capital appreciation with a focus on long-term growth.
OTHER SPECIALIZED MUTUAL FUNDS
Index Funds
- Index funds track the performance of a specific market index like Nifty 50, Sensex, and S&P 500.
- They are a popular option for passive investors since they provide diversification and lower fees.
- Index funds are passively managed i.e. the fund manager invests in the same securities as the underlying index.
- Index funds ensure to invest in all the securities tracked by the index, intending to match or exceed their benchmark.
ETF-Exchange Traded Mutual Funds
- ETFs combine elements of Mutual Funds and Stocks, providing liquidity and diversified exposure.
MUTUAL FUND ELSS | MUTUAL FUND TAX SAVING
- Mutual Fund ELSS (Equity Linked Savings Scheme) provides tax benefits under Sec. 80C of the Income Tax Act.
- Tax-saving mutual funds are also known as ELSS funds.
- They invest primarily in equities and have a lock-in period of 3 years.
- Suitable for long-term investors seeking to save on taxes.
- After the lock-in period, withdrawals are subject to 10% long-term capital gain tax (LTCG) over 1 lakh without indexation benefit.
International Funds
- International funds invest assets in global markets i.e. outside the investor’s home country.
- They offer diversification and exposure to international markets but have currency risk.
Global Funds
- Global Funds combine both domestic and foreign investments, providing a wide geographic diversification.
Commodity-focused Stock Funds
- Commodity-focused stock funds provide indirect exposure to the commodity market by investing in businesses involved in commodities.
Real Estate Funds
- Real Estate Funds invest in properties.
- Providing investors exposure to the Real Estate market without purchasing physical assets.
EQUITY MUTUAL FUNDS
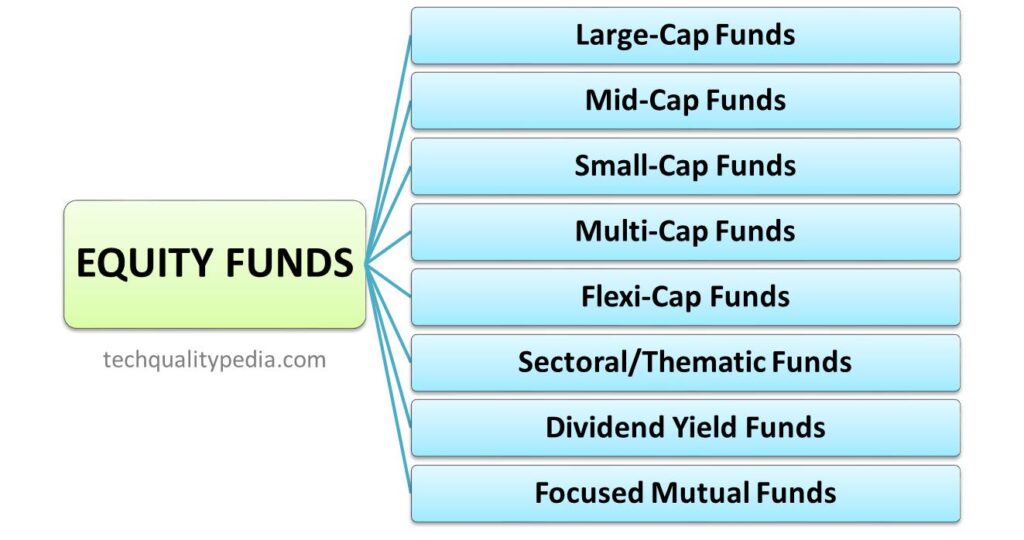
Large-Cap Funds
- Large-cap funds invest in big-size companies with a large market capitalization.
- Large-cap companies are usually well-established and financially secure/ stable.
- Offering moderate returns and lower risk.
Mid-Cap Funds
- Mid-cap funds invest in medium-sized companies.
- They provide a balance between the stability of large-cap funds and small-cap funds.
- Suitable for investors who are looking for moderate risk and higher returns.
Small-Cap Funds
- Small-cap funds invest in smaller companies with high growth potential.
- They provide significant returns but come with higher risk.
- Suitable for aggressive investors.
Multi-Cap Funds
- Multi-cap funds are diversified mutual funds that invest in large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap size companies.
- According to Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) mandates, these funds must allocate a minimum of 25% of their portfolio to each of these categories.
Flexi-Cap Funds
- Flexi-cap funds invest in stocks of large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap size companies without any mandated allocation percentages.
- These funds provide full flexibility to the fund manager to change the proportion of investments based on market conditions.
Sectoral/Thematic Funds
- Sector funds focus on specific sectors of the economy, such as technology, energy, or healthcare.
- They are perfect for investors who want to target a specific industry but come with higher risks because of their lack of diversification.
Dividend Yield Funds
- Dividend yield funds derive their name from the approach they employ, which is investing in firms that pay out dividends relatively frequently.
Investors in dividend yield funds benefit from regular income streams and can leave their money in the fund to grow while receiving dividend income on a continual basis.
- Because these funds must allocate at least 65% of their corpus to equities and equity-related instruments and leave 35% for other investments, they can further diversify their portfolio.
Focused Mutual Funds
- Typically, 70-80 companies’ stocks lie under a mutual fund scheme, but Focused Mutual Funds purchased only up to 30 companies’s stocks.
- Before investing, fund managers thoroughly examine every company’s information.
- According to SEBI’s regulation, Focused Funds have to invest at least 65% of their assets in equities and other equity-related securities.
They create a small, focused portfolio of stocks to give all of their attention to each investment and maximize growth while managing risk.
DEBT MUTUAL FUNDS
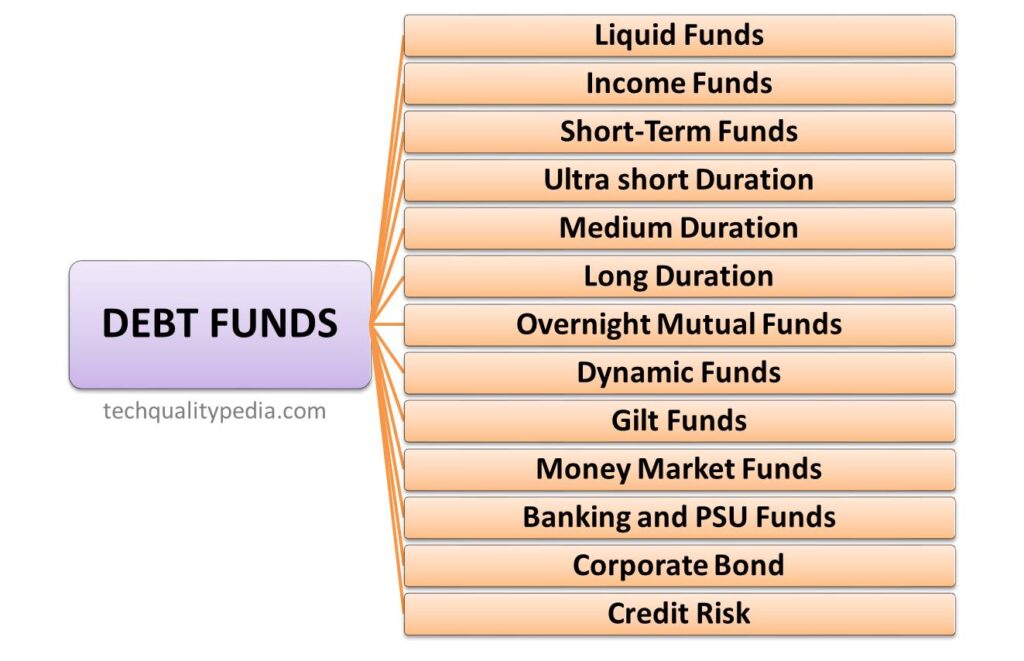
Liquid Funds
- Liquid funds invest in short-term debt securities, offering high liquidity with low risk.
- They are perfect for storing surplus funds for short periods.
Income Funds
- Income funds invest in bonds, government securities, and other fixed-income assets.
- They are made to offer a steady income stream, making them appropriate for retirees or those seeking regular income.
Short-Term Funds
- Short-term funds invest in short-term securities with a maturity period of 1 to 3 years.
- They offer slightly higher returns than liquid funds with moderate risk.
Ultra Short Duration Funds
- Ultra short-duration funds invest in short-term securities and money market instruments, with a very short duration of 3 to 6 months.
- These funds are designed to minimize interest rate risk, making them a safer choice as compared to longer-duration funds.
- These funds invest in instruments like treasury bills, commercial papers, and certificates of deposit.
- The focus is on liquidity and capital preservation, offering slightly higher returns than regular savings accounts.
Medium Duration Mutual Funds
- Medium-duration mutual funds invest in securities with a 3 to 4 year maturity period.
- These funds usually invest in a combination of government securities, corporate bonds, and other debt instruments.
- These funds provide a balance between risk and return and are suitable for investors with a moderate risk appetite.
- These funds aim to achieve a balance between capital appreciation and income creation.
- Gilt funds invest in government securities, which are generally considered risk-free investments.
- They are perfect for conservative investors seeking security and consistent returns.
Overnight Mutual Funds
- Overnight funds invest in assets that mature within a 24-hour window, while liquid funds invest in debt options with a maximum maturity duration of 91 days.
- This security is governed by the Reserve Bank of India and is known as Tri-party-repo or Trep.
- Credit risk is extremely minimal because of this one-day maturity window.
Dynamic Funds
- Dynamic funds can modify their Macaulay duration to maximize their investment returns.
- Fund managers in dynamic funds change the duration of their portfolio by adjusting the proportion of short- and long-term debt instruments in their portfolio.
- The risk associated with this fund lies in the fund manager’s decision to change the portfolio and not fulfill the payment obligation by the issuer of the debt instrument.
Money Market Funds
- These funds invest in money market securities with a maturity period of up to one year while maintaining a high degree of liquidity.
- Money market funds make investments in commercial papers, repurchase agreements, certificates of deposit, and treasury bills.
- Compared with traditional fixed-income instruments like savings accounts and fixed deposits, they provide higher interest rates.
HYBRID MUTUAL FUNDS
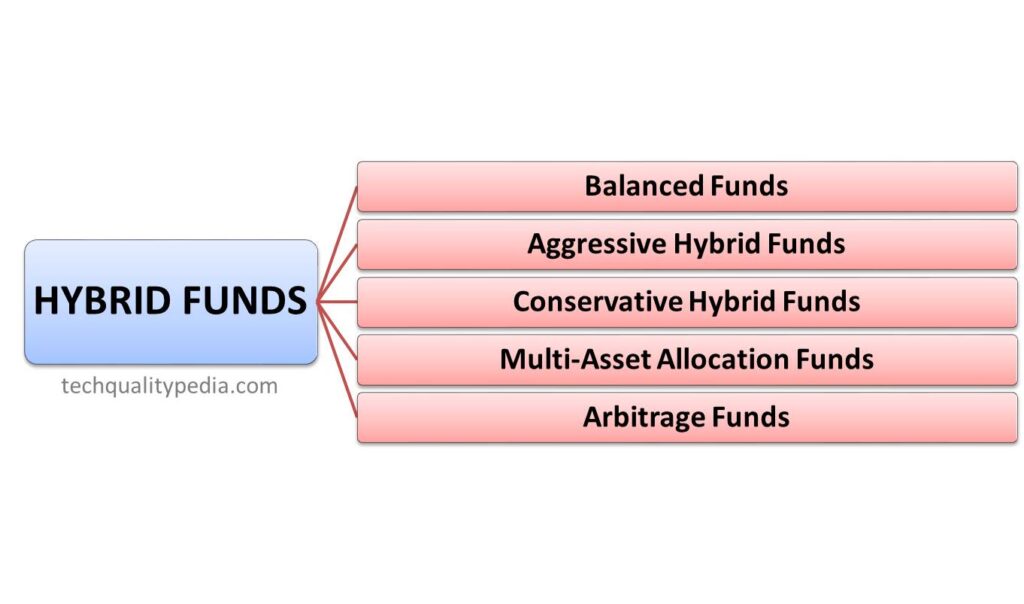
Balanced Funds
- Balanced funds invest in stocks and bonds, providing a balanced approach to risk and return.
- They are suitable for investors seeking growth and income with moderate risk.
Aggressive Hybrid Funds
- Aggressive hybrid funds have a maximum allocation to equities, therefore making them more volatile but providing significant growth potential.
- They are ideal for investors with a larger risk tolerance.
Conservative Hybrid Funds
- Compared to aggressive hybrid funds, conservative hybrid funds are less risky since they give priority to fixed-income assets.
- They are perfect for conservative investors seeking stability with some exposure to stocks or equities.
Multi-Asset Allocation Funds
- Multi Asset Funds spread their investments throughout several asset classes, which diversifies their portfolio and lowers risk.
- According to SEBI, these funds invest at least in three asset classes and allocate a minimum of 10% of their capital in each category.
- The two main asset classes are debt and equity; the third assets include gold, real estate, and more.
- These funds take advantage of the market as conditions change since they possess a variety of asset classes.
Arbitrage Funds
- Arbitrage funds seek to generate returns by taking advantage of price differences in different markets.
- The fund manager earns a profit from these price differences by buying and selling securities simultaneously.
- According to SEBI’s rule, arbitrage funds must invest a minimum of 65% of their assets in equity and equity-related instruments.
RISK FACTORS IN MUTUAL FUNDS
- Market Risk
- Credit Risk
- Interest Rate Risk
Market Risk
- Risk of capital loss due to changes in market dynamics or conditions.
- Equity funds are more risky but offer greater returns, whereas debt funds are secure but provide lower returns.
Credit Risk
- The possibility that a debt security issuer would miss payments on its obligations is known as credit risk.
- Credit risk affects debt funds, particularly those that invest in corporate bonds.
Interest Rate Risk
- Interest rate risk is the threat of losing money due to fluctuations or changes in interest rates.
- When interest rates increase, the value of existing bonds usually decreases, affecting debt fund returns.
How to Choose the Right Mutual Fund?
When you decide to invest in mutual funds then consider the following factors:
- Financial Goals
- Risk Appetite/tolerance
- Expense Ratios
- Past Performance
- Diversification
- Investment Horizon
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of mutual funds is essential for constructing a well-diversified investing portfolio. There is a mutual fund that fits your needs or goals, regardless of whether you are a conservative investor seeking stability or an aggressive investor chasing growth. You may make selections that fit your entire financial strategy by assessing your investing horizon, risk tolerance, and financial goals.
