Unsafe acts can be defined as any activity by workers that is not in accordance with the established safety standard or practice and that can or is likely to create accidents, the risk to oneself or others at work, damage equipment, and cause reputational and financial losses to the employer.
Unsafe conditions are the risks/hazards present at the workplace that may lead to human injury or death.
Table of Contents
Cause of Accidents
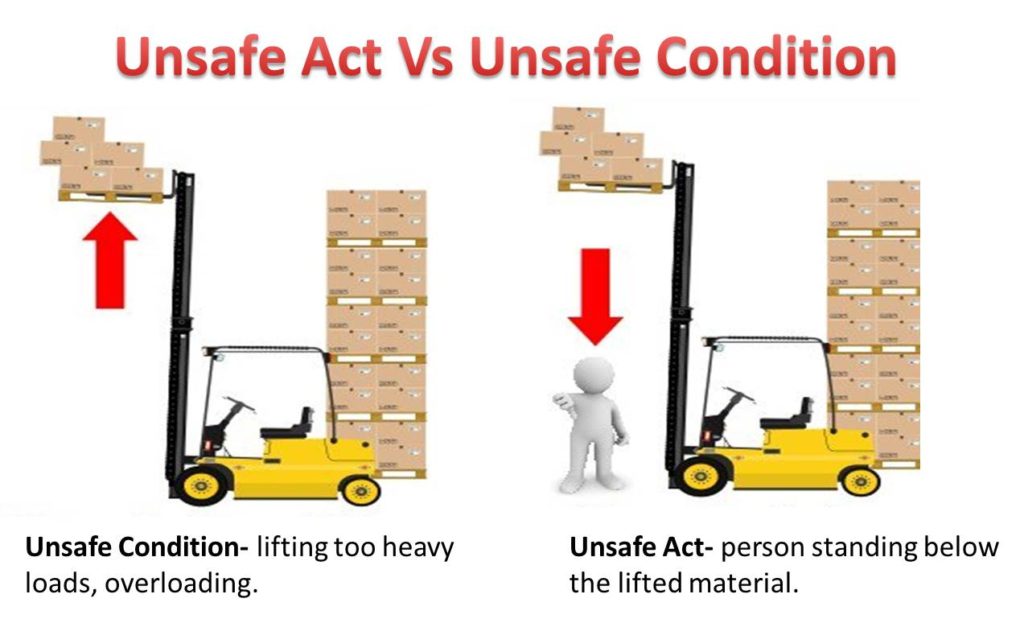
- UNSAFE CONDITION-Working conditions/environment which are prone to have an accident.
- UNSAFE ACT-People make the violation of the standard rules & meet with an accident.
Accident Analysis
FRANK BIRD’S THEORY OF ACCIDENT
- 88% accidents occur due to unsafe acts/attitudes.
- 10% accidents occur due to unsafe equipment/conditions.
- 2% accidents occur due to natural calamities.
Unsafe act and unsafe condition difference
- Oil/Coolant on the floor is an UNSAFE CONDITION, but walking on or near an oily/contaminated surface by a worker is an UNSAFE ACT.
- A machine rotating part without a safety guard is example of an unsafe condition, & operating that machine is an unsafe act performed by a worker.
- Working at height is an unsafe condition, & not wearing PPEs while working at height is an unsafe act.
Unsafe Act | Examples
- SHORT CUT METHODS – Not following safety rules.
- LAZINESS – Not wearing PPEs/safety appliances.
- HASTINESS – Overfeeding & speeding the machines/vehicles.
- ARROGANCE – Smoking in prohibited areas, ignorance of safety risk/hazard.
- OVER CONFIDENCE – Performing unauthorized work/operation.
- Working on dangerous equipment.
- Using defective tools.
- Unsafe position- Lifting with back bent, walking or standing under suspended load.
Working on Dangerous Equipment
- Cleaning oiling or adjusting during TPM
- Getting on or off moving vehicle conveyors and elevators
- Working on electrical equipment when it is on. (During Maintenance)
- Welding/repairing equipment containing dangerous material (During Repair)
Failing to shut off Machines
•Leaving Machines running when finished with them
Unsafe Position
- Standing under a suspended load
- Lifting with back bent
- Riding in fork lift
Unsafe Speeds
- Operating machines at unsafe speeds
- Feeding machines too rapidly
Making Safety Devices Inoperative
- Removing guards
- Blocking out two-hand control system
Unsafe Unloading
- Lifting too heavy loads
- Piling/Stacking Improperly
- Overloading
Using defective tool
- Worn out wrenches
- Using hands to feed, adjust, or clean Equipment instead of tools
Unsafe Conditions | Examples
- Uncovered hole or drain or pits.
- Fragile roof or damaged ladders.
- Blocking and obstructing pathways and gangways.
- Contaminated floor- Oil/coolant leakage or spillage on the floor.
- Metal chips are scattered around the machine/on the floor.
- Rotating machine parts without safety guard or defective guard or inadequately guarded.
- Improper/Low lux level (illumination).
- Improper ventilation at workplace-not enough air, contamination of air.
- Unwanted items/tools lying on the machine(poor 5S at the workplace).
- Unsafe unloading- lifting too heavy loads, overloading.
- Loose wiring on the machine or at the workplace can lead to an electrical fire or electric shocks.
- Equipment defects- sharp edges, poorly designed, not strong enough, worn out, cracked etc.
Hazardous Arrangement
- Unsafely stored material or tools
- Congested workplaces.
- Narrow blocked stairs or exits. Overloaded floors, platforms, vehicles, and trolleys
Equipment Defects
- Sharp edges
- Poorly designed & Slippery
- Not strong enough
- Worn out
- Cracked
Personal protection
Lack of goggles, safety shoes, respirators, gloves, apron, ear plug etc.
Improper Ventilation
- Not enough air,
- Contamination of air
- Too hot or cold air
Improper Illumination
- Not enough light
- Glare
Improper Guarding
- Unguarded
- Inadequately guarded,
- Lack of support to the Guard
