A Process Flow Chart (PFC) in manufacturing is a diagram of the separate steps of a operations/process in sequential order. PFC also known as process flow diagram (PFD), and Process Map.
PFC is a process analysis tool that can be used to describe various processes, such as: Manufacturing process, Project planning, and Service sectors etc.
Process flow chart in manufacturing is one of the basic seven quality control tools or 7 QC tools and is widely used in quality problem solving methodologies like 8D and Six Sigma.
It is prepared during APQP and PPAP process for new product development, and one of the important document of PPAP lists.
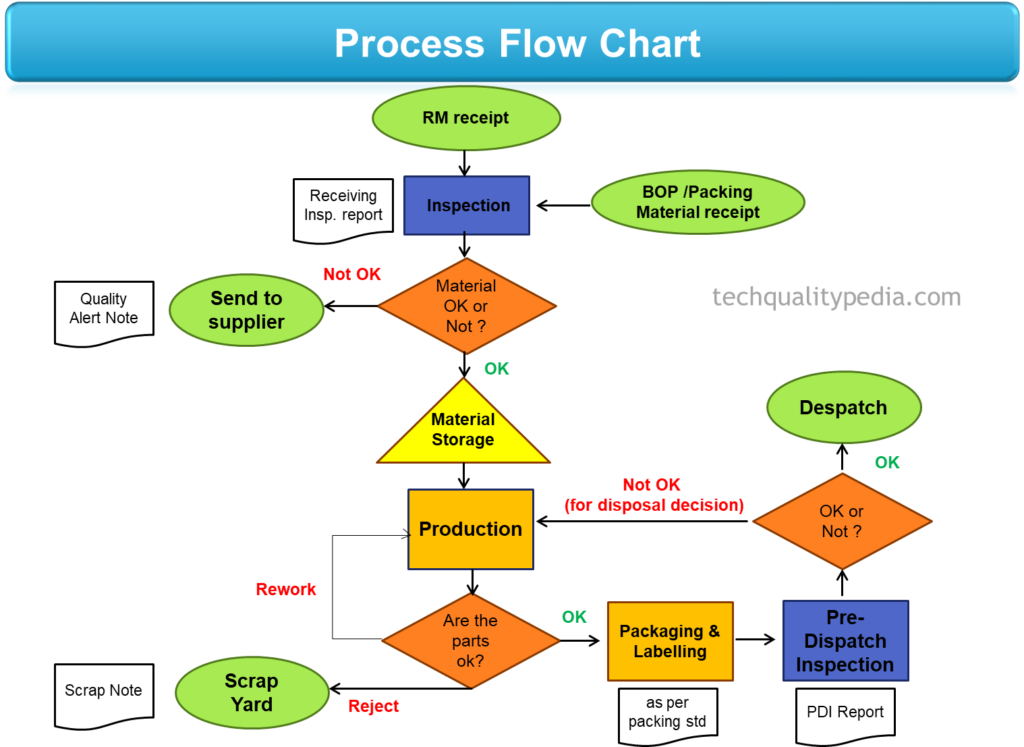
Table of Contents
When to use a Process Flow Chart
- For defining or analyzing new process.
- For standardize or redesign of a existing process.
- To find opportunity for improvement in a process such as unnecessary steps/activities, bottlenecks, and gaps etc.
Process flow chart types
There are mainly two types of process flow charts that are commonly used in manufacturing for quality improvement activities/projects.
- High level Process Flow Chart
- Detailed Process Flow Chart
High Level Process Flow Chart
A high-level process flow chart provides a high-level picture/view (macro view of activity) of a process that generally having 6~10 main phases/steps. The major blocks of action/activity of a process are depicted in these process flowcharts. These charts are particularly useful in the early stages of a project and helps in the identification of improvement priorities.

Detailed Process Flow Chart
A detailed process flow chart depicts a process in detail (micro view of activity) usually greater than 15 phases/steps. Process flow charts of these kind are useful for identifying complexity, excessive steps, and other issues in a process and should be utilized when standardizing or modifying the existing process.

Symbols for process flow chart
The common symbols used for making process flow chart in manufacturing industries are shown below.

- Start or End : An elongated circle represents the start or end of a process.
- Step/Flow-line: Represents direction of flow/process from one step to another.
- Process/Operation: Rectangle/square box shows instructions/actions/activity.
- Decision: Diamond box represents decision on particular activity.
- Storage: Represents storage of material/parts.
- Delay/Wait: Represents delay in operation/process/activity.
- Document: Represents supportive documents required.
- Start or End: Alternate of elongated circle that also used to represents the start or end of a process
Process flow Diagram | Key points
Following key points need to be addressed while making the manufacturing process flowchart or process flow diagram:
- Process flow diagram (PFD) reflect the complete process from receiving to shipping of product.
- Identify outsourced operations on the flow diagram.
- Identify stations where special characteristics are verified.
- Include sequence numbers and required manufacturing/inspection stations.
- Include identification of unique and/or dedicated process equipment.
- Include rework/repair operations, including re-inspection of the product.
- Process flow diagrams include packaging, labeling and storage.
You’ll also like:
Template for process flow chart
Download Process flow chart template power point & process flow chart word template



r33swe
Guys, you won’t believe this particular site I discovered. It’s packed together with thousands of porno pics of undressed chicks with large, gorgeous boobs. They love doing solo shots in alluring photo sessions. how to send nudes girls porn galleries offers the goods.
Fantastic beat ! I would like to apprentice while you amend your site, how can i subscribe for a blog web site? The account aided me a acceptable deal. I had been tiny bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided bright clear concept
i0fsyg
derfd5
Valuable information. Lucky me I found your site by accident, and I am shocked why this accident did not happened earlier! I bookmarked it.
Hello there, simply was aware of your blog thru Google, and located that it is really informative. I am going to watch out for brussels. I will appreciate should you continue this in future. A lot of other people will likely be benefited out of your writing. Cheers!
It?¦s actually a nice and helpful piece of info. I am glad that you simply shared this useful info with us. Please stay us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.
Very interesting topic, appreciate it for posting. “The season of failure is the best time for sowing the seeds of success.” by Paramahansa Yogananda.
Nice post. I learn something more challenging on different blogs everyday. It will always be stimulating to read content from other writers and practice a little something from their store. I’d prefer to use some with the content on my blog whether you don’t mind. Natually I’ll give you a link on your web blog. Thanks for sharing.
Hello There. I discovered your weblog the use of msn. This is a very well written article. I will make sure to bookmark it and come back to read extra of your helpful info. Thank you for the post. I’ll certainly comeback.
We are a group of volunteers and starting a new scheme in our community. Your web site offered us with valuable information to work on. You have done an impressive job and our whole community will be thankful to you.
I was reading some of your blog posts on this website and I think this web site is real instructive! Keep on posting.
Its fantastic as your other posts : D, thankyou for posting. “A gift in season is a double favor to the needy.” by Publilius Syrus.
Today, I went to the beachfront with my kids. I found a sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She put the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear. She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is totally off topic but I had to tell someone!
Greetings! Very helpful advice on this article! It is the little changes that make the biggest changes. Thanks a lot for sharing!
I like this weblog so much, bookmarked. “To hold a pen is to be at war.” by Francois Marie Arouet Voltaire.
Enjoyed reading through this, very good stuff, regards.
As a Newbie, I am continuously searching online for articles that can be of assistance to me. Thank you
I really appreciate this post. I?¦ve been looking everywhere for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You have made my day! Thank you again
Aw, this was a really nice post. In concept I would like to put in writing like this additionally – taking time and actual effort to make an excellent article… however what can I say… I procrastinate alot and not at all appear to get something done.
I always was concerned in this subject and stock still am, regards for putting up.
rk8b9b
This actually answered my drawback, thank you!
Rattling superb information can be found on site. “Education is what most receive, many pass on, and few possess.” by Karl Kraus.
With everything that seems to be building within this particular area, many of your opinions tend to be rather exciting. Nevertheless, I appologize, because I do not give credence to your entire strategy, all be it exhilarating none the less. It looks to us that your remarks are generally not entirely validated and in reality you are yourself not completely certain of the argument. In any event I did enjoy reading through it.
I¦ll immediately snatch your rss as I can not find your email subscription link or e-newsletter service. Do you have any? Please allow me know so that I could subscribe. Thanks.
Good web site! I truly love how it is simple on my eyes and the data are well written. I’m wondering how I could be notified when a new post has been made. I have subscribed to your RSS which must do the trick! Have a great day!
I genuinely enjoy reading through on this site, it contains excellent content.
Thanks for helping out, fantastic info. “If at first you don’t succeed, find out if the loser gets anything.” by Bill Lyon.
I like meeting useful information , this post has got me even more info! .
You are my breathing in, I possess few web logs and occasionally run out from brand :). “‘Tis the most tender part of love, each other to forgive.” by John Sheffield.
Absolutely indited subject matter, Really enjoyed studying.
Rattling nice design and style and good articles, hardly anything else we require : D.
I went over this internet site and I conceive you have a lot of fantastic information, saved to bookmarks (:.
Utterly written articles, Really enjoyed looking through.
Hi there! Someone in my Myspace group shared this website with us so I came to check it out. I’m definitely loving the information. I’m bookmarking and will be tweeting this to my followers! Superb blog and outstanding design.
Wow! Thank you! I continually needed to write on my website something like that. Can I include a fragment of your post to my website?
Hi there, i read your blog from time to time and i own a similar one and i was just curious if you get a lot of spam feedback? If so how do you stop it, any plugin or anything you can suggest? I get so much lately it’s driving me insane so any help is very much appreciated.
Hi, Neat post. There is a problem with your website in internet explorer, would check this… IE still is the market leader and a large portion of people will miss your excellent writing because of this problem.
I think this is among the most vital information for me. And i’m glad reading your article. But want to remark on few general things, The site style is great, the articles is really excellent : D. Good job, cheers
This is really interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger. I’ve joined your rss feed and look forward to seeking more of your magnificent post. Also, I’ve shared your website in my social networks!
Hello there, I found your web site via Google while searching for a related topic, your web site came up, it looks good. I’ve bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
Thank you for sharing superb informations. Your web site is very cool. I am impressed by the details that you¦ve on this website. It reveals how nicely you perceive this subject. Bookmarked this website page, will come back for extra articles. You, my pal, ROCK! I found simply the info I already searched everywhere and just couldn’t come across. What a great site.
A lot of the things you mention happens to be astonishingly appropriate and that makes me ponder the reason why I hadn’t looked at this with this light before. This particular article really did switch the light on for me as far as this particular subject matter goes. Nonetheless at this time there is 1 point I am not really too comfy with and whilst I attempt to reconcile that with the core idea of the point, permit me see exactly what the rest of the readers have to point out.Well done.
I appreciate, cause I found exactly what I was looking for. You have ended my 4 day long hunt! God Bless you man. Have a great day. Bye
Hello there, simply was aware of your weblog via Google, and found that it is truly informative. I’m going to be careful for brussels. I’ll appreciate in case you proceed this in future. Many people might be benefited out of your writing. Cheers!
You have brought up a very excellent points, regards for the post.
Excellent website. Plenty of useful info here. I’m sending it to a few friends ans also sharing in delicious. And of course, thanks for your sweat!
Hi, i think that i noticed you visited my weblog thus i came to “go back the desire”.I am attempting to find issues to enhance my web site!I suppose its good enough to make use of some of your ideas!!
I’ve been exploring for a bit for any high-quality articles or blog posts on this kind of area . Exploring in Yahoo I at last stumbled upon this website. Reading this info So i’m happy to convey that I’ve an incredibly good uncanny feeling I discovered just what I needed. I most certainly will make certain to don’t forget this web site and give it a glance on a constant basis.
I like what you guys are up also. Such intelligent work and reporting! Keep up the superb works guys I?¦ve incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it’ll improve the value of my site 🙂
After examine just a few of the weblog posts in your website now, and I really like your way of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark web site listing and will likely be checking back soon. Pls try my web site as properly and let me know what you think.
Wonderful items from you, man. I have understand your stuff prior to and you are simply too fantastic. I really like what you’ve received here, really like what you’re stating and the way in which by which you are saying it. You’re making it enjoyable and you continue to take care of to stay it wise. I cant wait to read far more from you. This is really a wonderful website.
Hey this is somewhat of off topic but I was wondering if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding expertise so I wanted to get guidance from someone with experience. Any help would be greatly appreciated!
Great website. Plenty of useful info here. I?¦m sending it to several buddies ans also sharing in delicious. And naturally, thank you in your sweat!
Do you mind if I quote a couple of your posts as long as I provide credit and sources back to your website? My website is in the very same area of interest as yours and my visitors would really benefit from a lot of the information you provide here. Please let me know if this alright with you. Thanks a lot!
Your style is so unique compared to many other people. Thank you for publishing when you have the opportunity,Guess I will just make this bookmarked.2
The Salt Trick is a natural technique that involves using specific salts, such as Blue Salt, to enhance male performance
This actually answered my problem, thanks!
This is the right weblog for anyone who needs to find out about this topic. You realize a lot its almost hard to argue with you (not that I really would want…HaHa). You definitely put a brand new spin on a topic thats been written about for years. Nice stuff, simply great!
Awsome site! I am loving it!! Will be back later to read some more. I am bookmarking your feeds also.
The Natural Mounjaro Recipe is more than just a diet—it’s a sustainable and natural approach to weight management and overall health.
I’ve been absent for a while, but now I remember why I used to love this website. Thanks , I¦ll try and check back more often. How frequently you update your website?
Mitolyn is a cutting-edge natural dietary supplement designed to support effective weight loss and improve overall wellness.
Undeniably consider that that you stated. Your favorite reason seemed to be on the net the simplest thing to bear in mind of. I say to you, I definitely get annoyed whilst other people think about issues that they just do not realize about. You controlled to hit the nail upon the highest and outlined out the whole thing with no need side effect , other folks could take a signal. Will likely be again to get more. Thanks
I enjoy what you guys are usually up too. Such clever work and exposure! Keep up the wonderful works guys I’ve you guys to blogroll.
Hi, Neat post. There’s a problem together with your website in internet explorer, could check this?K IE still is the marketplace leader and a big component of other folks will pass over your fantastic writing due to this problem.
I got what you intend, regards for posting.Woh I am happy to find this website through google. “If one does not know to which port one is sailing, no wind is favorable.” by Seneca.
Hiya, I am really glad I have found this info. Today bloggers publish only about gossips and internet and this is actually irritating. A good site with interesting content, that’s what I need. Thank you for keeping this site, I’ll be visiting it. Do you do newsletters? Cant find it.
I have been exploring for a little for any high quality articles or blog posts in this sort of house . Exploring in Yahoo I at last stumbled upon this site. Reading this info So i am satisfied to convey that I have an incredibly good uncanny feeling I discovered exactly what I needed. I most surely will make sure to do not omit this site and give it a glance on a constant basis.
Great article and right to the point. I don’t know if this is truly the best place to ask but do you folks have any thoughts on where to get some professional writers? Thanks 🙂
Nice read, I just passed this onto a friend who was doing a little research on that. And he just bought me lunch since I found it for him smile Thus let me rephrase that: Thank you for lunch!
Perfectly pent subject material, thankyou for entropy.
I am not sure where you’re getting your information, but great topic. I needs to spend some time learning more or understanding more. Thanks for wonderful info I was looking for this info for my mission.
You are my aspiration, I have few web logs and sometimes run out from to post : (.
Wow! This could be one particular of the most beneficial blogs We have ever arrive across on this subject. Actually Wonderful. I’m also a specialist in this topic so I can understand your effort.
Its like you read my mind! You appear to know a lot about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you could do with some pics to drive the message home a bit, but other than that, this is wonderful blog. A great read. I’ll certainly be back.
There’s noticeably a bundle to learn about this. I assume you made sure good points in features also.
Hi, Neat post. There is a problem with your web site in internet explorer, would check this… IE still is the market leader and a huge portion of people will miss your excellent writing because of this problem.
Having read this I thought it was very informative. I appreciate you taking the time and effort to put this article together. I once again find myself spending way to much time both reading and commenting. But so what, it was still worth it!
Keep functioning ,great job!
An impressive share, I simply given this onto a colleague who was doing a little analysis on this. And he in fact bought me breakfast because I discovered it for him.. smile. So let me reword that: Thnx for the treat! But yeah Thnkx for spending the time to debate this, I feel strongly about it and love reading extra on this topic. If attainable, as you change into experience, would you thoughts updating your weblog with more particulars? It is highly useful for me. Huge thumb up for this blog submit!
Pretty! This was a really wonderful post. Thank you for your provided information.
Hi , I do believe this is an excellent blog. I stumbled upon it on Yahoo , i will come back once again. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and help other people.
Hi , I do believe this is an excellent blog. I stumbled upon it on Yahoo , i will come back once again. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and help other people.
so much fantastic info on here, : D.
You are my inhalation, I possess few blogs and often run out from to post : (.
I truly appreciate your piece of work, Great post.
Compre visualizações e espectadores reais para suas lives no YouTube, Instagram, Twitch, TikTok e Facebook. Aumente seu engajamento e credibilidade online com serviços seguros e confiáveis. Impulsione suas transmissões ao vivo hoje!
What i don’t realize is in truth how you are now not actually a lot more neatly-preferred than you might be right now. You’re so intelligent. You realize therefore considerably on the subject of this subject, produced me in my view believe it from numerous varied angles. Its like men and women aren’t involved until it is one thing to do with Woman gaga! Your individual stuffs great. Always care for it up!
You actually make it appear so easy along with your presentation but I in finding this topic to be actually something that I believe I’d never understand. It kind of feels too complex and very huge for me. I am having a look forward to your subsequent post, I’ll attempt to get the cling of it!
Spot on with this write-up, I really assume this web site wants much more consideration. I’ll probably be again to learn far more, thanks for that info.
Good write-up, I’m normal visitor of one’s website, maintain up the excellent operate, and It is going to be a regular visitor for a long time.
Undeniably imagine that that you said. Your favorite reason appeared to be at the web the easiest thing to remember of. I say to you, I definitely get annoyed while other people think about issues that they plainly do not recognize about. You managed to hit the nail upon the top as neatly as outlined out the whole thing with no need side-effects , people can take a signal. Will likely be again to get more. Thank you
If you’re in to big, naked tits, then bignudetits.com is the site to suit your needs. This site is filled with totally free porn photos showcasing some of the hottest Blond Witth Huge Tits Blowjob Nude Pics big titted girls on the web. The adult section is really a small example from the amazing articles you’ll find right here, featuring everything from big natural juggs to firm, perky boobs which are sure to get a person hard.
My developer is trying to convince me to move to .net from PHP. I have always disliked the idea because of the expenses. But he’s tryiong none the less. I’ve been using Movable-type on a variety of websites for about a year and am nervous about switching to another platform. I have heard fantastic things about blogengine.net. Is there a way I can transfer all my wordpress content into it? Any help would be really appreciated!
Perfectly composed written content, Really enjoyed reading through.
I really like your writing style, fantastic info, thank you for posting :D. “You can complain because roses have thorns, or you can rejoice because thorns have roses.” by Ziggy.
Excellent post. I was checking continuously this blog and I’m impressed! Extremely helpful info specially the last part 🙂 I care for such information much. I was looking for this certain information for a very long time. Thank you and good luck.
My brother suggested I might like this web site. He was entirely right. This post truly made my day. You cann’t imagine simply how much time I had spent for this info! Thanks!
I appreciate, result in I discovered exactly what I was looking for. You’ve ended my four day long hunt! God Bless you man. Have a great day. Bye
I have been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this site. Thanks , I¦ll try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your website?
Thanks for sharing excellent informations. Your web-site is so cool. I’m impressed by the details that you’ve on this web site. It reveals how nicely you perceive this subject. Bookmarked this web page, will come back for more articles. You, my pal, ROCK! I found simply the info I already searched all over the place and simply couldn’t come across. What a great web-site.
Hiya, I’m really glad I’ve found this information. Nowadays bloggers publish just about gossips and internet and this is actually irritating. A good website with interesting content, that’s what I need. Thank you for keeping this web-site, I’ll be visiting it. Do you do newsletters? Can’t find it.
What i don’t understood is in fact how you’re not actually a lot more neatly-liked than you may be right now. You’re very intelligent. You realize therefore significantly in terms of this topic, made me in my opinion consider it from a lot of numerous angles. Its like men and women aren’t fascinated except it?¦s one thing to do with Woman gaga! Your own stuffs outstanding. Always deal with it up!
The Salt Trick is a natural technique that involves using specific salts, such as Blue Salt, to enhance male performance
The Salt Trick is a natural technique that involves using specific salts, such as Blue Salt, to enhance male performance
Hello, you used to write great, but the last several posts have been kinda boring… I miss your great writings. Past few posts are just a bit out of track! come on!
Just wanna remark that you have a very nice website , I love the style it actually stands out.
I like this site so much, bookmarked.
ProDentim is a chewable oral probiotic supplement formulated with a unique mix of probiotics, prebiotics, herbs, and nutrients.
The Ice Water Hack has been gaining popularity as a simple method to aid weight loss. After reading about its potential benefits, I decided to give it a shot and see how it worked for me. Here’s what I found!
wonderful put up, very informative. I’m wondering why the opposite experts of this sector do not understand this. You must proceed your writing. I’m sure, you have a huge readers’ base already!
Normally I do not read post on blogs, but I would like to say that this write-up very forced me to try and do so! Your writing style has been amazed me. Thanks, quite nice post.
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself? Plz reply back as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to know wheere u got this from. thanks
What i do not realize is actually how you are not actually much more well-liked than you may be right now. You’re very intelligent. You realize thus significantly relating to this subject, made me personally consider it from numerous varied angles. Its like men and women aren’t fascinated unless it is one thing to do with Lady gaga! Your own stuffs nice. Always maintain it up!
Mitolyn is a cutting-edge natural dietary supplement designed to support effective weight loss and improve overall wellness.
Perfect piece of work you have done, this web site is really cool with good information.
I was looking through some of your posts on this site and I conceive this website is rattling instructive! Continue putting up.
Fantastic beat ! I wish to apprentice whilst you amend your web site, how can i subscribe for a blog site? The account helped me a appropriate deal. I have been tiny bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided bright clear concept
Schau dir MILFMUTTERFOTOS.COM an und genieГџe oben ohne reife Frau Bilder wie du sie noch nie gesehen hast. Jede Mutter zeigt stolz ihren Figur und will einfach nur Ficken. Alles ist kostenlos und voller heiГџer Momente.
When I originally commented I clicked the “Notify me when new comments are added” checkbox and now each time a comment is added I get three emails with the same comment. Is there any way you can remove people from that service? Appreciate it!
There is obviously a bundle to realize about this. I think you made various nice points in features also.
You are my aspiration, I have few blogs and rarely run out from brand :). “Fiat justitia et pereat mundus.Let justice be done, though the world perish.” by Ferdinand I.
I simply could not depart your site prior to suggesting that I really enjoyed the standard information a person provide on your guests? Is gonna be again ceaselessly in order to check up on new posts.
Hello there! Would you mind if I share your blog with my twitter group? There’s a lot of folks that I think would really enjoy your content. Please let me know. Thank you
If you’ve been looking for a way to unlock your full mental potential and attract wealth effortlessly, Billionaire Brain Wave might just be the breakthrough you’ve been waiting for!
Hello. fantastic job. I did not anticipate this. This is a impressive story. Thanks!
Great blog! Is your theme custom made or did you download it from somewhere? A design like yours with a few simple tweeks would really make my blog jump out. Please let me know where you got your design. Thank you
This is a very good tips especially to those new to blogosphere, brief and accurate information… Thanks for sharing this one. A must read article.
In MILFMUTTERFOTOS findest du freizügige heisse Muttis, die sich nach echtem Rammeln sehnen. Diese Mutters zeigen alles – Zonen, die nur darauf warten, benutzt zu werden. Unsere Fotogalerie ist gratis und komplett anzüglich.
What¦s Happening i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve discovered It absolutely helpful and it has aided me out loads. I’m hoping to contribute & assist different customers like its aided me. Great job.
Very interesting topic, thankyou for putting up. “The season of failure is the best time for sowing the seeds of success.” by Paramahansa Yogananda.
You completed several good points there. I did a search on the issue and found nearly all persons will consent with your blog.
very nice put up, i certainly love this web site, keep on it
Unsere Pic-Stash bei https://milfmutterfotos.com explodiert vor heißen oben ohneen reife Fraus. Du bekommst Bilder, die deine Hose sprengen – alles kostenlos, ungezügelt und einfach nur Porno pur.
I like this web blog its a master peace ! Glad I detected this on google .
You are my inhalation, I possess few web logs and infrequently run out from to brand.
Simply want to say your article is as surprising. The clarity to your publish is simply nice and that i can think you’re knowledgeable on this subject. Fine together with your permission let me to clutch your RSS feed to stay updated with forthcoming post. Thanks 1,000,000 and please keep up the enjoyable work.
I’ve been absent for a while, but now I remember why I used to love this blog. Thanks, I?¦ll try and check back more often. How frequently you update your web site?
Hmm is anyone else experiencing problems with the pictures on this blog loading? I’m trying to find out if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog. Any suggestions would be greatly appreciated.
I’m not sure exactly why but this site is loading extremely slow for me. Is anyone else having this issue or is it a issue on my end? I’ll check back later and see if the problem still exists.
Youre so cool! I dont suppose Ive read something like this before. So good to seek out any individual with some unique thoughts on this subject. realy thanks for starting this up. this website is something that is needed on the web, somebody with somewhat originality. helpful job for bringing something new to the internet!
Hey there! This is kind of off topic but I need some help from an established blog. Is it very hard to set up your own blog? I’m not very techincal but I can figure things out pretty fast. I’m thinking about creating my own but I’m not sure where to begin. Do you have any ideas or suggestions? Thank you
Some really nice and useful info on this web site, besides I think the style and design holds superb features.
hello there and thank you on your info – I have definitely picked up something new from proper here. I did on the other hand experience some technical points using this web site, since I skilled to reload the website lots of occasions previous to I could get it to load correctly. I had been thinking about in case your hosting is OK? Not that I am complaining, but slow loading cases times will very frequently have an effect on your placement in google and can damage your high-quality ranking if ads and ***********|advertising|advertising|advertising and *********** with Adwords. Anyway I am including this RSS to my email and could look out for much more of your respective exciting content. Make sure you replace this again soon..
I do consider all of the concepts you have offered on your post. They are very convincing and will definitely work. Nonetheless, the posts are very brief for beginners. May just you please lengthen them a bit from next time? Thanks for the post.
Hey! I know this is kind of off topic but I was wondering which blog platform are you using for this website? I’m getting tired of WordPress because I’ve had issues with hackers and I’m looking at options for another platform. I would be awesome if you could point me in the direction of a good platform.
Howdy very cool web site!! Man .. Beautiful .. Amazing .. I will bookmark your blog and take the feeds also…I’m happy to search out numerous helpful info here in the submit, we’d like work out more strategies in this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
Some genuinely nice and useful information on this website, likewise I believe the style has got excellent features.
I conceive you have observed some very interesting details , thanks for the post.
Your place is valueble for me. Thanks!…
Have you ever considered about adding a little bit more than just your articles? I mean, what you say is fundamental and all. Nevertheless just imagine if you added some great visuals or videos to give your posts more, “pop”! Your content is excellent but with images and videos, this website could definitely be one of the most beneficial in its field. Good blog!
Hey! Do you know if they make any plugins to protect against hackers? I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard on. Any suggestions?
I believe this site holds some really superb info for everyone : D.
I very pleased to find this internet site on bing, just what I was searching for : D too bookmarked.
I really like assembling utile info, this post has got me even more info! .
Some truly great posts on this website , thanks for contribution.
Oh my goodness! an amazing article dude. Thank you However I’m experiencing situation with ur rss . Don’t know why Unable to subscribe to it. Is there anyone getting identical rss drawback? Anybody who knows kindly respond. Thnkx
BESTSEXPICS.NET is packed with vaults of real silver vixen getting their slit stretched and backdoor drilled. Some even take double stuffing. It’s raw, filthy, and totally nude.
Hmm is anyone else having problems with the images on this blog loading? I’m trying to find out if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog. Any responses would be greatly appreciated.
You are my aspiration, I have few blogs and often run out from to post .
Today, I went to the beach with my children. I found a sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She put the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear. She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is completely off topic but I had to tell someone!
Very interesting info!Perfect just what I was looking for!
I have to voice my love for your kind-heartedness giving support to individuals who must have guidance on your field. Your special dedication to passing the message across turned out to be definitely interesting and have truly permitted others just like me to reach their endeavors. Your entire invaluable useful information means this much to me and additionally to my office workers. Regards; from each one of us.
Catch a mature silver vixen giving BJ to a young stud, then taking load deep in her booty. That’s the kind of nasty we keep live on https://www.bestsexpics.net, and it’s all free to click.
Heya i am for the first time here. I came across this board and I to find It really helpful & it helped me out much. I am hoping to give one thing again and help others like you helped me.
You like watching hubby scenes? MATUREMILFPUSSY. has aged horny moms getting railed while their men watch. Add some gushing, threesomes and train rides and you’re good to go.
What i do not realize is in reality how you are now not really a lot more well-preferred than you may be now. You are so intelligent. You understand thus significantly in terms of this matter, made me in my opinion consider it from numerous numerous angles. Its like women and men aren’t fascinated except it’s something to accomplish with Lady gaga! Your own stuffs nice. All the time care for it up!
Hello there, just was aware of your weblog thru Google, and found that it is really informative. I am gonna be careful for brussels. I’ll appreciate in the event you proceed this in future. Lots of other people will probably be benefited out of your writing. Cheers!
Have you ever considered about including a little bit more than just your articles? I mean, what you say is important and all. But just imagine if you added some great photos or videos to give your posts more, “pop”! Your content is excellent but with images and clips, this blog could undeniably be one of the very best in its niche. Wonderful blog!
Greetings from Idaho! I’m bored at work so I decided to browse your website on my iphone during lunch break. I really like the information you provide here and can’t wait to take a look when I get home. I’m surprised at how fast your blog loaded on my phone .. I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyways, superb blog!
MATUREMILFPUSSY. features juicy and super-sized seasoned horny moms spreading out and taking that kitty deep. These girls are thick, nasty, and begging to ride your next session.
What’s Happening i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve found It positively helpful and it has aided me out loads. I’m hoping to give a contribution & aid different users like its aided me. Great job.
Nice read, I just passed this onto a colleague who was doing some research on that. And he just bought me lunch because I found it for him smile Thus let me rephrase that: Thanks for lunch! “The capacity to care is what gives life its most deepest significance.” by Pablo Casals.
Some truly interesting details you have written.Aided me a lot, just what I was searching for : D.
Very interesting details you have observed, regards for putting up. “Ignorance, the root and the stem of every evil.” by Plato.
Heya i’m for the first time here. I came across this board and I in finding It truly helpful & it helped me out much. I am hoping to present something back and help others like you aided me.
You actually make it seem so easy with your presentation but I find this matter to be actually something that I think I would never understand. It seems too complex and very broad for me. I’m looking forward for your next post, I’ll try to get the hang of it!
https://www.bestsexpics.net/ is all about hard hole work—old chicks with fuck-me shoes and lingerie showing off and begging to be used. These mature old slut babes don’t play around when it’s fuck time.
Get into https://maturemilfpussy.net/ and see seasoned girl-on-girl lick, grind, and finger like the freaky pros they are. No scripts, no fake moans—just real raw kitty to devour.
magnificent issues altogether, you simply received a brand new reader. What could you suggest about your submit that you simply made a few days in the past? Any positive?
Hi this is kinda of off topic but I was wondering if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding know-how so I wanted to get advice from someone with experience. Any help would be greatly appreciated!
I haven¦t checked in here for a while because I thought it was getting boring, but the last several posts are good quality so I guess I will add you back to my daily bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
Its excellent as your other blog posts : D, appreciate it for putting up. “It takes less time to do things right than to explain why you did it wrong.” by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow.
Its wonderful as your other content : D, appreciate it for posting. “If Christ were here now there is one thing he would not be–a christian.” by Mark Twain.
I have been surfing online greater than three hours today, yet I by no means discovered any attention-grabbing article like yours. It¦s pretty worth sufficient for me. In my view, if all web owners and bloggers made excellent content as you did, the net will be much more helpful than ever before.
Very interesting topic, appreciate it for posting.
I’d should check with you here. Which isn’t one thing I often do! I take pleasure in studying a submit that may make people think. Also, thanks for permitting me to comment!
Greetings from Los angeles! I’m bored to tears at work so I decided to check out your site on my iphone during lunch break. I really like the knowledge you present here and can’t wait to take a look when I get home. I’m shocked at how fast your blog loaded on my phone .. I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyways, excellent blog!
Whats up very nice blog!! Guy .. Excellent .. Amazing .. I will bookmark your site and take the feeds additionally…I am happy to seek out numerous helpful info right here within the put up, we want work out extra strategies on this regard, thank you for sharing.
I like this web site so much, saved to favorites. “American soldiers must be turned into lambs and eating them is tolerated.” by Muammar Qaddafi.
This is very interesting, You are a very skilled blogger. I’ve joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your excellent post. Also, I’ve shared your web site in my social networks!
excellent points altogether, you simply won a new reader. What would you suggest in regards to your publish that you simply made a few days in the past? Any sure?
Write more, thats all I have to say. Literally, it seems as though you relied on the video to make your point. You obviously know what youre talking about, why waste your intelligence on just posting videos to your site when you could be giving us something enlightening to read?
The next time I read a blog, I hope that it doesnt disappoint me as much as this one. I mean, I know it was my choice to read, but I actually thought youd have something interesting to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something that you could fix if you werent too busy looking for attention.
Thank you for helping out, superb info. “I have witnessed the softening of the hardest of hearts by a simple smile.” by Goldie Hawn.
I like this website so much, saved to favorites. “Respect for the fragility and importance of an individual life is still the mark of an educated man.” by Norman Cousins.
Mitolyn is a cutting-edge natural dietary supplement designed to support effective weight loss and improve overall wellness.
Some truly interesting info , well written and broadly user friendly.
Wonderful beat ! I wish to apprentice while you amend your site, how could i subscribe for a blog web site? The account helped me a acceptable deal. I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast offered bright clear idea
Mitolyn is a cutting-edge natural dietary supplement designed to support effective weight loss and improve overall wellness.
Hello there, just became aware of your blog through Google, and found that it’s truly informative. I am gonna watch out for brussels. I will be grateful if you continue this in future. A lot of people will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
Howdy! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading this post reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this post to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Thanks for sharing!
I don’t unremarkably comment but I gotta tell thankyou for the post on this perfect one : D.
My brother suggested I would possibly like this website. He was once entirely right. This put up truly made my day. You can not imagine just how a lot time I had spent for this info! Thank you!
The Natural Mounjaro Recipe is more than just a diet—it’s a sustainable and natural approach to weight management and overall health.
The Natural Mounjaro Recipe is more than just a diet—it’s a sustainable and natural approach to weight management and overall health.
Hello.This post was really remarkable, particularly because I was browsing for thoughts on this topic last week.
I truly enjoy reading through on this web site, it has got superb blog posts.
Your home is valueble for me. Thanks!…
It is perfect time to make some plans for the longer term and it is time to be happy. I’ve learn this post and if I may I wish to recommend you some fascinating issues or suggestions. Perhaps you could write subsequent articles referring to this article. I wish to read even more issues about it!
Some genuinely wonderful blog posts on this internet site, thank you for contribution. “Give me the splendid silent sun with all his beams full-dazzling.” by Walt Whitman.
Excellent read, I just passed this onto a colleague who was doing a little research on that. And he actually bought me lunch because I found it for him smile Therefore let me rephrase that: Thank you for lunch!
Good post and straight to the point. I am not sure if this is in fact the best place to ask but do you guys have any thoughts on where to employ some professional writers? Thx 🙂
PrimeBiome is a dietary supplement designed to support gut health by promoting a balanced microbiome, enhancing digestion, and boosting overall well-being.
What i do not realize is in fact how you’re not really much more neatly-appreciated than you might be right now. You are so intelligent. You understand thus significantly in relation to this topic, produced me for my part believe it from a lot of numerous angles. Its like men and women are not fascinated unless it is one thing to accomplish with Woman gaga! Your personal stuffs nice. All the time maintain it up!
I got what you intend, regards for putting up.Woh I am glad to find this website through google. “Success is dependent on effort.” by Sophocles.
PrimeBiome is a dietary supplement designed to support gut health by promoting a balanced microbiome, enhancing digestion, and boosting overall well-being.
I am often to blogging and i really appreciate your content. The article has really peaks my interest. I am going to bookmark your site and keep checking for new information.
I’d have to examine with you here. Which is not one thing I usually do! I take pleasure in reading a post that may make folks think. Additionally, thanks for permitting me to comment!
Thanks , I’ve just been looking for information approximately this subject for a while and yours is the best I’ve found out so far. But, what concerning the conclusion? Are you positive about the source?
An attention-grabbing discussion is value comment. I believe that you need to write more on this subject, it may not be a taboo topic but generally persons are not enough to speak on such topics. To the next. Cheers
There is noticeably a bunch to know about this. I suppose you made some nice points in features also.
Good day I am so happy I found your blog, I really found you by mistake, while I was looking on Bing for something else, Nonetheless I am here now and would just like to say thanks for a fantastic post and a all round entertaining blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to browse it all at the moment but I have book-marked it and also added your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read much more, Please do keep up the great work.
I like this website very much, Its a real nice place to read and get information. “Words are like leaves and where they most abound, Much fruit of sense beneath is rarely found.” by Alexander Pope.
Some times its a pain in the ass to read what blog owners wrote but this website is real user pleasant! .
I like this post, enjoyed this one appreciate it for putting up. “The goal of revival is conformity to the image of Christ, not imitation of animals.” by Richard F. Lovelace.
Howdy! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my old room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this write-up to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Thanks for sharing!
Howdy just wanted to give you a quick heads up. The words in your content seem to be running off the screen in Opera. I’m not sure if this is a format issue or something to do with web browser compatibility but I figured I’d post to let you know. The design look great though! Hope you get the problem resolved soon. Cheers
I enjoy studying and I think this website got some genuinely useful stuff on it! .
Hey there! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading this post reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this page to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Many thanks for sharing!
Wow, incredible blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you make blogging look easy. The overall look of your website is fantastic, as well as the content!
I was reading some of your posts on this internet site and I think this web site is real instructive! Keep on posting.
Its like you read my mind! You appear to know a lot about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you can do with some pics to drive the message home a bit, but other than that, this is excellent blog. A great read. I’ll definitely be back.
I conceive you have remarked some very interesting points, thanks for the post.
I was studying some of your posts on this internet site and I believe this web site is very instructive! Continue posting.
Hi, Neat post. There is a problem along with your site in web explorer, could test this?K IE still is the market chief and a big portion of folks will miss your great writing due to this problem.
A lot of thanks for each of your hard work on this blog. My mum really loves carrying out internet research and it is easy to see why. We know all relating to the powerful mode you create advantageous strategies via your website and even recommend participation from others about this concept plus our princess is actually discovering a lot. Enjoy the remaining portion of the new year. You’re performing a remarkable job.
Very interesting info!Perfect just what I was looking for!
What¦s Going down i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve found It absolutely helpful and it has aided me out loads. I’m hoping to contribute & help other users like its aided me. Great job.
When I originally commented I clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now each time a comment is added I get four emails with the same comment. Is there any way you can remove me from that service? Thanks!
Greetings! Very helpful advice on this article! It is the little changes that make the biggest changes. Thanks a lot for sharing!
Enjoyed reading through this, very good stuff, regards.
My partner and I absolutely love your blog and find the majority of your post’s to be exactly I’m looking for. Does one offer guest writers to write content for you? I wouldn’t mind publishing a post or elaborating on a lot of the subjects you write in relation to here. Again, awesome blog!
hello!,I love your writing very much! percentage we keep in touch more approximately your post on AOL? I require a specialist on this space to resolve my problem. May be that’s you! Having a look forward to look you.
hello there and thank you for your information – I have certainly picked up something new from right here. I did however expertise some technical issues using this web site, as I experienced to reload the site a lot of times previous to I could get it to load properly. I had been wondering if your web host is OK? Not that I am complaining, but slow loading instances times will sometimes affect your placement in google and could damage your high quality score if ads and marketing with Adwords. Well I am adding this RSS to my e-mail and could look out for much more of your respective intriguing content. Ensure that you update this again soon..
Thank you, I’ve recently been looking for information approximately this subject for a while and yours is the best I’ve discovered so far. But, what in regards to the bottom line? Are you sure about the supply?
F*ckin’ amazing things here. I am very satisfied to see your post. Thanks so much and i am having a look ahead to touch you. Will you please drop me a e-mail?
Have you ever considered creating an ebook or guest authoring on other sites? I have a blog centered on the same ideas you discuss and would love to have you share some stories/information. I know my subscribers would appreciate your work. If you’re even remotely interested, feel free to send me an e mail.
Perfectly pent subject matter, Really enjoyed studying.
Can I simply say what a relief to search out someone who truly knows what theyre speaking about on the internet. You undoubtedly know learn how to convey an issue to mild and make it important. More people must learn this and understand this facet of the story. I cant consider youre no more widespread since you positively have the gift.
Simply desire to say your article is as astonishing. The clarity in your post is just spectacular and that i could suppose you’re a professional in this subject. Fine with your permission allow me to grab your feed to keep up to date with coming near near post. Thanks a million and please carry on the rewarding work.
Great write-up, I’m normal visitor of one’s website, maintain up the nice operate, and It is going to be a regular visitor for a long time.
You are my intake, I have few web logs and occasionally run out from post :). “Truth springs from argument amongst friends.” by David Hume.
I am often to blogging and i really appreciate your content. The article has really peaks my interest. I am going to bookmark your site and keep checking for new information.
I?¦ve learn some excellent stuff here. Certainly price bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how much effort you place to make this kind of magnificent informative website.
Great website you have here but I was curious if you knew of any forums that cover the same topics talked about here? I’d really like to be a part of online community where I can get feedback from other experienced individuals that share the same interest. If you have any suggestions, please let me know. Appreciate it!
Write more, thats all I have to say. Literally, it seems as though you relied on the video to make your point. You clearly know what youre talking about, why waste your intelligence on just posting videos to your blog when you could be giving us something informative to read?
Nice post. I learn something tougher on totally different blogs everyday. It should all the time be stimulating to read content material from other writers and apply somewhat something from their store. I’d desire to make use of some with the content material on my blog whether you don’t mind. Natually I’ll provide you with a hyperlink on your web blog. Thanks for sharing.
This is a topic close to my heart cheers, where are your contact details though?
Magnificent web site. Plenty of helpful information here. I am sending it to several buddies ans additionally sharing in delicious. And obviously, thanks on your effort!
Enjoyed reading this, very good stuff, regards. “Success doesn’t come to you…you go to it.” by Marva Collins.
Hello, you used to write great, but the last several posts have been kinda boring… I miss your tremendous writings. Past several posts are just a little bit out of track! come on!
I love what you guys are usually up too. Such clever work and coverage! Keep up the very good works guys I’ve included you guys to my own blogroll.
Great site. Lots of helpful info here. I am sending it to some friends ans additionally sharing in delicious. And obviously, thank you to your effort!
Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your weblog and wanted to say that I have truly enjoyed browsing your blog posts. In any case I’ll be subscribing to your rss feed and I hope you write again soon!
I just like the helpful info you provide on your articles. I’ll bookmark your blog and check again right here regularly. I am quite sure I’ll learn a lot of new stuff proper here! Best of luck for the next!
I think this site has got some real wonderful information for everyone. “A man’s dreams are an index to his greatness.” by Zadok Rabinwitz.
The very core of your writing while sounding reasonable at first, did not sit well with me after some time. Somewhere within the paragraphs you managed to make me a believer but just for a very short while. I nevertheless have got a problem with your jumps in logic and one would do nicely to help fill in those gaps. In the event that you can accomplish that, I will definitely end up being fascinated.
There is noticeably a bundle to know about this. I assume you made certain nice points in features also.
he blog was how do i say it… relevant, finally something that helped me. Thanks
As soon as I found this web site I went on reddit to share some of the love with them.
Those are yours alright! . We at least need to get these people stealing images to start blogging! They probably just did a image search and grabbed them. They look good though!
An interesting discussion is worth comment. I think that you should write more on this topic, it might not be a taboo subject but generally people are not enough to speak on such topics. To the next. Cheers
Hey there! I know this is kinda off topic nevertheless I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in exchanging links or maybe guest authoring a blog post or vice-versa? My site goes over a lot of the same subjects as yours and I think we could greatly benefit from each other. If you happen to be interested feel free to send me an e-mail. I look forward to hearing from you! Terrific blog by the way!
You have noted very interesting points! ps nice internet site. “Do not quench your inspiration and your inmagination do not become the slave of your model.” by Vincent Van Gogh.
Wow, superb weblog structure! How long have you ever been running a blog for? you make running a blog glance easy. The total glance of your site is magnificent, let alone the content!
It¦s actually a nice and useful piece of information. I am glad that you shared this helpful info with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
Usually I do not read post on blogs, but I would like to say that this write-up very forced me to try and do so! Your writing style has been amazed me. Thanks, very nice post.
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
I love the efforts you have put in this, thank you for all the great content.
This design is spectacular! You obviously know how to keep a reader amused. Between your wit and your videos, I was almost moved to start my own blog (well, almost…HaHa!) Great job. I really loved what you had to say, and more than that, how you presented it. Too cool!
When I originally commented I clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now each time a comment is added I get four emails with the same comment. Is there any way you can remove me from that service? Thanks!
Crypto payment gateway for your business. Boost your sales, cut costs, and streamline your operations by accepting cryptocurrency payments. Experience secure, fast transactions and unlock global business opportunities
I?¦ve recently started a website, the info you provide on this website has helped me greatly. Thanks for all of your time & work.
Hello I am so glad I found your site, I really found you by mistake, while I was researching on Digg for something else, Anyways I am here now and would just like to say thank you for a remarkable post and a all round entertaining blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to read it all at the minute but I have saved it and also included your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read a great deal more, Please do keep up the excellent job.
Hmm is anyone else having problems with the images on this blog loading? I’m trying to find out if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog. Any feed-back would be greatly appreciated.
You really make it seem so easy with your presentation however I to find this topic to be actually one thing which I feel I might never understand. It sort of feels too complicated and extremely extensive for me. I am taking a look ahead on your next post, I will attempt to get the dangle of it!
You should take part in a contest for one of the best blogs on the web. I will recommend this site!
Howdy this is somewhat of off topic but I was wondering if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding knowledge so I wanted to get guidance from someone with experience. Any help would be enormously appreciated!
Thank you for another informative web site. Where else could I get that kind of info written in such an ideal way? I’ve a project that I am just now working on, and I have been on the look out for such information.
Hiya, I’m really glad I’ve found this info. Today bloggers publish only about gossips and web and this is actually annoying. A good website with interesting content, this is what I need. Thank you for keeping this web-site, I’ll be visiting it. Do you do newsletters? Cant find it.
Great wordpress blog here.. It’s hard to find quality writing like yours these days. I really appreciate people like you! take care
Wow! This blog looks exactly like my old one! It’s on a totally different topic but it has pretty much the same layout and design. Superb choice of colors!
I’ve been surfing online greater than 3 hours today, yet I by no means found any attention-grabbing article like yours. It is lovely price enough for me. In my opinion, if all website owners and bloggers made good content as you probably did, the net shall be much more helpful than ever before.
Howdy! I know this is kinda off topic however , I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in trading links or maybe guest authoring a blog article or vice-versa? My blog addresses a lot of the same topics as yours and I believe we could greatly benefit from each other. If you might be interested feel free to send me an e-mail. I look forward to hearing from you! Fantastic blog by the way!
Some really interesting details you have written.Helped me a lot, just what I was searching for : D.
Excellent site. Lots of helpful info here. I am sending it to some friends ans also sharing in delicious. And of course, thank you to your effort!
Thanks for the good writeup. It in truth was a enjoyment account it. Look complicated to far brought agreeable from you! By the way, how could we communicate?
I went over this web site and I conceive you have a lot of superb info, saved to bookmarks (:.
Whats up very nice site!! Man .. Excellent .. Amazing .. I will bookmark your web site and take the feeds alsoKI’m happy to seek out so many helpful info here in the submit, we need develop extra techniques on this regard, thank you for sharing. . . . . .
Useful information. Lucky me I discovered your site accidentally, and I’m surprised why this twist of fate did not came about earlier! I bookmarked it.
This site can be a stroll-via for all of the info you wished about this and didn’t know who to ask. Glimpse here, and also you’ll definitely uncover it.
Good day! This is my 1st comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and say I genuinely enjoy reading through your blog posts. Can you suggest any other blogs/websites/forums that cover the same topics? Thanks!
What i don’t understood is in truth how you’re not really much more neatly-liked than you might be now. You’re very intelligent. You realize thus significantly in relation to this topic, made me in my view believe it from so many various angles. Its like men and women aren’t involved except it’s one thing to do with Lady gaga! Your personal stuffs outstanding. At all times deal with it up!
he blog was how do i say it… relevant, finally something that helped me. Thanks
Hello, I think your website might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your blog site in Chrome, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, fantastic blog!
I think this is among the most vital info for me. And i am glad reading your article. But wanna remark on few general things, The site style is great, the articles is really nice : D. Good job, cheers
It’s hard to find knowledgeable people on this topic, but you sound like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
You like native girls? On https://WWW.AFRICANPUSSYPICS.COM we got fat and slick kitty up close and juicy. This is what real black heat looks like when it’s dripping and ready.
I’ve read a few good stuff here. Definitely worth bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how much effort you put to make such a wonderful informative website.
This web site is really a walk-through for all of the info you wanted about this and didn’t know who to ask. Glimpse here, and you’ll definitely discover it.
Great – I should definitely pronounce, impressed with your web site. I had no trouble navigating through all the tabs as well as related info ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it at all. Quite unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or something, web site theme . a tones way for your customer to communicate. Excellent task..
Some really excellent information, Glad I noticed this.
Hey! I just wanted to ask if you ever have any problems with hackers? My last blog (wordpress) was hacked and I ended up losing a few months of hard work due to no back up. Do you have any solutions to stop hackers?
No games on http://WWW.AFRICANPUSSYPICS.COM — just chocolate cuties with jugs out, dripping kitty spread, and zero limits. These queens grind and drain every shaft in reach.
I was very happy to search out this internet-site.I wished to thanks in your time for this excellent learn!! I positively having fun with every little bit of it and I have you bookmarked to take a look at new stuff you weblog post.
I’m not that much of a online reader to be honest but your sites really nice, keep it up! I’ll go ahead and bookmark your website to come back down the road. Many thanks
Howdy! I’m at work browsing your blog from my new iphone 3gs! Just wanted to say I love reading through your blog and look forward to all your posts! Keep up the fantastic work!
My coder is trying to convince me to move to .net from PHP. I have always disliked the idea because of the costs. But he’s tryiong none the less. I’ve been using Movable-type on various websites for about a year and am worried about switching to another platform. I have heard fantastic things about blogengine.net. Is there a way I can transfer all my wordpress posts into it? Any help would be really appreciated!
I do like the way you have presented this specific matter and it does indeed offer us a lot of fodder for thought. Nonetheless, from just what I have experienced, I only hope when the actual opinions pile on that people today stay on point and don’t embark on a soap box of some other news du jour. Still, thank you for this outstanding piece and even though I do not necessarily go along with this in totality, I respect your standpoint.
I must get across my gratitude for your kind-heartedness in support of men who really want assistance with this important theme. Your very own commitment to getting the message along had been particularly valuable and has allowed individuals just like me to arrive at their objectives. Your own warm and helpful information means a great deal to me and even more to my mates. Many thanks; from all of us.
It is really a nice and useful piece of info. I’m glad that you shared this useful information with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thank you for sharing.
Some times its a pain in the ass to read what people wrote but this internet site is rattling user genial! .
Thank you for some other informative web site. Where else may I get that kind of info written in such a perfect method? I have a challenge that I am simply now working on, and I’ve been on the glance out for such information.
It’s really a nice and useful piece of info. I’m glad that you shared this helpful information with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
Hello. magnificent job. I did not anticipate this. This is a excellent story. Thanks!
Thanks for the good writeup. It in reality was a amusement account it. Glance complicated to far brought agreeable from you! However, how could we communicate?
I am often to blogging and i really appreciate your content. The article has really peaks my interest. I am going to bookmark your site and keep checking for new information.
We absolutely love your blog and find nearly all of your post’s to be precisely what I’m looking for. Does one offer guest writers to write content for yourself? I wouldn’t mind creating a post or elaborating on a lot of the subjects you write regarding here. Again, awesome web site!
Hi, i read your blog from time to time and i own a similar one and i was just curious if you get a lot of spam comments? If so how do you reduce it, any plugin or anything you can recommend? I get so much lately it’s driving me insane so any support is very much appreciated.
Great site. Plenty of helpful information here. I’m sending it to a few buddies ans additionally sharing in delicious. And of course, thanks in your sweat!
It’s truly a nice and useful piece of info. I am happy that you shared this helpful information with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thank you for sharing.
You have brought up a very excellent details , thanks for the post.
Hello. impressive job. I did not imagine this. This is a excellent story. Thanks!
I’ve learn some just right stuff here. Definitely price bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how so much effort you set to create the sort of fantastic informative web site.
you are really a good webmaster. The site loading speed is incredible. It seems that you’re doing any unique trick. Also, The contents are masterwork. you have done a wonderful job on this topic!
What i don’t understood is in reality how you’re now not really much more well-liked than you might be now. You are so intelligent. You realize therefore significantly in relation to this subject, made me personally consider it from numerous varied angles. Its like men and women don’t seem to be interested unless it is something to do with Woman gaga! Your individual stuffs nice. At all times deal with it up!
With every little thing that seems to be building inside this subject material, a significant percentage of opinions happen to be fairly radical. Even so, I am sorry, because I do not subscribe to your whole idea, all be it exhilarating none the less. It appears to me that your comments are actually not totally validated and in actuality you are generally yourself not really fully convinced of your point. In any event I did take pleasure in examining it.
Great – I should certainly pronounce, impressed with your web site. I had no trouble navigating through all the tabs as well as related information ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it in the least. Reasonably unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or something, site theme . a tones way for your client to communicate. Excellent task.
Hey There. I found your weblog using msn. That is a really well written article. I’ll make sure to bookmark it and come back to learn more of your helpful information. Thank you for the post. I’ll definitely comeback.
This is the suitable blog for anyone who needs to seek out out about this topic. You realize a lot its virtually exhausting to argue with you (not that I actually would want…HaHa). You undoubtedly put a brand new spin on a topic thats been written about for years. Great stuff, just nice!
After study a few of the blog posts on your website now, and I truly like your way of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back soon. Pls check out my web site as well and let me know what you think.
It’s a shame you don’t have a donate button! I’d without a doubt donate to this excellent blog! I guess for now i’ll settle for bookmarking and adding your RSS feed to my Google account. I look forward to new updates and will share this blog with my Facebook group. Talk soon!
Unquestionably believe that which you said. Your favorite justification appeared to be on the web the easiest thing to be aware of. I say to you, I certainly get irked while people think about worries that they plainly don’t know about. You managed to hit the nail upon the top and defined out the whole thing without having side effect , people can take a signal. Will likely be back to get more. Thanks
of course like your web site however you have to take a look at the spelling on several of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling issues and I find it very bothersome to inform the reality however I?¦ll surely come again again.
fantastic points altogether, you just gained a new reader. What would you recommend in regards to your post that you made a few days ago? Any positive?
I and also my pals have been studying the good helpful tips located on your site and then suddenly I got an awful feeling I never expressed respect to the blog owner for those strategies. All the men appeared to be as a result warmed to see them and have clearly been taking pleasure in them. Thank you for simply being well thoughtful and for making a choice on such excellent ideas most people are really wanting to learn about. Our own sincere apologies for not expressing gratitude to you sooner.
Very nice post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wanted to say that I have really loved surfing around your weblog posts. In any case I’ll be subscribing for your feed and I’m hoping you write once more very soon!
The heart of your writing while sounding agreeable in the beginning, did not settle very well with me personally after some time. Somewhere within the paragraphs you managed to make me a believer but only for a short while. I however have got a problem with your jumps in assumptions and you would do well to fill in those breaks. In the event you can accomplish that, I will surely be impressed.
Simply want to say your article is as amazing. The clarity on your publish is just nice and i could think you are a professional in this subject. Well with your permission let me to take hold of your feed to stay updated with forthcoming post. Thank you a million and please continue the rewarding work.
Write more, thats all I have to say. Literally, it seems as though you relied on the video to make your point. You obviously know what youre talking about, why waste your intelligence on just posting videos to your site when you could be giving us something informative to read?
It?¦s actually a great and helpful piece of information. I am happy that you shared this useful information with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
I am glad to be a visitor of this utter web site! , appreciate it for this rare information! .
I’m typically to running a blog and i really appreciate your content. The article has really peaks my interest. I am going to bookmark your site and maintain checking for brand spanking new information.
Nice blog! Is your theme custom made or did you download it from somewhere? A theme like yours with a few simple tweeks would really make my blog jump out. Please let me know where you got your theme. Appreciate it
I real happy to find this web site on bing, just what I was searching for : D likewise saved to fav.
I’ve been surfing online more than 3 hours as of late, but I never discovered any fascinating article like yours. It is beautiful value sufficient for me. In my opinion, if all site owners and bloggers made excellent content as you probably did, the internet might be much more helpful than ever before.
Hello.This post was really fascinating, particularly since I was investigating for thoughts on this issue last Wednesday.
Oh my goodness! an incredible article dude. Thank you Nevertheless I’m experiencing issue with ur rss . Don’t know why Unable to subscribe to it. Is there anyone getting equivalent rss drawback? Anyone who is aware of kindly respond. Thnkx
I’m not sure why but this website is loading incredibly slow for me. Is anyone else having this issue or is it a issue on my end? I’ll check back later and see if the problem still exists.
This web page is really a walk-through for all of the info you wished about this and didn’t know who to ask. Glimpse here, and also you’ll positively discover it.
I dugg some of you post as I thought they were very useful very beneficial
Woah! I’m really digging the template/theme of this blog. It’s simple, yet effective. A lot of times it’s tough to get that “perfect balance” between usability and visual appearance. I must say you’ve done a great job with this. Additionally, the blog loads very fast for me on Safari. Exceptional Blog!
F*ckin¦ tremendous issues here. I¦m very glad to look your post. Thanks a lot and i’m looking forward to contact you. Will you please drop me a e-mail?
Prostadine is a liquid supplement made from a blend of natural plant-based ingredients, minerals, and antioxidants. Its primary goal is to help
I will right away grasp your rss as I can’t to find your email subscription hyperlink or newsletter service. Do you have any? Please let me recognize so that I may subscribe. Thanks.
I like this post, enjoyed this one regards for putting up.
I do agree with all the ideas you have presented in your post. They’re very convincing and will certainly work. Still, the posts are very short for beginners. Could you please extend them a bit from next time? Thanks for the post.
I’m really impressed together with your writing skills as neatly as with the format in your blog. Is that this a paid subject or did you modify it your self? Either way keep up the excellent quality writing, it is uncommon to see a nice weblog like this one today..
Precisely what I was searching for, thankyou for posting.
I have been absent for a while, but now I remember why I used to love this site. Thanks, I’ll try and check back more often. How frequently you update your web site?
This blog is definitely rather handy since I’m at the moment creating an internet floral website – although I am only starting out therefore it’s really fairly small, nothing like this site. Can link to a few of the posts here as they are quite. Thanks much. Zoey Olsen
I am very happy to read this. This is the type of manual that needs to be given and not the random misinformation that’s at the other blogs. Appreciate your sharing this greatest doc.
Very interesting info !Perfect just what I was searching for!
You actually make it seem so easy with your presentation but I find this matter to be actually something which I feel I would by no means understand. It seems too complex and extremely large for me. I am looking ahead on your subsequent submit, I will attempt to get the cling of it!
Merely wanna say that this is handy, Thanks for taking your time to write this.
Just a smiling visitant here to share the love (:, btw great pattern. “Treat the other man’s faith gently it is all he has to believe with.” by Athenus.
Does your blog have a contact page? I’m having problems locating it but, I’d like to shoot you an email. I’ve got some suggestions for your blog you might be interested in hearing. Either way, great site and I look forward to seeing it expand over time.
Thanks for sharing excellent informations. Your web site is very cool. I’m impressed by the details that you’ve on this website. It reveals how nicely you understand this subject. Bookmarked this web page, will come back for more articles. You, my friend, ROCK! I found just the information I already searched all over the place and just could not come across. What an ideal site.
Some genuinely nice and utilitarian info on this website, besides I believe the design holds superb features.
I was reading some of your posts on this internet site and I believe this internet site is real instructive! Keep putting up.
This is a very good tips especially to those new to blogosphere, brief and accurate information… Thanks for sharing this one. A must read article.
Hi , I do believe this is an excellent blog. I stumbled upon it on Yahoo , i will come back once again. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and help other people.
I believe you have observed some very interesting points, thanks for the post.
of course like your website but you need to test the spelling on quite a few of your posts. A number of them are rife with spelling problems and I in finding it very bothersome to tell the reality then again I¦ll surely come again again.
Hey would you mind sharing which blog platform you’re using? I’m planning to start my own blog soon but I’m having a tough time deciding between BlogEngine/Wordpress/B2evolution and Drupal. The reason I ask is because your design seems different then most blogs and I’m looking for something unique. P.S Apologies for being off-topic but I had to ask!
Great blog! Do you have any tips for aspiring writers? I’m planning to start my own site soon but I’m a little lost on everything. Would you advise starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There are so many choices out there that I’m totally overwhelmed .. Any recommendations? Thank you!
Once I initially commented I clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now every time a remark is added I get 4 emails with the identical comment. Is there any means you may take away me from that service? Thanks!
I would like to thank you for the efforts you’ve put in writing this website. I am hoping the same high-grade blog post from you in the upcoming also. In fact your creative writing skills has encouraged me to get my own blog now. Actually the blogging is spreading its wings quickly. Your write up is a good example of it.
You made some nice points there. I did a search on the topic and found most people will go along with with your site.
Good – I should certainly pronounce, impressed with your website. I had no trouble navigating through all tabs as well as related information ended up being truly simple to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it in the least. Quite unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or something, site theme . a tones way for your client to communicate. Excellent task..
You are my intake, I have few blogs and often run out from to brand.
It’s really a cool and helpful piece of info. I am glad that you shared this useful information with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
Very interesting subject, thanks for putting up.
Merely a smiling visitor here to share the love (:, btw great pattern. “Justice is always violent to the party offending, for every man is innocent in his own eyes.” by Daniel Defoe.
I’d have to examine with you here. Which is not one thing I usually do! I take pleasure in reading a post that may make folks think. Additionally, thanks for permitting me to comment!
What i don’t realize is if truth be told how you’re not really a lot more smartly-favored than you might be right now. You are so intelligent. You realize thus significantly when it comes to this topic, made me in my opinion believe it from numerous numerous angles. Its like men and women aren’t involved except it is something to accomplish with Lady gaga! Your own stuffs great. Always care for it up!
Have you ever thought about creating an e-book or guest authoring on other blogs? I have a blog based upon on the same ideas you discuss and would really like to have you share some stories/information. I know my audience would enjoy your work. If you are even remotely interested, feel free to send me an e-mail.
Do you have a spam issue on this website; I also am a blogger, and I was wondering your situation; many of us have developed some nice procedures and we are looking to exchange techniques with others, be sure to shoot me an e-mail if interested.
I was looking through some of your articles on this website and I conceive this internet site is rattling informative ! Retain putting up.
Your place is valueble for me. Thanks!…
ProstaVive is a premium, plant-based dietary supplement specifically formulated to support prostate health, reduce inflammation, and enhance urinary function, especially for men over the age of 40.
Can I just say what a relief to find someone who actually knows what theyre talking about on the internet. You definitely know how to bring an issue to light and make it important. More people need to read this and understand this side of the story. I cant believe youre not more popular because you definitely have the gift.
Your place is valueble for me. Thanks!…
Have you ever thought about adding a little bit more than just your articles? I mean, what you say is important and everything. However just imagine if you added some great visuals or video clips to give your posts more, “pop”! Your content is excellent but with images and videos, this website could undeniably be one of the very best in its niche. Good blog!
Thankyou for all your efforts that you have put in this. very interesting information.
As soon as I discovered this internet site I went on reddit to share some of the love with them.
Thanks for another excellent article. Where else could anybody get that type of information in such an ideal way of writing? I’ve a presentation next week, and I am on the look for such information.
Howdy! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading this post reminds me of my good old room mate! He always kept chatting about this. I will forward this article to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Many thanks for sharing!
I do like the way you have framed this specific concern plus it does indeed present me a lot of fodder for thought. On the other hand, through everything that I have observed, I only hope as other opinions pack on that people keep on issue and don’t get started on a tirade involving the news du jour. Still, thank you for this outstanding point and though I do not concur with this in totality, I respect the viewpoint.